Source: Haitong Research
Author: Wu Xinkun
① Looking ahead to 2025, the liquidity in Hong Kong stocks is expected to remain loose, with the macro trend of the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts unchanged and the micro aspect seeing net inflows from the Hong Kong Stock Connect, as well as a potential phase of foreign capital inflows. ② The recovery of Hong Kong stocks has a relatively clear overall direction, and the key to the recovery process lies in the speed of the implementation of incremental policies, while Trump's policies towards China may also cause disturbances to the fundamentals. ③ The sentiment in Hong Kong stocks may be influenced by the pace of policies introduced by Trump, while institutional reforms in Hong Kong could help boost investor confidence in the long run.
In 2024, Hong Kong stocks are expected to trend upward but remain at a low level. Looking back at 2024, the overall performance of Hong Kong stocks has trended upward, which can be divided into three phases: ① from January 2 to January 31, it continues to decline to form a bottom, ② from February 1 to September 11, it rebounds from a low level and then corrects, ③ from September 12 to December 31, it experiences a surge followed by high position fluctuations. Since October 8, Hong Kong stocks have been fluctuating at a high level, and the index has shown a correction. Based on indicators such as valuation, trading, and risk preference, it is believed that Hong Kong stocks are still in a high cost-performance range. In terms of valuation, Hong Kong stocks are relatively undervalued compared to overseas counterparts. As for sentiment, the current trading volume in Hong Kong stocks is low, and the short-selling ratio is high. Regarding risk preference, Hong Kong stocks have a high risk premium and declining expected volatility.
 Variable 1: Will the pace of interest rate cuts in the USA slow down? Historically, after 1982, the average duration of the Federal Reserve's preemptive interest rate cuts lasted 8 months and amounted to a decrease of 174 basis points, indicating that there is still some time and space for future cuts. Current USA economic indicators show contradictions, and Powell adopted a hawkish tone at the December FOMC meeting, suggesting that the pace of interest rate cuts in 2025 may slow down. Given the inflationary nature of Trump's policies, future interest rate cuts may be constrained by the interplay between inflation and employment data, introducing more variability into the timing of cuts, with market expectations currently suggesting 1-2 cuts in 2025.
Variable 1: Will the pace of interest rate cuts in the USA slow down? Historically, after 1982, the average duration of the Federal Reserve's preemptive interest rate cuts lasted 8 months and amounted to a decrease of 174 basis points, indicating that there is still some time and space for future cuts. Current USA economic indicators show contradictions, and Powell adopted a hawkish tone at the December FOMC meeting, suggesting that the pace of interest rate cuts in 2025 may slow down. Given the inflationary nature of Trump's policies, future interest rate cuts may be constrained by the interplay between inflation and employment data, introducing more variability into the timing of cuts, with market expectations currently suggesting 1-2 cuts in 2025.
Variable 2: What new changes are there in the capital flow of Hong Kong stocks? The Hong Kong Stock Connect is likely to continue its inflow, while the sustainability of foreign capital return remains uncertain. Looking ahead to 2025, the Hong Kong Stock Connect is likely to continue inflowing, and the AH risk premium is already at a historical high, making Hong Kong stocks more cost-effective. Regarding foreign capital, with the domestic policy gaining momentum, the trend of fundamental recovery in 2025 is relatively clear, and there is a hope for a phased return of foreign capital driven by profit-seeking demands. Furthermore, from a global asset allocation perspective, the cost-performance ratio of foreign capital investing in Hong Kong stocks' dividends and Technology sector is marginally improving.
Variable 3: How is the domestic economic recovery progressing? Since September 24, the domestic policy tone has shifted significantly; according to the spirit of the December Politburo meeting and the Central Economic Work Conference, macro policies in 2025 will be 'more proactive and effective,' with monetary and fiscal policy tones being the most aggressive in history, also explicitly stating to 'stabilize the property and stock markets,' indicating that there is already space for future policy efforts. The current policy effects have reflected in some macro fundamental data, and if future incremental policies can be quickly implemented and effective, it is expected to support the performance of Hong Kong stocks in 2025.
Variable 4: How will Trump's policies advance? The policy direction after Trump's return to power in 2025 may be relatively certain, but the pace of policy implementation remains uncertain. Currently, Trump has largely completed his cabinet formation, which includes many hawkish representatives towards China, indicating a clearer overarching direction in his policies towards China. However, the timing of policy rollout is still variable, necessitating close monitoring of the actual progress of policies after Trump’s return to power. If Trump's policies in trade are quickly realized, it may disrupt the fundamentals and sentiment regarding Hong Kong stocks in 2025.
