Microsoft and Quantinuum today announced a major breakthrough in quantum error correction. Using Quantinuum’s ion-trap hardware and Microsoft’s new qubit-virtualization system, the team was able to run more than 14,000 experiments without a single error. This new system also allowed the team to check the logical qubits and correct any errors it encountered without destroying the logical qubits.
This, the two companies say, has now moved the state-of-the-art of quantum computing out of what has typically been dubbed the era of noisy intermediate scale quantum (NISQ) computers. “Noisy” because even the smallest changes in the environment can lead a quantum system to essentially become random (or “decohere”), and “intermediate scale” because the current generation of quantum computers is still limited to just over a thousand qubits at best. A qubit is the fundamental unit of computing in quantum systems, analogous to a bit in a classic computer, but each qubit can be in multiple states at the same time and doesn’t fall into a specific position until measured, which underlies the potential of quantum to deliver a huge leap in computing power.
It doesn’t matter how many qubits you have, though, if you barely have time to run a basic algorithm before the system becomes too noisy to get a useful result — or any result at all.
Combining several different techniques, the team was able to run thousands of experiments with virtually no errors. That involved quite a bit of preparation and pre-selecting systems that already looked to be in good shape for a successful run, but still, that’s a massive improvement from where the industry was just a short while ago.
It’s a step in the right direction for quantum computing. There are still plenty of problems to be solved (and these results need to be replicated, too, of course), but theoretically, a computer with 100 of these logical qubits could already be useful for solving some problems, while a machine with 1,000 qubits could, Microsoft says, “unlock commercial advantage.”
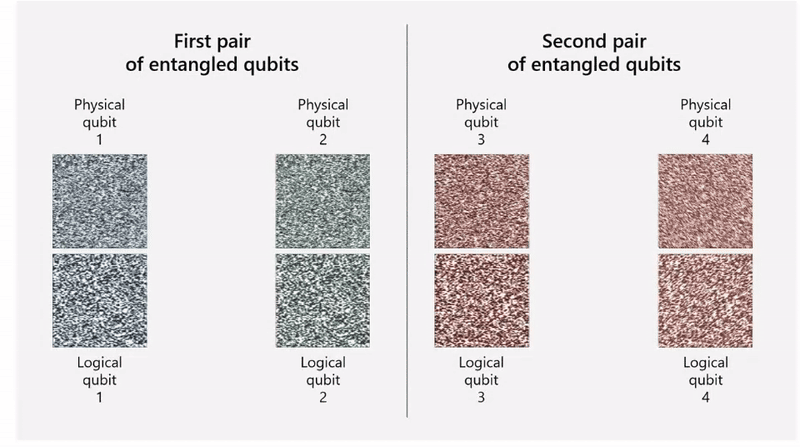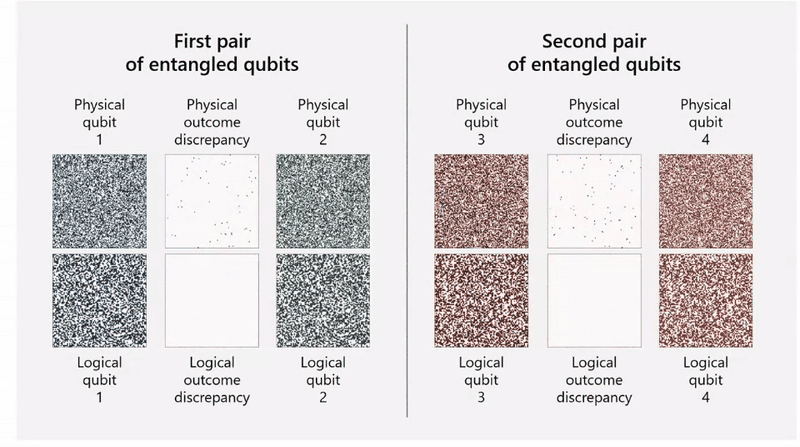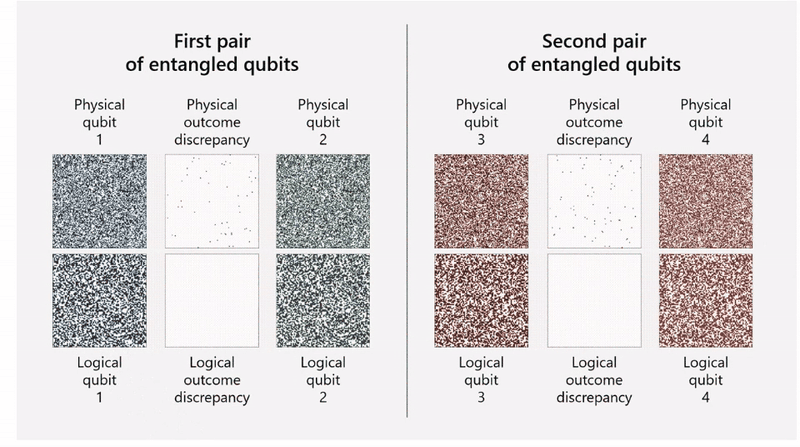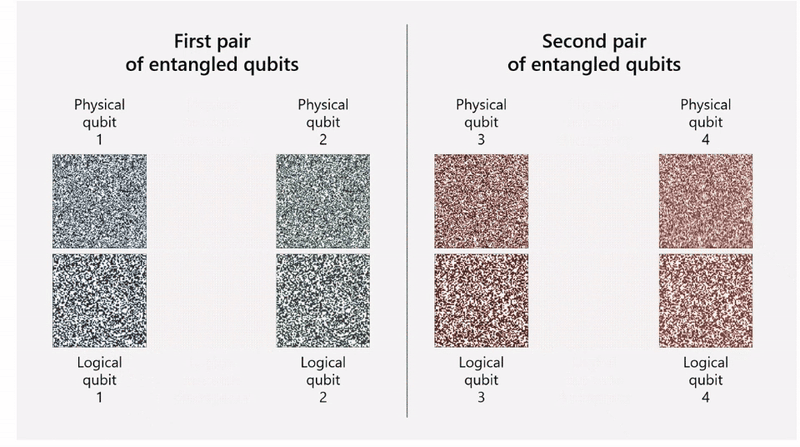
The team used Quantinuum’s H2 trapped-ion processor and was able to combine 30 physical qubits into four highly reliable logical qubits. Encoding multiple physical qubits into a single logical qubit helps protect the system from errors. The physical qubits are entangled together so that it becomes possible to detect an error in a physical qubit and fix it.
