- For printing
- September 12, 2024
National Cancer Center
Eisai Co., Ltd
Presentation points
- A cross-cancer drug efficacy evaluation of Eisai's targeted proteolytic inducer E7820 was performed on a patient-derived tissue transplantation (PDX) model (pancreatic cancer, biliary cancer, stomach cancer, endometrial cancer) in which patient-derived cancer tissue was transplanted into immunodeficient mice, and tumor shrinkage was observed at 38.1% overall, 58.3% for biliary tract cancer, and 55.6% for endometrial cancer.
- The PDX model is highly accurate in predicting treatment effects, and since there is high similarity between clinical data and PDX model responsiveness, the results of this study suggest tumor reduction effects of E7820 in biliary tract cancer and endometrial cancer.
- All exon sequences of the PDX model were performed, and genetic mutations that can be expected as biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of E7820 were identified.
- The results of this research were published in the peer-reviewed academic journal “NPJ Precision Oncology.”
- Based on information on cancer types and biomarkers that are expected to be effective of E7820 revealed in this study, physician-led clinical trials aimed at safety evaluation and exploratory efficacy evaluation, including tolerability in Japanese people, will begin at the National Cancer Center Central Hospital and East Hospital.
- By using the National Cancer Center's J-PDX (tissue transplantation model derived from Japanese cancer patients) library for drug discovery and development, it is now possible to quickly implement drug efficacy evaluation for each cancer type, identification of biomarkers that predict efficacy, and even launch clinical trials all at once. In the future, we aim to accumulate such cases and establish it as a drug discovery research system to accelerate the development of new anticancer drugs.
 summary
summary
National Cancer Center (Location: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; Chairman: Nakagama Hitoshi; hereafter National Cancer Center) and Eisai Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo; Representative Executive Officer and CEO: Haruo Naito; hereafter Eisai) aim to establish a drug discovery research system to accelerate the development of new anticancer drugs, and with the support of the Medical Research and Development Infrastructure Creation Project (CiCle) of the Japan Medical Research and Development Organization (AMED) “Research on drug discovery research methods to accelerate anticancer drug treatment development for intractable cancers” has been carried out since 2021.
In this study, the National Cancer Center and Eisai conducted non-clinical tests on the new drug candidate E7820 created by Eisai using the J-PDX library, which is an animal model in which tumor tissue derived from Japanese cancer patients is transplanted into immunodeficient mice constructed by the National Cancer Center Research Institute (Director: Hiroyuki Mano), and performed drug effects with 42 PDX Note 1 models (12 pancreatic cancer models, 12 models for gastric cancer, 9 models for endometrial cancer) I rated it.
As a result, tumor shrinkage was observed in 16 of 42 models (38.1%) due to E7820 100 mg/kg administration, 7 out of 12 models (58.3%) for biliary tract cancer, and 5 out of 9 models (55.6%) for endometrial cancer. The PDX model has high predictive accuracy of treatment effects, and since there is high similarity between clinical data and PDX model responsiveness, the results of this study suggest tumor reduction effects of E7820 in biliary tract cancer and endometrial cancer.
Furthermore, in order to search for biomarkers Note 2 correlated with the tumor reduction effect of E7820, when all exon sequence note 3 of the PDX model were performed, mutations in homologous recombination repair (HRR) related gene note 4, which is one of the DNA repair mechanisms, such as BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM, were observed at a high frequency in the PDX model where tumor reduction effects were observed, and there is a possibility that this gene mutation will become a biomarker for the efficacy of E7820 It was suggested.
The results of this research were published in the peer-reviewed academic journal “NPJ Precision Oncology.”