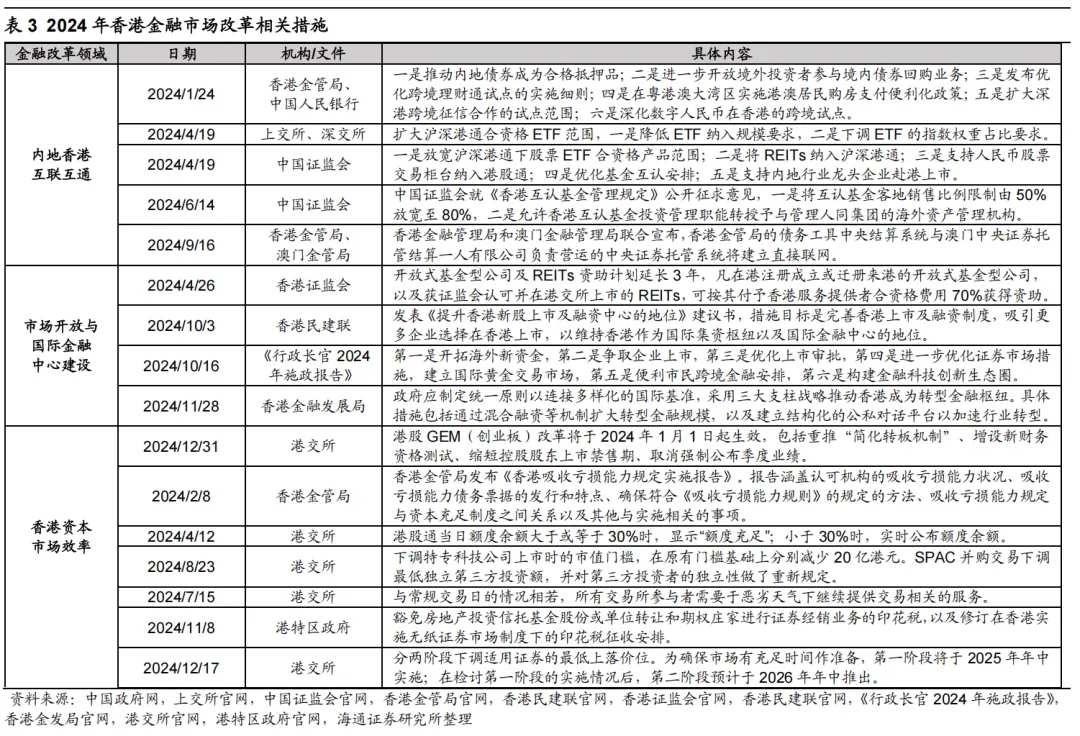
Variable 5: How is the reform of the Hong Kong stock system progressing? If the reform of the Hong Kong financial market continues, the investment environment is expected to improve. In 2024, Hong Kong will accelerate its institutional reforms, and this trend is likely to continue into 2025, thereby boosting investor confidence and providing long-term positive support for the performance of Hong Kong stocks. Specifically, referring to the reforms focused on in 2024, future reforms may concentrate on three main directions: first, deepening the connectivity between the mainland and Hong Kong; second, strengthening the construction of Hong Kong as an international financial center; and third, enhancing market efficiency and improving the trading environment.
Risk Warning: The Fed's interest rate cuts may occur faster than expected, U.S. policy is unpredictable, the implementation of growth-stabilizing policies is not progressing as anticipated, and the recovery of the domestic economy is not meeting expectations.
Main text
Since October 8, the Hong Kong stock market has entered a phase of volatile adjustment, and as of December 31, the Hang Seng Index has cumulatively declined by 13%. Looking forward to 2025, the performance of Hong Kong stocks still faces many uncertainties; in light of domestic and international changes, what will be the direction of Hong Kong stocks? The following will explore five key variables that may affect the performance of Hong Kong stocks in 2025, aiming to provide useful references for investors.
1. In 2024, Hong Kong stocks will oscillate upward but remain at a low level.
In 2024, the Hong Kong stock market exhibits a volatile upward trend. Looking back at 2024, the main indices of Hong Kong stocks performed strongly, with the Hang Seng Index increasing by over 17% during the year, ranking among the top in major global markets. However, due to multiple domestic and international influencing factors, the rise of Hong Kong stocks has not been smooth. Specifically:
Phase 1: Continuing the downtrend before forming a bottom. Due to the tightening economic policies set at several important meetings at the end of 2023 for 2024, market fundamentals are expected to be weak. This, combined with outflows of foreign capital and reductions in quantitative investments leading to a tightening of market liquidity, resulted in Hong Kong stocks continuing the downtrend at the beginning of the year, with the Hang Seng Index cumulatively dropping by -9.2% during the period from January 2 to January 31, with the maximum drop at -13.7%.
Phase 2: After a bottom rebound, a pullback occurs. Thanks to the implementation of domestic monetary and real estate policies, along with the central government's capital injections into ETFs, Hong Kong stocks began to rebound from February; however, due to a weakening of policy momentum and a slower pace of fundamental recovery, Hong Kong stocks pulled back after the end of May, with the Hang Seng Index cumulatively increasing by 10.5% with a maximum increase of 28.5% during the period from February 1 to September 11.
Phase ③: Sharp rise followed by high-level fluctuations. Starting from mid-September, the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts led to an early rise in Hong Kong stocks compared to A-shares. Subsequently, the domestic policy bottom on 9/24 and the strong mid-year report for Hong Kong stocks accelerated the index's rise. However, since 10/8, Hong Kong stocks entered a phase of high-level fluctuations, with adjustments potentially caused by profit-taking after the rapid rise. At the same time, the increased probability of Trump's victory has disrupted the liquidity and risk preferences for Hong Kong stocks. From 9/12 to 12/31, the Hang Seng Index had a cumulative/max gain of 17.2%/35.7%.
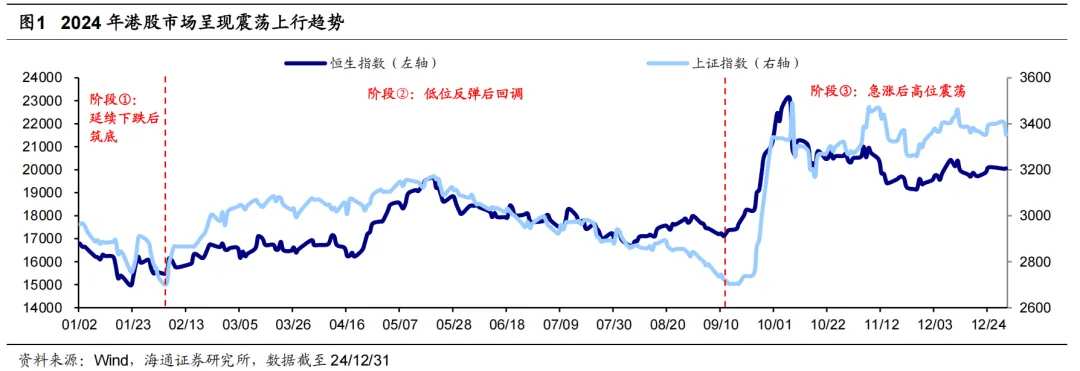
Taking into account valuation, sentiment, and risk preferences, Hong Kong stocks are currently still at historically low levels. Since 10/8, Hong Kong stocks have entered a high-level fluctuation phase, with the index undergoing some corrections. Based on various indicators such as valuation, trading, and risk preferences, it is believed that Hong Kong stocks are currently still in a highly cost-effective range.
