National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Toshiba Corporation (Toshiba), Renesas Electronics Corporation (Renesas), Landis Gyr Japan Co., Ltd. (Landis & Gyr), I.S.V. Co., Ltd., and Okiden Electric Industry Co., Ltd. jointly use the electric smart meter system to jointly check gas/water meters and non-standard measuring instruments by using Wi-SUN enhanced HAN (Home Area Network) wireless standard for the 'IoT route' defined to be used for joint inspection.*1 Enhanced HAN standard for the Wi-SUN Alliance international radio communication standardization group was officially established. It is the standard adopted for the 'IoT route' defined to be used for joint inspection. It was also adopted by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry's Next-Generation Smart Meter System Study Group as the wireless standard communication interface TTC JJ-300.10 established by the Information and Communication Technology Committee (TTC) based on this standard.*2With the enactment of this standard, services that utilize the Wi-SUN system will accelerate, and the utilization of joint inspection of electric power smart meters, water/gas meters, and non-standard measuring instruments will also advance in Japan.
Background
Electric smart meters, which have communication functions to collect meter reading data and control meters, have been introduced since 2013 and have already been installed in millions of units. The Wi-SUN HAN (Home Area Network) system standardized by the Wi-SUN Alliance, which is currently adopted as the wireless communication standard for this electric power smart meter, is mainly adopted for 'B routes,' which are communication routes connecting energy management systems installed in homes and buildings.*3On the other hand, for water and gas meters, each operator mainly uses its own communication equipment for remote meter reading, or workers visually read the meter one house at a time. However, due to investment efficiency and work efficiency, there is an increasing demand for collective meter reading via the electric power smart meter.
In addition, the specific measurement system started in April 2022, and even meters that have not undergone metering verification and meet certain standards can now be used for electricity transactions. This meter is called a non-standard measuring instrument and is used in EV charging systems, photovoltaic power generation systems, and others. With the establishment of the 'IoT route,' which is a communication route for joint inspection of non-standard measuring instruments, gas meters, and water meters, the demand for collective inspection via the electric power smart meter is expected to increase.
Furthermore, Wi-SUN enhanced HAN system, which is a wireless communication standard for electric power smart meters, which is based on this standard, is appropriate for use as the communication method in the 'IoT route.' This adoption was concluded in May 2022 at the Next-Generation Smart Meter System Study Group of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. Wi-SUN HAN (Chairman: NICT, Technical Editor: Toshiba), a working group of the Wi-SUN Alliance, based on this standard for 'IoT routes,' established a standard specification book that includes technical specifications and specifications required for mutual interconnection testing in February 2024.
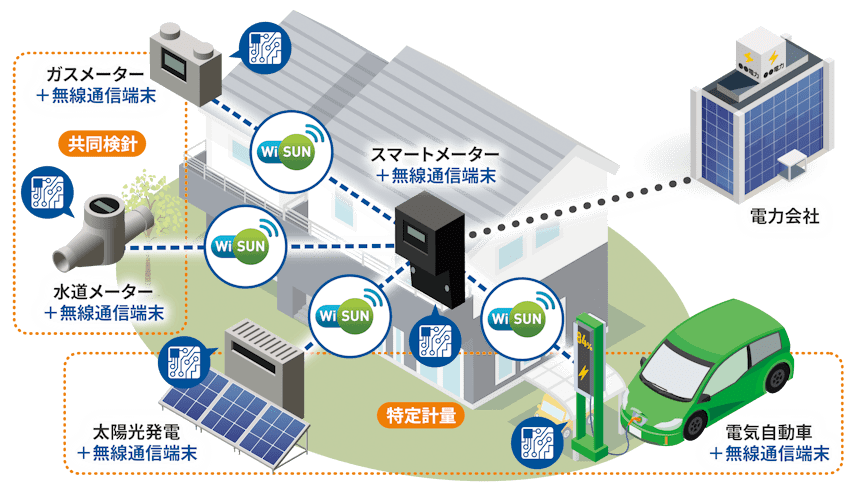
Figure 1: Use image of the IoT route
(Wi-SUN enhanced HAN is installed in the wireless terminal in the figure and connected to the electric meter)
This achievement
Based on the above standard specifications, the Information and Communication Technology Committee, a domestic standardization organization, revised the standard specification TTC JJ-300.10 for home network communication interfaces, which was officially enforced on May 16th, 2024. By introducing wireless terminals compliant with TTC JJ-300.10 in the future, joint inspection using water and gas meters will be possible.
The Wi-SUN enhanced HAN system, which corresponds to this 'IoT route,' has the following features.
