According to FX168 Financial News (North America), over the past 12 months, the Nasdaq Composite Index has risen more than 31%, the S&P 500 Index has risen more than 25%, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average's increase has been relatively moderate at only 14%.
Despite a market correction in recent weeks, investors still find reasons for optimism about the future from significant news over the past year. In 2024, the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates for the first time in four years, while news of a change of administration at the White House also boosted the stock market.
Corporate earnings growth has accelerated, and the range of market rebound has expanded. Despite concerns about a brief growth scare at the end of summer, the USA economy ended 2024 on a strong note.
 Here are 10 charts showcasing the market and economic resilience over the past year, as the market's gaze has already shifted towards 2025.
Here are 10 charts showcasing the market and economic resilience over the past year, as the market's gaze has already shifted towards 2025.
The Bull Market continues to roar.
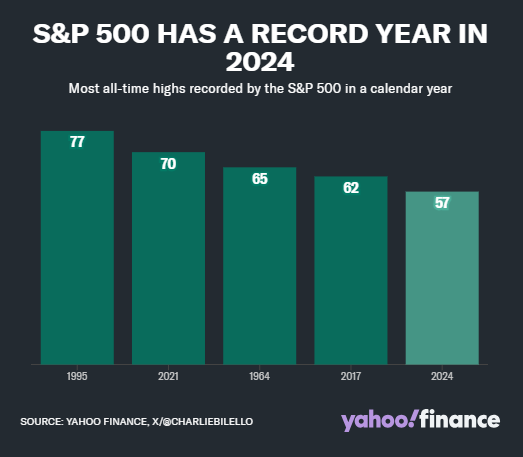
2024 has been a record-breaking year for Wall Street, with the S&P 500 Index setting 57 all-time highs, making it one of the top five years for the most historical annual high counts.
The bull market has lasted for two years, with strategists attributing the rebound to strong corporate earnings and the robust performance of the "Magnificent Seven" technology stocks. These tech stocks include chip maker NVIDIA (Nvidia, NVDA), Tesla (Tesla, TSLA), Google's parent company Alphabet (GOOGL, GOOG), Amazon (Amazon, AMZN), Apple (Apple, AAPL), Microsoft (Microsoft, MSFT), and Meta (META).
(Source: Yahoo Finance)
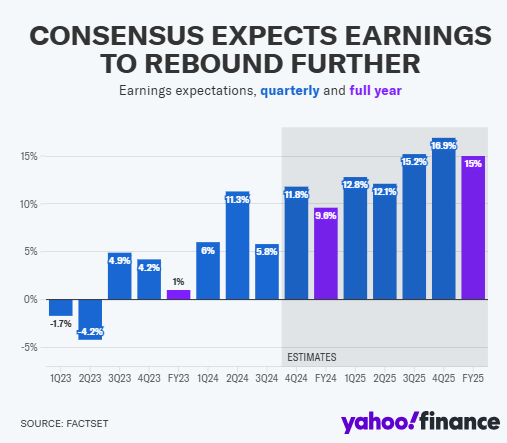
In 2024, the other 493 companies in the S&P 500 Index also ended their profit recession, with growth Range exceeding the 'seven major Technology stocks'.
According to FactSet data, profits in the S&P 500 Index are expected to grow by 15% year-on-year in 2025, with sustained profit growth becoming a key driver of interest for many Call strategists.
Truist co-chief investment officer Keith Lerner wrote in the 2025 market outlook: 'Various evidence indicates that the main market trends remain upward, driven by profit growth in 2025.'
(Source: Yahoo Finance)
Despite the expansion of the market rebound Range, the 'seven major Technology stocks' still performed brilliantly. NVIDIA rose over 175%, while Google, Amazon, Tesla, and Meta all rose more than 30%, outperforming the Nasdaq Composite Index and S&P 500 Index.
However, this has also led to increased market concentration. As of December 23, the top 10 stocks by market capitalization in the S&P 500 Index accounted for 39.9% of the total market capitalization, the highest proportion in at least the past 30 years.