From a valuation perspective, Hong Kong stocks are generally undervalued compared to the global perspective. First, the valuation of Hong Kong stocks is at a historically low level. Currently (as of 12/31, the same below), the Hang Seng Index PE (TTM, same below) has dropped below the average level over the past 14 years (3-year rolling), at 9.2 times, placing it in the 26th percentile over the past 14 years. Secondly, in the context of international comparisons, the valuation of Hong Kong stocks is also low. Currently, the Hang Seng Index's PE percentile over the past ten years is 21%, and the Hang Seng Technology Index is 9%, lower than the S&P 500's 94%, the Nasdaq's 92%, as well as lower than the United Kingdom's FTSE 100's 72%, India's Nifty 50's 68%, Japan's Nikkei 225's 36%, and France's CAC 40's 35%. The valuation percentile of Hong Kong stocks is significantly low, especially for the Hang Seng Technology Index.
From a sentiment perspective, the trading volume of Hong Kong stocks has decreased, and the short-selling ratio is relatively high. On one hand, the trading volume of Hong Kong stocks is at a historically low level and is significantly lower compared to A-shares. After the National Day holiday, the trading volume of Hong Kong stocks shrank, with the Hang Seng Index trading volume falling from 620.4 billion yuan on 10/8 to 74.5 billion yuan on 12/31. Notably, the trading volume reduction in this round of Hong Kong stocks is more pronounced compared to A-shares. On the other hand, the proportion of short selling in Hong Kong stocks is relatively high compared to historical levels. As of 12/31, the trading volume of short selling in Hong Kong stocks accounted for 14.7% of the total market trading volume, higher than the average level of 14.5% over the past 14 years.
From a risk preference perspective, the risk premium of Hong Kong stocks is high, and the expected volatility is decreasing. From the asset pricing perspective, the stock market sentiment is at a historically low level. Currently, the risk premium rate of Hong Kong stocks (1/Hang Seng Index PE-10Y China/USA Treasury yield average) is 7.77%, at the 35th percentile from high to low over the past 14 years, higher than the average level over the past 14 years. From the perspective of expected volatility, as of 12/31, the Hang Seng Index volatility index (measuring the expected range of the Hong Kong stock market over 30 trading days) has dropped to 22.4, which is near the average level over the past 14 years, indicating an improvement in investor expectations.
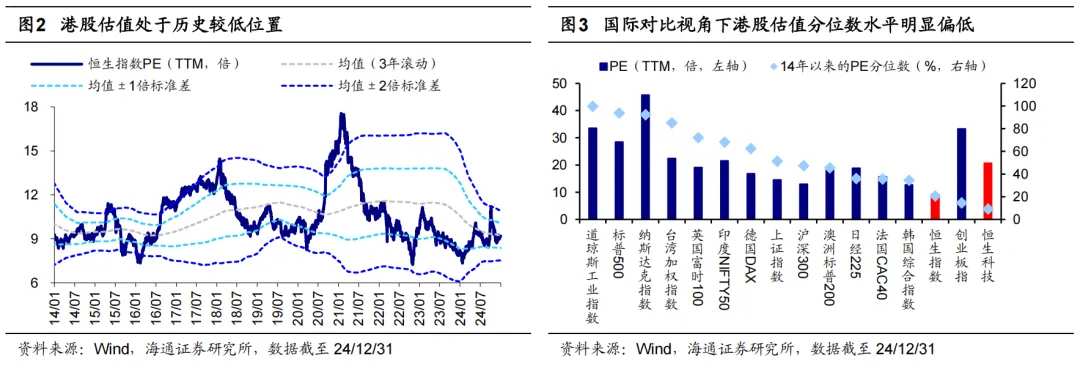
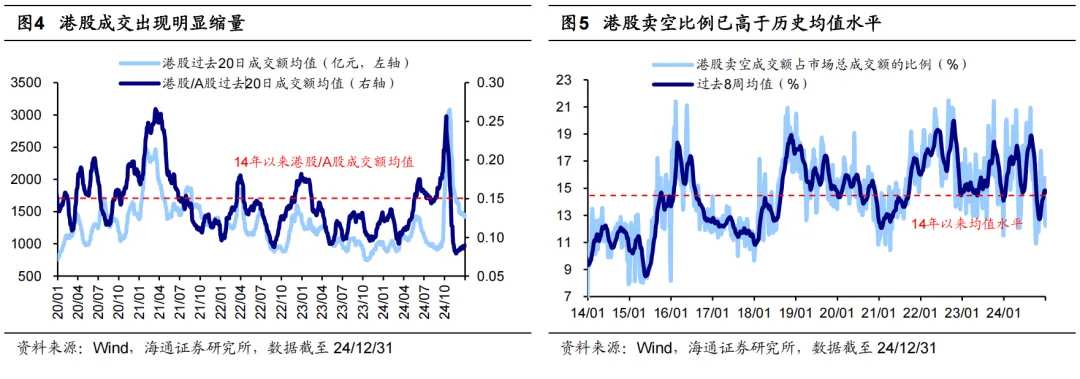
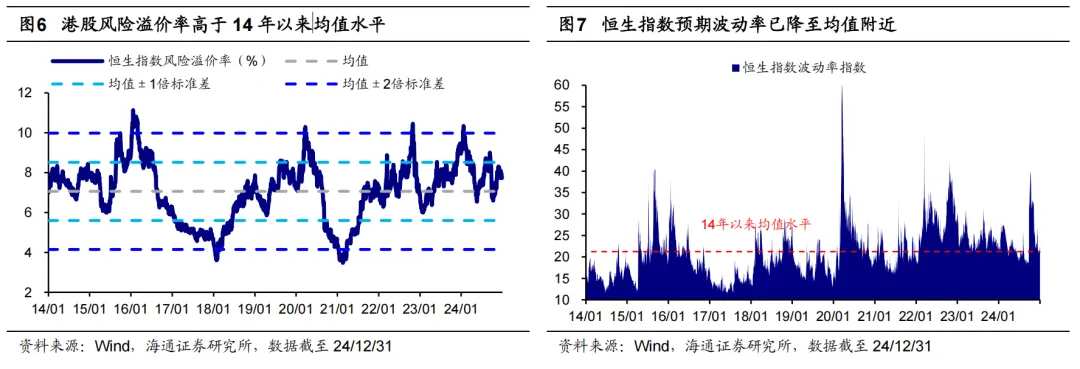
Currently, Hong Kong stocks have adjusted to a high cost-effective range, but whether they can achieve upward movement in the future still depends on the influence of many uncertain factors. Compared to A-shares, Hong Kong stocks are not only more sensitive to changes in the overseas environment but also affected by political and economic changes in mainland China and Hong Kong. Looking ahead to 2025, it is believed that based on the DDM model, there are five key variables that may determine the overall trend of Hong Kong stocks, which will be analyzed in detail in sections 2-6.