It’s this error correction that has long vexed the industry: The lower the noise and the higher the quality of the physical qubits, the better, of course, but without sophisticated error correction, there is no way out of the NISQ era because these systems will all decohere sooner rather than later.
“Merely increasing the number of physical qubits with a high error rate — without improving that error rate — is futile because doing so would result in a large quantum computer that is not any more powerful than before,” Dennis Tom, the general manager for Azure Quantum, and Krysta Svore, the VP of Advanced Quantum Development at Microsoft, wrote in today’s announcement. “In contrast, when physical qubits with sufficient quality of operation are used with a specialized orchestration-and-diagnostics system to enable virtual qubits, only then does increasing the number of physical qubits result in powerful, fault-tolerant quantum computers able to perform longer, more complex computation.”
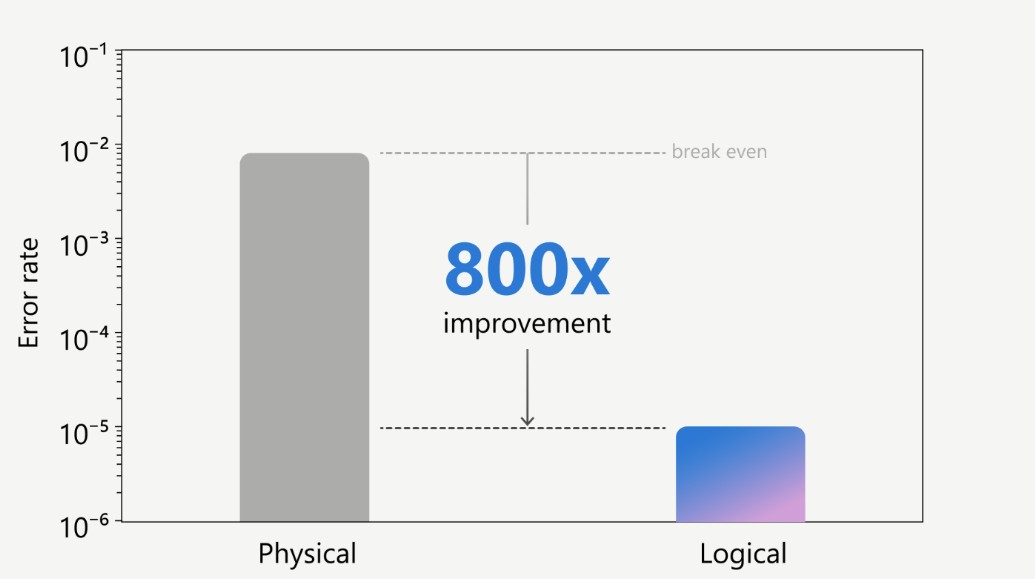
It was only a couple of years ago that logical qubits started outperforming physical qubits. Now, Microsoft and Quantinuum argue that their new hardware/software system demonstrates the largest gap between physical and logical error rates, improving on using only physical qubits by up to 800x.
The researchers note that to move beyond NISQ, a large separation between logical and physical qubit error rates is necessary, as is the ability to correct individual circuit errors and to generate entanglement between at least two logical qubits. If these results hold up, then the team achieved all three and we have indeed entered a stable era the era of resilient quantum computing.
As it turns out, the most important result here may actually be the team’s ability to perform “active syndrome extraction” — that is, the ability to diagnose an error and correct it, without destroying the logical qubit in the process.
“This achievement marks the first step in being able to correct errors while not destroying the logical qubits and showcases a fundamental milestone in quantum error correction,” Tom and Svore explain. “We demonstrated this critical component of reliable quantum computing with our qubit-virtualization system, which resulted in a low logical error rate over multiple rounds of syndrome extraction.”
It’ll now be up to the rest of the quantum community to replicate these results and implement similar error correction systems. That’s likely just a matter of time, though.
“Today’s results mark a historic achievement and are a wonderful reflection of how this collaboration continues to push the boundaries for the quantum ecosystem,” said Ilyas Khan, founder and chief product officer of Quantinuum. “With Microsoft’s state-of-the-art error correction aligned with the world’s most powerful quantum computer and a fully integrated approach, we are so excited for the next evolution in quantum applications and can’t wait to see how our customers and partners will benefit from our solutions especially as we move towards quantum processors at scale.”
For more details, you can find the technical paper here.































Comment