Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We can see that The St. Joe Company (NYSE:JOE) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
What Is St. Joe's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at March 2024 St. Joe had debt of US$630.2m, up from US$598.6m in one year. However, it does have US$93.4m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about US$536.9m.
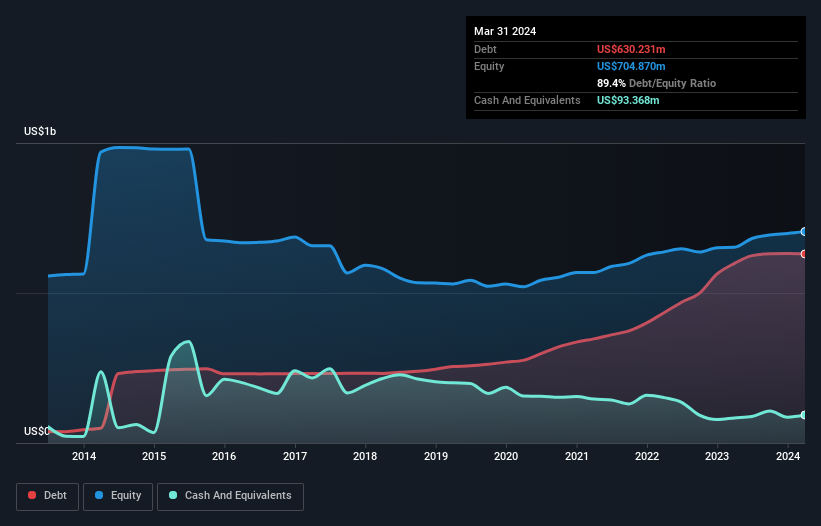
How Strong Is St. Joe's Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that St. Joe had liabilities of US$85.9m falling due within a year, and liabilities of US$746.9m due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of US$93.4m and US$55.3m worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling US$684.1m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
St. Joe has a market capitalization of US$3.42b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
St. Joe has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 3.9 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 5.0 times. This suggests that while the debt levels are significant, we'd stop short of calling them problematic. It is well worth noting that St. Joe's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 82% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is St. Joe's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, St. Joe actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. There's nothing better than incoming cash when it comes to staying in your lenders' good graces.
Our View
St. Joe's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow suggests it can handle its debt as easily as Cristiano Ronaldo could score a goal against an under 14's goalkeeper. But truth be told we feel its net debt to EBITDA does undermine this impression a bit. When we consider the range of factors above, it looks like St. Joe is pretty sensible with its use of debt. That means they are taking on a bit more risk, in the hope of boosting shareholder returns. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 1 warning sign for St. Joe you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