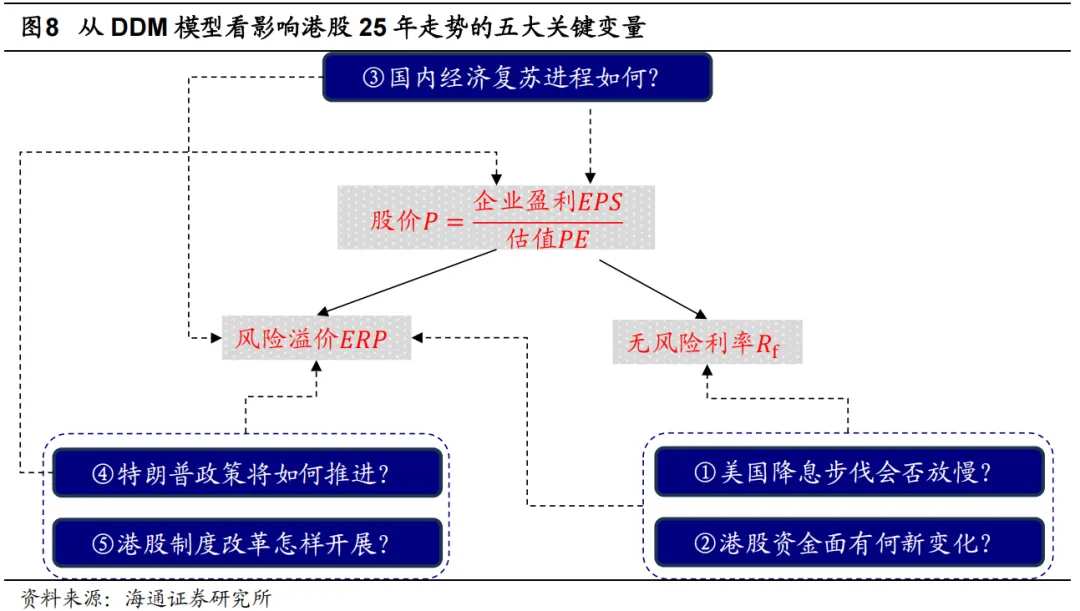
2. Variable 1: Will the USA slow down its interest rate cuts?
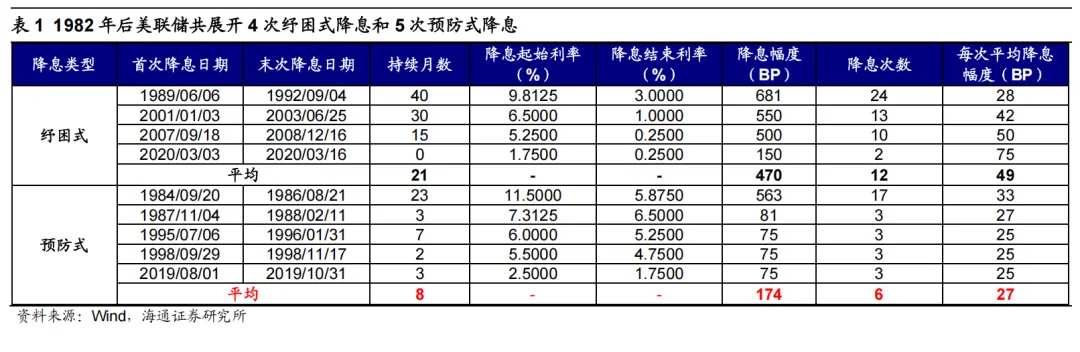
Variable 1: The pace of rate cuts by the Federal Reserve has many uncertainties, with the market currently expecting 1-2 rate cuts in 2025. As the Hong Kong dollar is pegged to the US dollar, the interconnectedness of interest rate policies means that Federal Reserve rate cuts can directly influence the macro liquidity of Hong Kong stocks. In addition, Federal Reserve rate cuts often boost global risk preferences, which in turn affect the micro liquidity of Hong Kong stocks. The current cycle of Federal Reserve rate cuts may be more precautionary, and the pace of rate cuts may be slower.