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
Unique Presidential Election
In a record-breaking year for the stock market, the presidential election of 2024 became another historic event.
Donald Trump defeated Vice President Kamala Harris to win the election just three months after current President Joe Biden announced his withdrawal. The election was tumultuous due to news of assassination attempts and criminal prosecutions.
After the election, small-cap stocks surged quickly. The E-mini Russell 2000 Index outperformed major market indices the day after the election. However, small-cap stocks subsequently gave back some gains, still rising about 11% by the end of the year, which is less than half the gain of the S&P 500 Index during the same period.

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
Small stocks (including regional Banks and small local enterprises) are expected to benefit from the anticipated tax cuts and deregulation policies of the Trump administration. Furthermore, Trump's repeatedly hinted tariff policies have strengthened the dollar, which is Bullish for small stocks that rely more on the domestic economy.
However, high tariffs are also expected to lead to increased inflation stickiness and maintain higher interest rates in the long term. This possibility has driven the yield on the 10-year US Treasury bonds to around 4.6%, a seven-month high.
Meanwhile, sectors such as Energy and Finance have also risen after Trump's victory, driven by market expectations of increased merger and acquisition activity, a steeper yield curve, and reduced regulation. However, similar to small stocks, the gains in these sectors have mostly been short-lived.
Bitcoin is an exception. Since the beginning of this year, this largest cryptocurrency has surged over 130% and remains one of the biggest beneficiaries of the post-election rebound.

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
Trump's victory has pushed Bitcoin prices to an all-time high, with the government seen as generally friendly towards alternative asset classes.
Although Cryptos lost some momentum after breaking the $0.1 million mark earlier this month, investors and Analysts remain largely optimistic for 2025.
In July, Trump attended a Bitcoin conference held in Nashville and promised to introduce more supportive regulations. His commitments also included appointing a Crypto Presidential Advisory Committee and dismissing current SEC Chairman Gary Gensler, who announced his resignation effective January 20.
Complex economic outlook.
In 2024, the USA economy exhibits significant resilience. Retail sales exceeded expectations again in November, GDP remained robust above trend levels, and the unemployment rate held around 4%, although the path to lower inflation has not been smooth, it is generally trending down.
This positive backdrop enhances investors' confidence in the USA economy achieving a 'soft landing,' characterized by price stability and low unemployment rates.
However, Trump's election complicates the economic outlook. Nancy Vanden Houten, Chief USA Economist at Oxford Economics, stated: 'The risks clearly lean towards higher inflation, particularly due to tariffs and immigration policies that the Trump administration may implement.'

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
Policies proposed by elected President Donald Trump, such as high tariffs on imported goods, corporate tax cuts, and restrictions on immigration, are seen by economists as potential inflationary factors. In addition to these concerns, inflation is expected to remain elevated, as recent monthly 'core' price increases have exceeded expectations (excluding the volatile food and Energy costs), thereby continuing to add to inflationary pressures.
In November, the core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Index and the core Consumer Price Index (CPI) that the central bank closely monitors increased by 2.8% and 3.3% respectively compared to the same period last year.
According to the Federal Reserve's latest economic forecasts in the Economic Projections Summary (SEP), central bank leaders expect the core inflation rate to reach 2.5% next year—higher than the 2.2% predicted in September—and then drop to 2.2% in 2026 and 2.0% in 2027.
Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell stated at the last policy meeting of the year on December 18: "Our inflation forecast for the end of the year has deviated. I can tell you that this may be the single largest factor—inflation again fell below expectations."
However, controlling inflation is not the only goal of the Federal Reserve for next year. The job market is also a key part of the Federal Reserve's dual mandate—maintaining a strong job market is crucial for the healthy development of the stock market and the USA economy.