Based on these results, National Cancer Center Central Hospital (Hospital Director: Seto Yasuyuki) and East Hospital (Hospital Director: Doi Toshihiko) have begun Phase I doctor-led clinical trial Note 5 (NCCH2303) to evaluate the safety and efficacy of E7820 against solid cancer in Japanese people. In this trial, after confirming the tolerability note 6 of E7820 and determining recommended usage/dosage, the National Cancer Center and Eisai will consider implementing phase II to confirm efficacy against specific cancer types and solid cancers with biomarkers, and further approval application tests, and aim for regulatory approval. Furthermore, we aim to establish the system constructed in this research as a drug discovery research system to accelerate the development of novel anticancer drugs.
backgrounds
The PDX model is a cancer model created by directly transplanting tumor tissue from cancer patients into immunodeficient mice, and is used in non-clinical trials and research. The PDX model maintains many of the tumor heterogeneity and genetic mutations of original cancer patients, and it has been reported that the accuracy of predicting treatment effects is high compared to conventionally used cell lines and model mice in which cell lines have been transplanted into mice, and there is high similarity between clinical data and PDX model responsiveness.
The National Cancer Center Laboratory built a J-PDX library derived from Japanese cancer patients with clinical information in 2020, possesses 651 PDX models across cancer types (as of 2024/7/3), and is being used in drug discovery development.
Using the cancer area as one of the strategically important areas, Eisai has created innovative new drugs with new targets and mechanisms of action under the Deep Human Biology Learning drug discovery system while utilizing experience with the microtubule dynamics inhibitor erevulin mesylate (product name: halaven) and the multi-kinase inhibitor lenvatinib mesylate (product name: renbima), which has obtained global approval, and contributed to the realization of cancer cure I aim to do it.
E7820 is a sulfonamide anticancer drug that acts as a molecular glue that binds DCAF15, which is involved in selective proteolysis, to the splicing factor RBM39, and selectively breaks down RBM39. This effect induces abnormalities in RNA splicing note 7, and is expected to have the effect of suppressing cancer growth. We have a track record of clinical trials using the E7820 overseas.
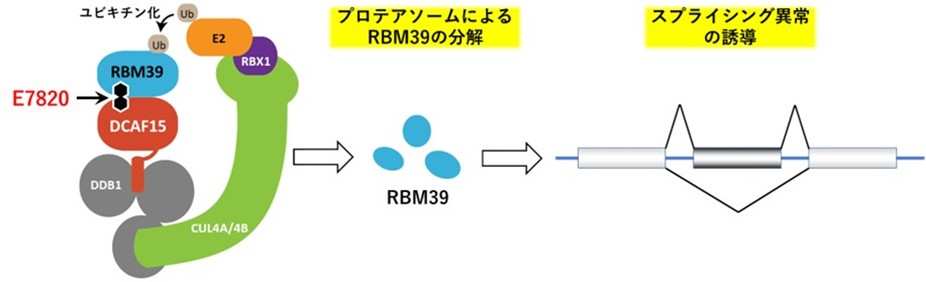
Figure 1. E7820 binds the splicing factor RBM39 to ubiquitin ligase DCAF15. RBM39 taken up by the ubiquitin ligase complex is ubiquitinated and degraded by proteasomes. Splicing abnormalities are induced by degradation of RBM39, and antitumor effects are exerted.
In “research on drug discovery research methods to accelerate anticancer drug treatment development for rare and intractable cancers,” the National Cancer Center and Eisai are conducting non-clinical trials across organs using J-PDX on new drug candidates created by Eisai, conducting physician-led clinical trials for rare cancers and intractable cancers, confirming clinical usefulness, and aiming to apply for approval (Fig. 2). Furthermore, PDX has been established from tumor tissues before and after treatment, comparative analysis of drug responsiveness and cancer genomes is carried out, we are working to search for new drug targets and elucidate drug resistance mechanisms, and are proceeding with investigations into new drug discovery. Through these efforts, we aim to establish a drug discovery research system to accelerate the development of new anticancer drugs.