On December 18, Eastern Time, the Federal Reserve's FOMC meeting announced another rate cut of 25 basis points, adjusting the benchmark interest rate to the range of 4.25%-4.5%. This is the third rate cut since September, with a cumulative reduction of 100 basis points. Historically, after 1982, the Federal Reserve has implemented five preemptive rate cuts, with each cut averaging eight months, a total of six rate cuts, and an accumulated reduction of 174 basis points, indicating that there is still some time and space for future rate cuts.
Currently, conflicting economic indicators in the USA are making the pace of the Federal Reserve's rate cuts more uncertain. Determining the direction of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy must ultimately return to the performance of economic indicators, which currently show contradictions between inflation and employment data in the USA.
From the perspective of inflation, the USA's CPI in November was 2.7% year-on-year, rising for two consecutive months, while the core CPI was 3.3% year-on-year, showing no decline for four consecutive months, indicating strong inflation persistence. In terms of employment, the unemployment rate in the USA for November was 4.2%, rising compared to October, with significant volatility in new non-farm employment data where only 0.078 million and 0.036 million people were added in August and October, respectively. The employment outlook still has potential risks.
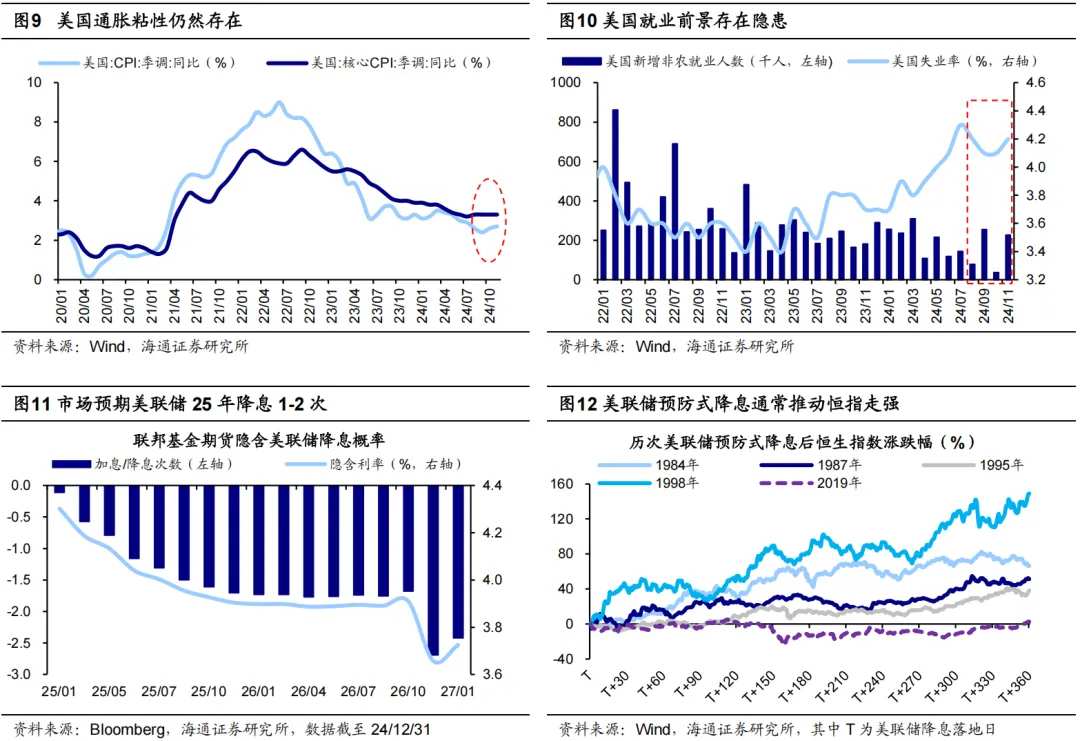
Against the backdrop of resilient inflation and unclear employment, Powell stated during the December FOMC meeting that the Federal Reserve will likely be 'more cautious' when considering adjustments to policy rates in the future. This suggests that the pace of rate cuts may slow down. Given the inflationary nature of Trump's policies, future rate cuts may be constrained by the interplay between inflation and employment data, introducing significant uncertainty to the pace of cuts. As of 24/12/31, Bloomberg's implied federal funds futures rates indicate that the market expects the Federal Reserve to cut rates 1-2 times in 2025. Overall, the liquidity environment abroad in 2025 appears loose; referencing the past, an easing environment following preemptive rate cuts typically drives the Hang Seng Index to strengthen.
