According to FX168 Financial News (Asia Pacific), the reserves in the USA banking system are a key factor in the Federal Reserve's decision to continue reducing its balance sheet, as these reserves have fallen below 3 trillion dollars, reaching the lowest level since October 2020. Amid ongoing "balance sheet reduction", the market fears a repeat of September 2019 when the Fed's tapering led to a scarcity of reserves, causing critical loan rates and the federal funds rate to spike.
In the USA, balance sheet reduction refers to the Federal Reserve's strategy of reducing its holdings of Bonds and other Financial Assets to relatively decrease liabilities and adjust the scale of its balance sheet when the economy reaches a certain level of stability and inflationary pressures increase. To prevent the economy from overheating and inflation from worsening, the Fed undertakes balance sheet reduction, which usually means gradually decreasing the monthly asset purchase amount until halting or slowing the asset purchase pace.
The aim of the balance sheet reduction policy is to gradually restore the market to a state of monetary policy that is more natural and not still under central bank intervention, alleviating potential risks of excessive expansion or inflation.
 According to data released by the Federal Reserve on Thursday (January 2), as of the week ending January 1, bank reserves had decreased by approximately 326 billion dollars, falling to 2.89 trillion dollars. This marks the largest weekly decline in two and a half years.
According to data released by the Federal Reserve on Thursday (January 2), as of the week ending January 1, bank reserves had decreased by approximately 326 billion dollars, falling to 2.89 trillion dollars. This marks the largest weekly decline in two and a half years.
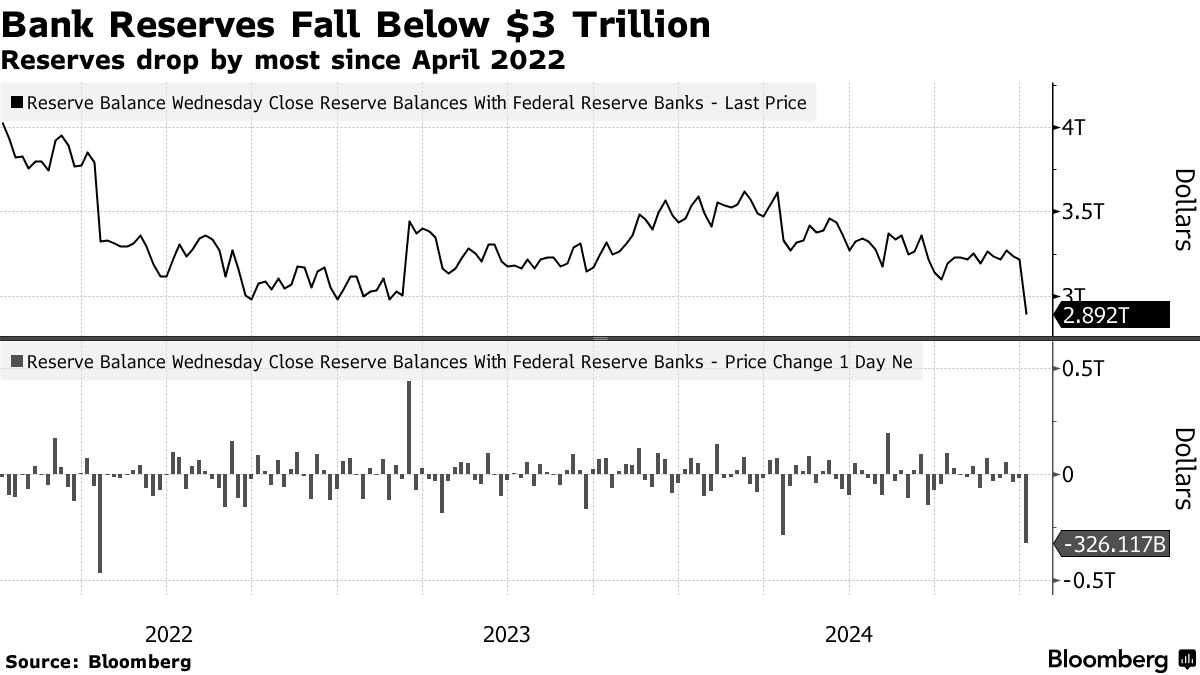
(Source: Bloomberg)
This decline occurred as year-end circumstances forced banks to trim balance sheet-intensive activities such as repurchase agreement transactions to strengthen regulatory books. This means that Cash was directed to places like the Fed's overnight reverse repurchase agreement tool, thereby draining liquidity from other liabilities on the Federal Reserve's books. During the period from December 20 to December 31, 2024, the RRP balance increased by 375 billion dollars, and on Thursday it decreased by 234 billion dollars.
Meanwhile, as Financial Institutions continue to repay Bank's Term Funding Program loans, the Federal Reserve has also been eliminating excess Cash from the financial system through its Algo tightening program.
As policymakers in the USA continue with quantitative easing, Wall Street strategists have been closely monitoring the lowest reserve levels - some estimate that, including buffers, reserve levels range between 3 trillion and 3.25 trillion dollars.
Federal Reserve policymakers indicated at last month's meeting that the Fed will continue to reduce its balance sheet.
The bank also adjusted the rate of the RRP tool to align it with the lower limit of the federal funds rate target range. This has put downward pressure on short-term interest rates, and some believe that this may be enough to alleviate reserve shortages for a while.
However, the debate over how much longer the Federal Reserve can maintain quantitative tightening without triggering memories of September 2019 continues. At that time, as the Fed reduced its balance sheet, reserves became too scarce, leading to a spike in key loan rates and the federal funds rate.
It was precisely because of this that the Federal Reserve was forced to intervene to stabilize the market.
Although the Federal Reserve reduced the cap on maturing Treasury securities that do not need to be reinvested in June 2024, it remains unclear when the plan will come to a complete end.
The recent resumption of the debt ceiling may make it more difficult for policymakers to determine the ideal level, as measures taken by the Treasury to maintain the ceiling often artificially increase liquidity in the financial system and obscure indicators of reserve scarcity.
In a survey conducted by the New York Fed's Open Market Desk among primary dealers and market participants, two-thirds of respondents expect quantitative tightening to conclude in the first or second quarter of 2025.