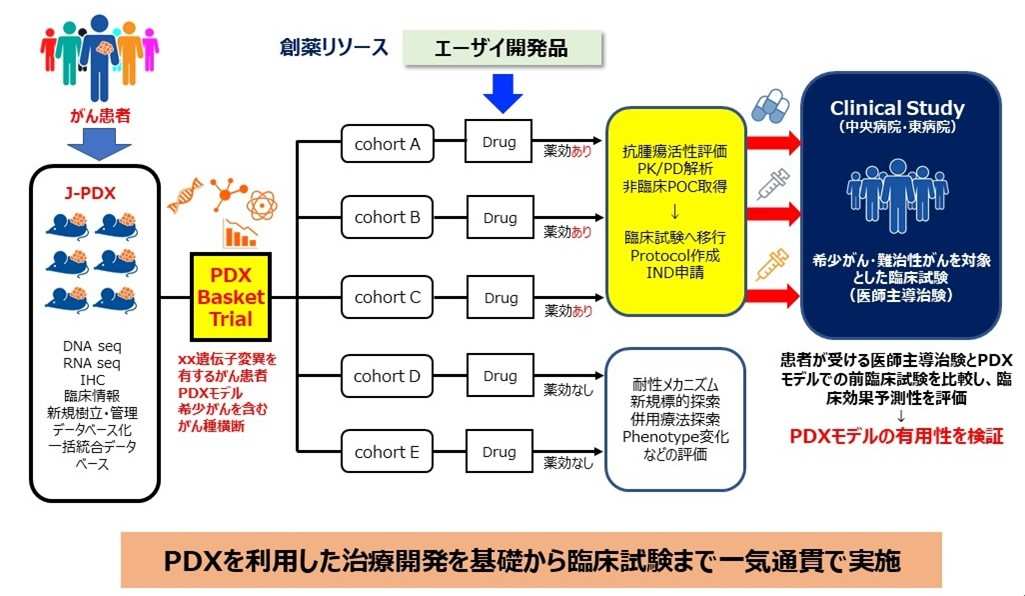
Figure 2 Overview of research and development between the National Cancer Center and Eisai
* May 14, 2021 Press Release
National Cancer Center and Eisai Co., Ltd. have high ability to predict treatment effects of PDX and cancer genomes
Start “research on drug discovery research methods to accelerate anticancer drug treatment development for rare and intractable cancers” using data
Research results
Drug efficacy evaluation screening of E7820 using a PDX mouse model
E7820 was orally administered 100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg for 21 days on 42 PDX models (12 pancreatic cancer models, 12 biliary tract cancer models, 9 gastric cancer models, 9 endometrial cancer models), and screening evaluations were performed.
As a result, significant tumor shrinkage (tumor volume increase rate < -30% in the drug-treated group) was observed (Fig. 3a). The overall response rate was 38.1% (16 cases) with 100 mg/kg administration of this drug and 54.8% (23 cases) with 200 mg/kg administration. The highest response rate at 100 mg/kg was biliary tract cancer (58.3%), followed by endometrial cancer (55.6%), and stomach cancer (33.3%). The lowest response rate was 8.3% for pancreatic cancer, and it was found that the effects varied depending on the type of cancer (Figure 3b).



Figure 3. Cancer types and biomarkers showing drug sensitivity of E7820 were identified by E7820 drug efficacy evaluation screening and full exon analysis using the PDX mouse model.
HRR related gene abnormalities are frequently observed in E7820 sensitive PDX
All exon sequences and total transcriptome analysis Note 8 were performed to identify molecular markers associated with E7820 sensitivity. Mutation analysis using all exon sequences showed that mutations in HRR-related genes such as BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM were observed at a high frequency in PDX where drug effects were observed (Fig. 3a). When comparing E7820 sensitivity between PDX with mutations and PDX without mutations, ATM mutations were significantly concentrated in the susceptible group (p = 4.5 × 10-3, FDR = 0.14), and BRCA2 mutations also tended to be concentrated in the susceptible group (p = 4.8 × 10-2, FDR = 0.51) (Fig. 3c). In contrast, TP53 was significantly mutated in the insensitive group (p=5.9×10-3, FDR=0.14), but it was thought that this concentration may be related to the high TP53 mutation positivity rate in pancreatic cancer.