2. Variable Two: What new changes are there in the funding situation of Hong Kong stocks?
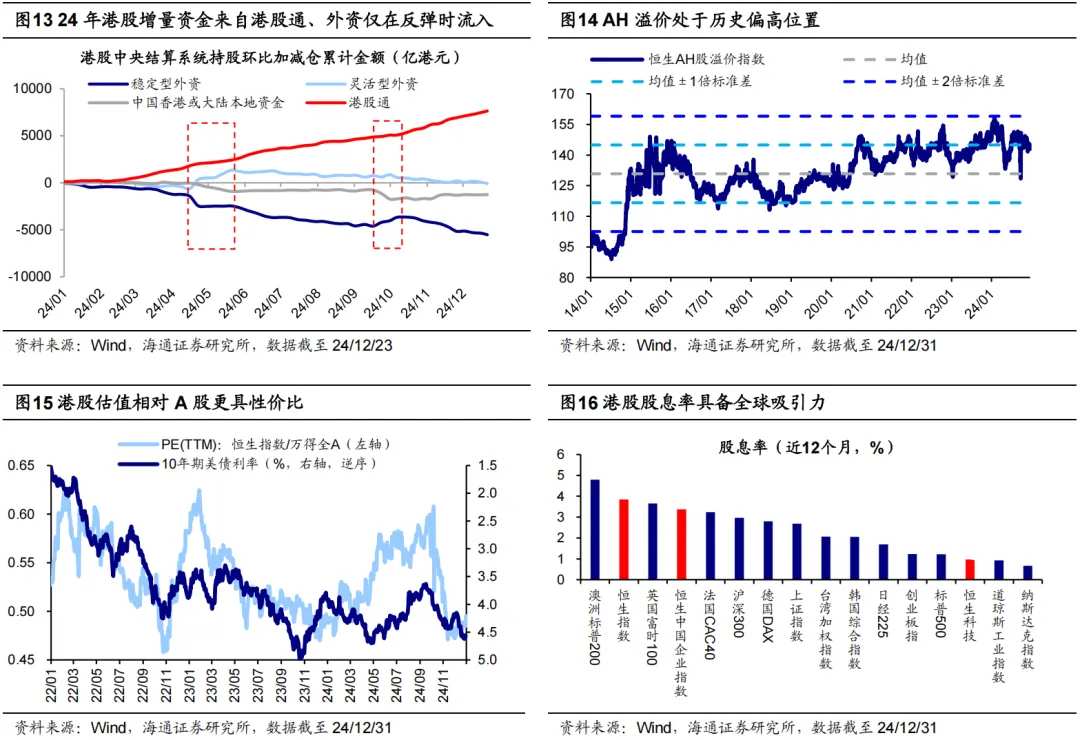
Variable Two: The Hong Kong Stock Connect is likely to continue inflowing, but there is uncertainty regarding the continuous return of foreign capital. The micro liquidity of Hong Kong stocks directly reflects the sufficiency of funds entering the Hong Kong stock market. Historically, increased micro liquidity often correlates with upward movements in Hong Kong stocks. Reviewing the micro funding structure of Hong Kong stocks in 2024, the Hong Kong Stock Connect contributed the largest increment, with flexible foreign capital flowing in at times, while stable foreign capital and local funds clearly flowed out. Looking ahead to 2025, whether the Hong Kong Stock Connect can maintain inflow and whether foreign capital can return will directly impact the micro funding situation of Hong Kong stocks.
The comparative advantage of Hong Kong stocks is likely to attract continued inflow from the Hong Kong Stock Connect. Since 2024, the Hong Kong Stock Connect has been continuously inflowing, with a total inflow of 762.3 billion HKD by the end of 24/12/23, which is more than double the level in the same period of 2023. Looking forward to 2025, the comparative advantage of Hong Kong stocks is expected to continue attracting inflow from the Hong Kong Stock Connect.
First, the AH risk premium is at a historically high level, with the Hang Seng AH premium index at 143.0 as of 24/12/31, approaching the mean of the past 14 years plus one standard deviation. This makes Hong Kong stock prices attractive. Second, the valuation of Hong Kong stocks is also more cost-effective. Since the correction on October 8, the valuation of Hong Kong stocks has significantly adjusted more than that of A-shares, with the PE ratio of Hong Kong stocks/A-shares decreasing from 0.60 to 0.50 by December 31. Meanwhile, the current valuation level of Hong Kong stocks relative to A-shares is at a historical low, indicating potential for relative valuation uplift in 2025.
There is still uncertainty regarding the continuous inflow of foreign capital. In 2024, there is an overall net outflow of foreign capital from the Hong Kong stock market, mainly due to the continuous outflow of stable foreign capital, which has accumulated an outflow of 554.4 billion Hong Kong dollars in 2024; while transactional foreign capital has intermittently flowed in during two market rebounds, with a total outflow of 10.2 billion Hong Kong dollars in 2024.
Looking ahead to 2025, as domestic policies strengthen, the overall trend of fundamental recovery has become clearer, and foreign capital is expected to flow back in phases to capture transactional opportunities, while the continued inflow still needs observation. Additionally, from a global asset allocation perspective, the cost-effectiveness of foreign capital allocating to Hong Kong stocks in the dividend + technology sector has marginally improved. Firstly, the current dividend yield of Hong Kong stocks ranks among the top globally, and the attractiveness of high dividends in the context of interest rate cuts has increased; secondly, the technology sector of Hong Kong stocks is currently considered undervalued, and with the backdrop of weakening technical development and regulation, earnings expectations are gradually improving, making it possible for foreign capital to increase allocations in the Hong Kong technology sector.
4. Variable three: How is the domestic economic recovery process?
Variable three: The space for domestic policy strengthening has already opened up, and the key factor is the recovery process of the fundamentals. Considering that many Chinese enterprises listed in the Hong Kong stock market are directly affected by the domestic economic recovery, and that the economic recovery also helps boost market confidence, the performance of Hong Kong stocks is closely related to the recovery process of domestic fundamentals. Since September 24, the tone of domestic policies has noticeably shifted, and looking ahead to 2025, the timing of the domestic policy implementation will become a key factor affecting the trend of Hong Kong stocks.
The spirit of important end-of-year meetings indicates that policies are still being continuously strengthened. According to the spirit of the December Politburo meeting and the Central Economic Work Conference, macro policies in 2025 will be 'more proactive and effective', and the space for policy implementation has already opened.
Specifically, there are three major changes in policy tone: first, the monetary policy has shifted to 'moderate easing', with the last occurrence of this statement being in 2008-2009; second, fiscal policy emphasizes 'more proactive' measures, including increasing the fiscal deficit rate, issuing more long-term special treasury bonds, and increasing the issuance of local government special bonds. The National Financial Work Conference held from December 23 to 24 has clearly defined 'supporting the expansion of domestic demand' as the primary task for fiscal work in 2025; third, it has clearly proposed 'stabilizing the property market and stock market', which is a relatively rare expression regarding stabilizing the stock market in past meetings.
It is believed that there may be significant room for fiscal expansion in 2025. In recent years, China has generally set its target deficit rate around 3%. During the epidemic in 2020, it was set at 3.6%. In 2023, it was originally set at 3%, but after the issuance of one trillion yuan in treasury bonds, it rose to 3.8%. It is expected that the target deficit rate for 2025 may rise to around 3.5-4.0%.