- Gas and water meters, special measuring instruments, wireless terminals for managing electric smart meters, and wireless endpoints for managing gas and water meters can be connected using the international standard IEEE 802.15.4g physical layer and MAC layer defined by IEEE 802.15.4. Also, communication via IPv6 is possible. It can be securely authenticated by the communication authentication standard, which has been introduced for electric smart meters since previously. It has a communication interface equipped with an application for the IoT Routes. The communication procedure for connecting is defined even for the sleeping device that turns off electricity when wireless endpoints for managing gas and water meters communicate. It has the function of being able to relay through one relay device even if wireless endpoints for managing gas and water meters are located outdoors. This document for TTC JJ-300.10 is published at the following URL: https://www.ttc.or.jp/application/files/2917/1616/4764/JJ-300.10v2.3.pdf. With the implementation of the Wi-SUN enhanced HAN for IoT routes and the JJ-300.10 standard, it is planned to develop test equipment for standard compliance and interoperability testing in the future. In addition to this, we will actively promote activities to ensure the stable operation of this standard by actively conducting interoperability testing to verify interoperability and compatibility and promoting moves toward joint meter reading and contributing to the development of an efficient energy management system.*4The physical layer for the international standard IEEE 802.15.4g was established.Feature quantity: A numerical value that quantitatively expresses the characteristics and properties of the data and subject matter analyzed.The MAC layer for IEEE 802.15.4 was established.*6The wireless endpoints for managing gas and water meters can be securely authenticated by the communication authentication standard, which has been introduced for electric smart meters since previously. Communication is possible via IPv6.
- It has a communication interface equipped with an application for the IoT Routes.
- Even if the wireless endpoints for managing gas and water meters are the sleeping device that turns off electricity when communicating, a communication procedure for connecting is defined.
- It has the function of being able to relay through one relay device even if wireless endpoints for managing gas and water meters are located outdoors.
This document for TTC JJ-300.10 is published at the following URL: https://www.ttc.or.jp/application/files/2917/1616/4764/JJ-300.10v2.3.pdf.
This document for TTC JJ-300.10 is published at the following URL: https://www.ttc.or.jp/application/files/2917/1616/4764/JJ-300.10v2.3.pdf.
Based on the results of this demonstration, Hitachi High-Tech and Hitachi will collaborate with various stakeholders such as material manufacturers including Sekisui Chemical to develop a more user-friendly environment and challenge One Hitachi to commercialize services using this system in Fiscal Year 2025. After the service is commercialized, Hitachi High-Tech will use its broad distribution network as a sales agent to expand to domestic and overseas product and material manufacturers. Companies (buyers and sellers) that participate in this business are being asked to join. Hitachi will work with Hitachi High-Tech and Sekisui Chemical to promote system development toward commercialization. Sekisui Chemical will continue to actively promote initiatives toward achieving a circular economy in 2050 by collaborating with Hitachi High-Tech and Hitachi.
With the implementation of the Wi-SUN enhanced HAN for IoT routes and the JJ-300.10 standard, it is planned to develop test equipment for standard compliance and interoperability testing in the future. In addition to this, we will actively promote activities to ensure the stable operation of this standard by actively conducting interoperability testing to verify interoperability and compatibility and promoting moves toward joint meter reading and contributing to the development of an efficient energy management system.
A communication standard for connecting household electricity smart meters, home appliances, and energy management systems. Communication standards have been established for connecting mainly electric power smart meters and energy management systems using the B Route communication standard, as well as for connecting home appliances, special measuring instruments, and energy management systems using the HAN communication standard. Wi-SUN HAN-compliant equipment that supports the B Route has already been introduced into several tens of millions of domestic smart meters in operation. The latest HAN communication specification is Wi-SUN enhanced HAN, which has a method for expanding the communication area through a relay and a connection function to a device called a Sleeping device that turns the power on only when communicating. Hiroshi Harada of NICT is serving as the chairman, and Mitsuru Kanda of Toshiba is the technical editor, leading standardization efforts.
IEEE 802.15.4g specifies the physical layer for the network to connect various equipment such as meters, sensors, and monitors.
IEEE 802.15.4g specifies the physical layer for the network to connect various equipment such as meters, sensors, and monitors.
A set of specifications that define the physical transmission and connection method of a network. Examples include modulation methods and encoding methods for wireless signals, basic packet frame construction for communication, and spectrum masks.
*6. MAC layer
A set of specifications that define the communication method between devices directly connected in a network.
Above.
*All product and service names in this release are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
The information (including product prices and specifications) posted in this news release is current as of the date of publication. Please note that it may be subject to change without notice.