Long-term administration of E7820 results in inhibition of growth of homologous recombination repair deficiency (HRD) positive cells
Recent reports have shown that E7820 affects RNA splicing in several HRR genes, but HRD, which is loss of function in the HRR pathway, was not shown to be a biomarker predicting E7820 reactivity. Since significant tumor shrinkage was observed in HRD-positive tumors in screening using the PDX model, it was predicted that long-term exposure to this compound would cause growth suppression. Therefore, colorectal cancer cell lines (DLD1-BRCA2-KO) that knocked out BRCA2 or parent lines that were not knocked out (DLD1-P) were treated with short-term culture (3 days) or long-term culture (12 days) to evaluate drug efficacy. Compared to DLD1-P cells, DLD1-BRCA2-KO cells showed higher sensitivity to E7820 on day 12 (Fig. 4a).
In order to further investigate whether other genes involved in the DNA damage response affect sensitivity to E7820, it became clear that when ATM, ATR, or BAP1 genes were knocked out in DLD1-P cells and then drugs were administered, DLD1-P cells became sensitive to E7820 (Fig. 4b).

BRCA2 dysfunction increases DNA double strand breaks by E7820
Since DLD1-BRCA2-KO showed sensitivity to E7820, we thought exposure to E7820 could cause DNA damage. When expression of γH2AX, which is a marker of DNA double strand breaks, was evaluated in cells cultured for 72 hours with E7820 or olaparib, which is a PARP inhibitor Note 9, administration of E7820 (1 μM) induced the appearance of more gammaH2AX than administration of olaparib (1 μM) (Figure 4c).
Transcriptome changes associated with E7820 administration
In order to clarify how E7820 induces DNA double strand breaks, full transcriptome analysis was performed, and genes commonly expressed increased or decreased due to E7820 treatment were evaluated in 6 cancer cell lines. As a result, 1,655 genes with elevated expression (fold change > 1.1) and 2,787 genes with reduced expression (fold change <0.9) were observed in 3 or more cell lines. Signal transduction pathways related to DNA damage repair, such as “nucleotide excision repair,” “hereditary breast cancer related signals,” and “BRCA1 related in DNA damage response,” were included in intracellular pathways concentrated in genes with reduced expression (Fig. 5a). HRR related genes such as PALB2, BRIP1, BRCA1, RAD50, MRE11, ATR, FANC family genes, and genes essential for nucleotide excision repair (NER) such as XPC and ERCC2 were also included as genes associated with these pathways. Next, when splicing abnormalities induced by E7820 were investigated, in both DLD1-P and DLD1-BRCA2-KO, intron retention was the most increased splicing anomaly with drug administration, and the splicing anomaly that decreased the most was single-exon skipping (Fig. 5b). Furthermore, intron retention was induced in 25 genes (61%) out of 41 genes associated with DNA repair whose expression was reduced due to drug administration (Fig. 5c).

Figure 5 When transcriptome changes associated with E7820 administration were analyzed, decreased expression of genes involved in signal transduction pathways related to DNA damage repair and induction of intron retention were seen.
mRNA missplicing has a significant impact on translation of corresponding mature proteins. Therefore, we measured protein levels of FANCD2 and FANCA in DLD1-BRCA2-KO cells (Figure 5d). With E7820 administration, levels of FANCD2 and FANCA proteins decreased markedly in a time-dependent manner. Importantly, decreased FANCD2/FANCA protein levels were consistent with the accumulation of γH2AX and caspase-3 cleavage (a characteristic of cellular apoptosis).
Drug discovery and use using PDX (patient-derived xenograft) models
One of the issues in anticancer drug development up until now is that experimental models using cell lines used to predict therapeutic effects are poor. Meanwhile, PDX is an animal model that reproduces tumors by transplanting cancer tissue from cancer patients into immunodeficient mice, and since it can retain the characteristics of cancer tissue, there are reports that it has a high reproduction rate, and drug discovery and use is progressing rapidly. The National Cancer Center has confirmed that clinical efficacy is consistent with predicting the effects of anti-HER2 therapy in PDX models created from uterine cancer sarcoma patients. *
The large-scale PDX library “J-PDX” derived from Japanese cancer patients constructed by the National Cancer Center is 1. PDX was established across organs, and in addition to major cancers, they also focused on rare cancers (osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, etc.) and cancers common in Asia, 2. The fact that PDX was established not only from surgical specimens but also from drug-resistant specimens, 3. It is characterized by being a PDX with detailed clinical information including treatment history, and is expected to promote utilization and accelerate development in the development of novel anticancer drugs.