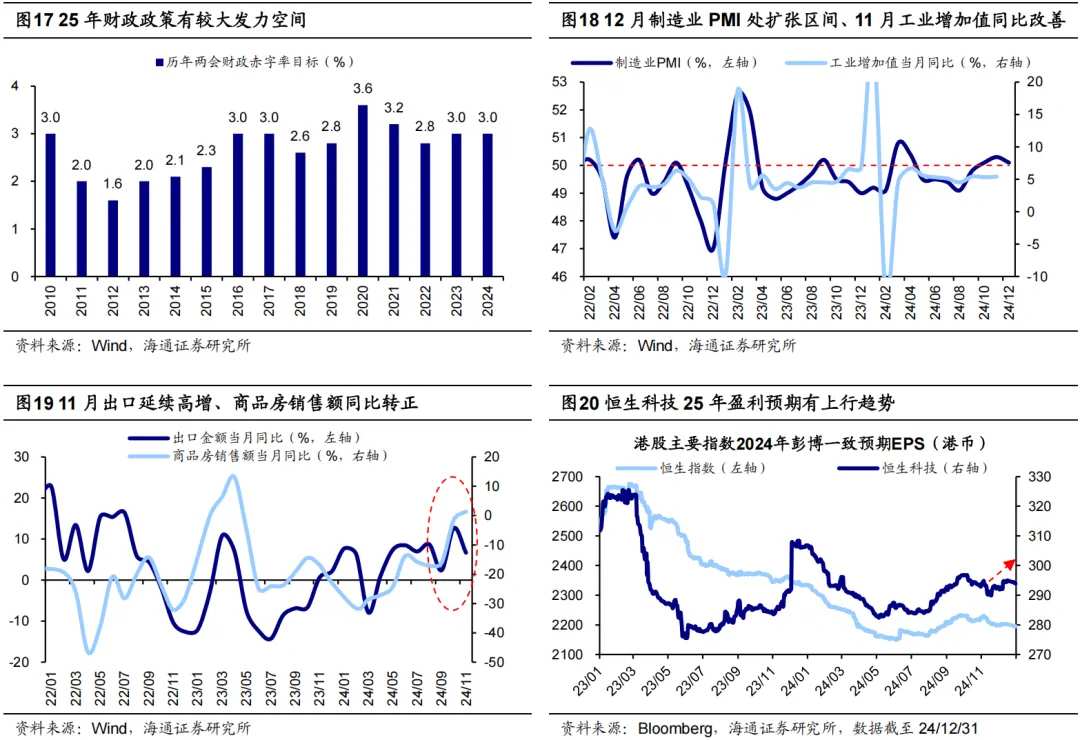
If incremental policies can accelerate the repair of macro and micro fundamentals, Hong Kong stocks may have better support in 2025. Since September 24, the bottom of domestic policies has already appeared, and the current effects of the policies have been reflected in some macro fundamental data, such as the manufacturing PMI in December being 50.1%, remaining in the expansion range for three consecutive months; in November, the year-on-year growth of industrial added value was 5.4%, slightly up from 5.3% in October; in November, the year-on-year growth of exports was 6.7%, maintaining high growth; in November, the monthly year-on-year growth rate of commodity housing sales was 1.4%, turning positive for the first time since April 2023.
In addition, there are signs of improvement in the micro fundamental aspects of the Hong Kong stock market. According to Bloomberg data, the market consensus for the Hang Seng Technology Index's EPS in 2025 has risen from 290 HKD on November 18 to 294 HKD on December 31. If future incremental policies can be implemented effectively, they may support the performance of Hong Kong stocks in 2025.
5. Variable four: How will Trump's policies advance?
Variable four: The direction of Trump's policies after he took office is relatively certain, but the pace of these policies remains variable. In recent years, the China-US relationship has become one of the key variables affecting the performance of Hong Kong stocks. Trump's hawkish policies towards China may disturb the fundamentals and sentiment of Hong Kong stocks, thus impacting their performance.
Currently, Trump has basically completed his cabinet formation, and his cabinet members include many hawkish representatives on China, such as the designated Secretary of State Marco Rubio and National Security Advisor Mike Waltz. Therefore, the direction of his policies towards China may be relatively certain. However, the pace of policy implementation remains variable, and the China-US relationship in 2025 could fluctuate between negotiations achieving results and negotiations breaking down, with a possibility of temporary easing in China-US relations. It will be necessary to closely monitor the actual advancement of Trump's policies after taking office, especially his specific measures in trade and technology with China.
If Trump's policies in the trade field are implemented quickly, they may disturb the fundamentals and sentiment of Hong Kong stocks in 2025. Looking ahead, if Trump accelerates trade friction and technological sanctions against China after officially taking office in 2025, it could impact the performance of Hong Kong stocks from both fundamental and sentiment perspectives.