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
The unemployment rate fluctuated throughout the year, but remained relatively stable at around 4%.
In July, the unemployment rate reached a high of 4.3% since 2024, triggering a closely watched recession indicator known as the Sam Rule. Generally, this rule suggests that if the three-month average of the national unemployment rate rises by 0.5% or more compared to the lowest point in the previous 12 months, the USA economy is in recession. In fact, once the unemployment rate begins to rise, it rarely reverses.
However, economists, including the rule's inventor Claudia Sam, quickly pointed out that considering other factors at play in the economy, this indicator may not issue a red warning signal this time.
Due to investor caution regarding the growth prospects of the USA economy, the employment report for July was weaker than expected, leading to a market sell-off, but the market rebounded afterward. The momentum of the rising unemployment rate has eased, the labor market seems to be cooling down, but the cooling speed is not as fast as many had feared.
Although the rapid rise in the unemployment rate has not fully materialized in 2024, the picture of a slowing labor market is becoming clear. Economists have begun using the phrase 'low hiring, low layoffs' when defining the current state of the labor market. It is largely seen as being consistent with a 'soft landing,' meaning inflation will eventually drop to the Federal Reserve's 2% target without the economy slipping into recession.
The chart below shows that both the hiring and resignation rates decreased throughout 2024, currently sitting at levels lower than those before the pandemic outbreak in 2020. Such data indicates how the labor market is cooling down in 2024 and prompts the Federal Reserve to cease further cooling in its dual mandate.
Powell stated on December 18: 'The downside risks in the labor market seem to have indeed weakened, but the labor market is now more relaxed than before the pandemic and is clearly still cooling down further. So far, the cooling process has been gradual. We believe it is not necessary for the labor market to cool further to bring the inflation rate down to 2%.'

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
The Federal Reserve's easing cycle is under close scrutiny.
At the last meeting of the year, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 25 basis points to a Range of 4.25%-4.5% and hinted that after a total of 100 basis points rate cuts in 2024, it will slow down the rate cut pace.
Federal Reserve officials expect that by 2025, the federal funds rate will drop to 3.9%, higher than the Federal Reserve's September forecast of 3.4%. In addition to a significant rate cut of 50 basis points in September, the Federal Reserve has been cutting rates in increments of 25 basis points over the past year or so, indicating that the Federal Reserve expects to cut rates two more times in 2025. In September, officials had anticipated four rate cuts next year.
According to Bloomberg data, before the Federal Reserve made this decision, the market expected two to three more rate cuts next year. This expectation has now shifted to one to two rate cuts.
In 2026, officials expect the Federal Reserve to cut rates two more times, bringing the federal funds rate down to 3.4%. In September, officials had anticipated that the rate would drop to 2.9% in 2026.
The latest forecasts indicate that after initiating the long-awaited easing cycle earlier this year, the Federal Reserve will take a more cautious stance.

(Source: Yahoo Finance)
As 2024 is coming to an end, strategists are encouraged by the story told by the above chart. Although the Federal Reserve expects the rate cut to be lower than initially anticipated, the economy remains stable, and corporate earnings are expected to continue to grow in the coming year.
Among the 17 strategists who set a target for the S&P 500 Index by the end of 2025, only one believes that the benchmark index will decline by the end of next year. The index's peak is projected to be 7,100 points, with a median of 6,600 points, representing an increase of about 11% from current levels.
Wells Fargo & Co stock strategist Christopher Harvey wrote in detail about the scenario of the S&P 500 Index reaching 7,007 points by the end of 2025, stating that he initially wanted to 'lean towards a reverse investment' considering the concerns regarding bullish market sentiment, high stock valuations, and already robust economic growth.
However, Harvey wrote that 'the data does not support' a weak performance or negative trend for the S&P 500 Index next year, similar to many people on Wall Street's feelings about 2025, unless an unexpected shock occurs.
Harvey stated, '2025 is likely to be a year of robust to strong performance.'

(Source: Yahoo Finance)