* April 10, 2023 Press Release
Confirmation of the efficacy of anti-HER2 therapy with trastuzumab delxtecan in uterine cancer sarcoma is consistent with effect predictions in the PDX model, paving the way for treatment development for rare cancers
Presented papers
Magazine name: NPJ Precision Oncology
Title: A Molecular Glue RBM39-Degrader Induces Synthetic Lethality in Cancer Cells with Homologous Recombination Repair
Authors: Shinji Kohsaka, Shigehiro Yagishita, Yukina Shirai, Yusuke Matsuno, Toshihide Ueno, Shinya Kojima, Hiroshi Ikeuchi, Masachika Ikegami, Rina Kitada, Ken-ichi Yoshioka, Kohta Toshimitsu, Kimiyo Tabata, Akira Yokoi, Toshihiko Doi, Noboru Yamamoto, Takashi Owa, Akinobu Hamada, Hiroyuki Mano
| National Cancer Center | |||
| laboratories | Cellular Informatics Division | Field manager | Takasaka Shinji |
| laboratories | Cellular Informatics Division | Unit chiefs | Ueno Toshihide |
| laboratories | Cellular Informatics Division | Chief Researcher | Ikegami Masashige |
| laboratories | Cellular Informatics Division | Voluntary trainees | Shirai Yukina |
| laboratories | Cellular Informatics Division | Voluntary trainees | Kojima Shinya |
| laboratories | Cellular Informatics Division | Voluntary trainees | Kurita Rina |
| laboratories | Molecular Pharmacology Research Area | Field manager | Hamada Tetsunobu |
| laboratories | Molecular Pharmacology Research Area | Unit chiefs | Yagishita, Motohiro |
| laboratories | Genome Stability Control Research Unit | Unit chiefs | YOSHIOKA Kenichi |
| laboratories | Genome Stability Control Research Unit | Academic Research Fellow | Matsuno Yusuke |
| laboratories | Genome Stability Control Research Unit | Visiting Research Fellows | Matsuo Rika |
| laboratories | Director | Mano Hiroyuki | |
| Central Hospital | Department of Advanced Medicine | section chief | Yamamoto Noboru |
| Higashi Hospital | Department of Advanced Medicine | section chief | Doi Toshihiko |
| Eisai Co., Ltd | ||
| DHBL Cell Lineage & Probation Domains | researchers | Toshimitsu Kota |
| DHBL Cell Lineage & Probation Domains | researchers | Tabata Kimiyo |
| DHBL Cell Lineage & Probation Domains | head | Yokoi Akira |
| Chief Scientific Officer | Managing Executive Officer | Yamato Takashi |
DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00610-0
Posted on: 2024/5/24
URL: (links to an external site)
Domestic doctor-led phase I clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of E7820 for solid cancer in Japanese people
This study will confirm the tolerability, pharmacokinetics, etc. of E7820 in Japanese people for solid cancer patients who are unresponsive or intolerant to standard treatment in the dose confirmation part. Continuing, in the expanded part, we will exploratively evaluate the efficacy and safety of E7820 for biliary tract cancer, endometrial cancer, and solid cancer patients with homologous recombinant repair gene mutations using usage/doses that were confirmed to be tolerable in the dose confirmation part. It will be carried out after receiving the provision of investigational drugs from Eisai. Overseas, there are results of clinical trials using E7820, and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) for oral administration once a day is 100 mg.
Exam name
Domestic doctor-led phase I clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of E7820 for solid cancer in Japanese people
(Clinical trial implementation plan number: NCCH2303, trial abbreviation: CIRCUS)
New drugs used (investigational drugs)
E7820 (oral medication: sulfonamide splicing control drug)
Physical conditions of patients eligible to participate in clinical trials (patient selection criteria)
1. Written consent can be obtained
2. It is a solid cancer and has been diagnosed as unresectable progression or recurrence
3. There is no standard treatment, or you have been diagnosed as unfit or intolerant to standard treatment
4. At the time of registration for clinical trials, the age is 18 years old or older
5. Each organ function is kept within regulations
Note: Please note that the patient selection criteria above are an overview, and even if you fall under the above, you may not be able to participate in this clinical trial.