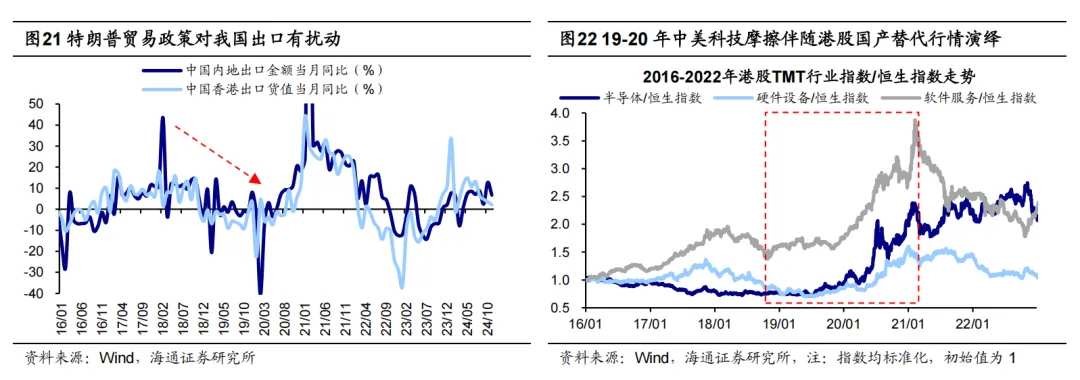
From a fundamental perspective, Trump advocates increasing tariffs on foreign goods, and if this policy is intensified, it could temporarily impact China's exports. Looking back during his first term, the USA issued four lists of tariff increases against China, with over 60% of Chinese export goods affected by American tariffs. During the same period, China's export data showed a clear slowdown, with the year-on-year exports from mainland China/Hong Kong dropping from 10.7%/18.1% at the beginning of 2018 to 8.1%/3.3% at the end of 2019.
From a sentiment perspective, Trump's technological sanctions against China may suppress risk appetite for Hong Kong stocks. During his last term, he continuously suppressed leading Chinese technology companies, which led to a decrease in the risk appetite for Hong Kong stocks, causing the risk premium of the Hang Seng Index to rise from 3.6% in January 2018 to 10.3% in March 2020. Moreover, structural investment opportunities are worth paying attention to, as trade disputes may give rise to domestic substitution trends. Between 2019 and 2020, the indices for Semiconductors, Hardware, and Software Services in Hong Kong stocks outperformed the Hang Seng Index by 180, 96, and 80 basis points, respectively.

6. Variable five: How will the reform of the Hong Kong stock system be carried out?
Variable Five: If the reform of Hong Kong's financial market continues to advance, the investment environment is expected to improve. In response to the trends of diversification, digitalization, and green transformation in the global Capital Markets, Hong Kong is accelerating financial market reforms in 2024, and this trend is expected to continue into 2025, thereby enhancing investor confidence and providing long-term positive support for the performance of Hong Kong stocks. Specifically, referring to the key reforms of 2024, Hong Kong's future institutional reforms may focus on the following three major directions:
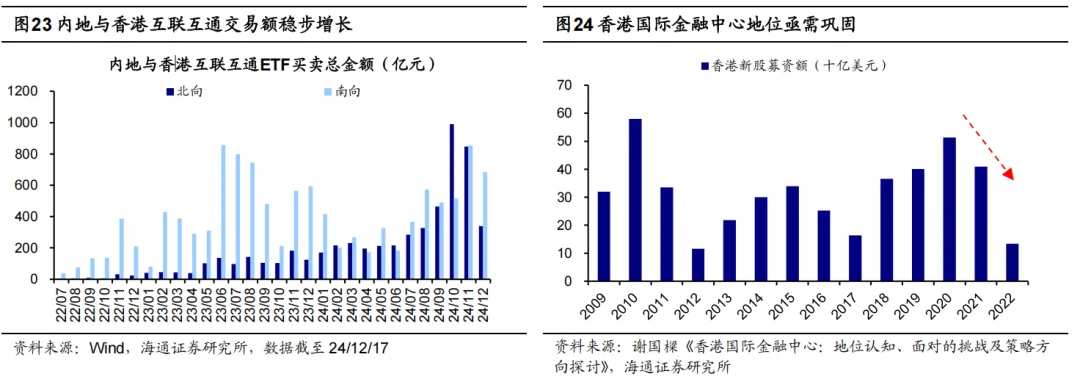
First, deepen the interconnection between the mainland and Hong Kong. In 2024, measures such as relaxing the range of eligible products for stock ETFs under the Shanghai-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect and relaxing the sales ratio of mutual recognition funds have been implemented. Since ETFs were included in the interconnection symbol in July 2022, the trading volume has continued to grow, with the total buy/sell amount for northbound/southbound interconnection ETFs reaching 84.7/85.6 billion yuan respectively in November 2024. In addition, measures such as including REITs in the Shanghai-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect and supporting RMB stock trading counters to be included in the Hong Kong Stock Connect are expected to be gradually introduced.
Second, strengthen the construction of Hong Kong as an international financial center. In October 2024, Chief Executive John Lee Ka-chiu proposed measures to optimize the listing approval process, tap into new overseas funds, attract companies to list, and optimize approval for listings in the 2024 Policy Address. In December, the Hong Kong Financial Development Council suggested that the government establish unified principles to align with international standards. In the future, Hong Kong is expected to continue cooperating with the mainland to introduce measures that consolidate Hong Kong's status as an international financial center and curb the downward trend, as the amount raised by new stocks in Hong Kong has significantly declined since 2020.
Third, enhance market efficiency and improve the trading environment. In 2024, Hong Kong announced the launch of GEM reforms, optimized information disclosure arrangements for the Hong Kong Stock Connect, approved trading during adverse weather conditions, modified special trading rules, and lowered the minimum price fluctuation levels for securities, effectively enhancing market transparency and improving operational efficiency. Additionally, the Monetary Authority also released an implementation report on the capacity to absorb losses, which strengthened the risk management of Financial Institutions and helped improve the trading environment. Looking ahead to 2025, as reforms continue to advance, Hong Kong's investment environment is expected to further improve, boosting investor confidence in the long term.
Overall, it is relatively certain that the domestic fundamentals will improve in 2025, the pace of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve may slow down, but easing remains the trend. On the micro level, foreign capital may stage a return to Hong Kong, while the timing of the rollout of Trump’s policies contains variables. The institutional environment in Hong Kong is expected to continue to improve, presenting more positive factors. Coupled with the fact that the current valuation and sentiment of Hong Kong stocks are still at historically low levels, it is believed that Hong Kong stocks have the potential to rise in 2025.
Editor/rice