Research Representative
Yamamoto Noboru (Director, Department of Advanced Medicine, National Cancer Center Central Hospital)
List of facilities participating in physician-led clinical trials (CIRCUS trials)
National Cancer Center Central Hospital (5-1-1 Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo)
National Cancer Center East Hospital (6-5-1 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba)
Clinical Research Implementation Plan and Research Outline Disclosure System
jRCT number: jRCT2031240210
For details of this clinical trial, please check the Clinical Research Implementation Plan and Research Overview Disclosure System.
(Link to an external site)
Research expenses
This exam will be conducted with the support of the following businesses.
Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development Medical Research and Development Innovation Infrastructure Project (CiCle) (JP20pc0101051)
Future prospects
By using the National Cancer Center's J-PDX library for drug discovery development in companies, it is now possible to quickly evaluate drug efficacy for new drug candidates, identify biomarkers to predict efficacy, and even launch clinical trials. In this study, after confirming safety, including tolerability of E7820, and determining recommended doses, the National Cancer Center and Eisai will consider implementing phase II and further approval application tests to confirm efficacy against specific cancer types and solid cancers with biomarkers, and aim for regulatory approval.
Furthermore, we aim to establish the system constructed in this research as a drug discovery research system to accelerate the development of novel anticancer drugs.
Explanation of terms
Note 1 PDX (patient-derived xenograft): mouse model
It is a cancer model created by directly transplanting tumor tissue from cancer patients into immunodeficient mice.
Note 2 Biomarkers
It is a molecule such as protein or gene, and is an indicator of the presence of disease, treatment selection, etc.
Note 3 All exon sequences
It is a method for selectively concentrating protein-coding exon regions in the human genome and efficiently analyzing them.
Note 4 Homologous recombination repair (homologous recombination repair)
It is one of the main mechanisms in DNA double strand break repair, and repair is performed using sister chromatids as templates.
Note 5 Physician-led clinical trials
Clinical development (clinical trials) of new drugs is necessary in order for new drugs to be approved and used with insurance. It is called a doctor-led clinical trial when doctors themselves conduct clinical trials with the cooperation of pharmaceutical companies for pharmaceuticals that are promising pharmaceuticals but are not subject to company-led clinical trials.
Note 6 Tolerability
Tolerability is a term that indicates whether side effects that occur when an investigational drug is administered are acceptable to humans. Specifically, when an investigational drug is administered to a person, it will be examined by referring to the frequency of onset of side effects that are considered intolerable and their severity.
Note 7 RNA splicing
RNA splicing is an essential mechanism for gene expression that removes introns from mRNA precursors to produce mature mRNA.
Note 8 Full transcriptome analysis
It is a method for analyzing the sequence and expression levels of all gene transcripts (transcriptomes) present in cells.
Note 9 PARP inhibitors
By inhibiting polyadenosine 5' diphosphate ribose polymerase (PARP: poly ADP-ribose polymerase), an enzyme that plays an important role in cells such as DNA repair, it induces synthetic lethality in tumor cells that have mutations in homologous recombination repair genes.
Contact information
● Inquiries about non-clinical trials
National Cancer Center
Laboratory Cell Informatics Division
Kosaka Shinji (Kosaka Shinji)
Phone number: 03-3542-2511 (representative)
E-mail: skohsaka@ncc.go.jp
● Inquiries about physician-led clinical trials
National Cancer Center
Central Hospital Clinical Research Support Division Research Planning Promotion Department International Research Support Office
Phone number: 03-3547-5201 (ext. 2686)
E-mail: ncch2303_office@ml.res.ncc.go.jp
● Public Relations Office
National Cancer Center
Planning and Strategy Bureau Public Relations Planning Office
Phone number: 03-3542-2511 (representative)
E-mail: ncc-admin@ncc.go.jp
Eisai Co., Ltd
PR department
Phone number: 03-3817-5120
- Full release

