Source: China International Capital Corporation's Insights
Authors: Chen Hao, Wen Hanjing, et al.
Summary
AI Agent is an intelligent agent that can perceive the environment, autonomously plan, make decisions, and execute actions to achieve goals, possessing essential characteristics such as autonomy, interactivity, reactivity, and adaptability, with large language models as its core driving force. With breakthroughs in underlying technologies powered by large models, we are seeing AI Agents gradually implemented in focused vertical + multiple agent collaborative application scenarios. According to market.us, the Global large model market size is expected to grow from 4.5 billion dollars in 2023 to 82.1 billion dollars by 2033, with a 10-year CAGR of 33.7%. We are Bullish about the future development trend of AI Agents and the investment opportunities brought by changes in the upstream and downstream Industry Chain.
 On the infrastructure side, AI Agents drive the emergence of more applications, increasing the demand for computing power, with multi-layer reasoning leading to exponential growth in computing volume. We have observed that major model vendors are accelerating the decrease in API input/output pricing, and the business model of large model vendors is gradually entering an era of exchanging price for volume, promoting the growth of reasoning volume. Considering that the demand for reasoning chips is mainly sensitive to latency, we believe that the future differentiated demand for edge-side hardware is expected to promote the diversification of reasoning chip performance and customized demand. We are bullish on domestic edge-side AI chip companies that are expected to establish a foothold in segmented scenarios, seeking a differentiated breakthrough.
On the infrastructure side, AI Agents drive the emergence of more applications, increasing the demand for computing power, with multi-layer reasoning leading to exponential growth in computing volume. We have observed that major model vendors are accelerating the decrease in API input/output pricing, and the business model of large model vendors is gradually entering an era of exchanging price for volume, promoting the growth of reasoning volume. Considering that the demand for reasoning chips is mainly sensitive to latency, we believe that the future differentiated demand for edge-side hardware is expected to promote the diversification of reasoning chip performance and customized demand. We are bullish on domestic edge-side AI chip companies that are expected to establish a foothold in segmented scenarios, seeking a differentiated breakthrough.
On the application side, consumer-side hardware may become a traffic entry point, while business-side production tools are expected to be upgraded comprehensively. 1) On the consumer side, AI Agents will fundamentally change human-computer interaction over the long term, with mobile devices likely to form a new traffic entry point, potentially impacting industrial business models profoundly. We are bullish on Internet and mobile manufacturers' layout of system-level AI, among which mobile manufacturers will upgrade voice assistants to intelligent agents; internet companies are successively launching self-developed intelligent agents that already possess the capability to 'take over phones' or 'take over computers'; 2) On the business side, AI Agents are expected to leverage specialized knowledge to penetrate the business market, achieving cost reduction and efficiency enhancement for enterprises, where empowering corporate efficiency improvement is the core consideration of decision-making. We are bullish on the efficiency improvement brought by AI Agents, which is expected to stimulate a new round of industrial investment.
On the embodied intelligence side, AI Agents endow robots with intelligence, with vast imagination space for industrial implementation. AI Agents based on large models are expected to enhance the intelligence level of embodied intelligent systems and accelerate the commercialization of embodied intelligence, with participating vendors including well-known companies such as Tesla, Figure.ai, as well as domestic firms like DJI and Yushu. We believe that the embodied intelligence empowered by AI Agents is expected to take root across various industries, with a broad development prospect. We estimate that the shipment volume of humanoid robots in China may reach 0.35 million units by 2030, and the market space is expected to reach 58.1 billion yuan by 2030.
Risks
The downturn in the macro economy affects consumer demand, technology iteration is below expectations, AI commercialization is below expectations, computing power supply is below expectations, and there is an increased risk of tighter data security regulation and intensified industry competition.
Main text
AI Agent, exploring the path to AGI.
What is an AI Agent.
An AI Agent is an intelligent entity that can perceive its environment, autonomously plan, make decisions, and execute actions to achieve goals, characterized by autonomy, interactivity, reactivity, and adaptability. Unlike large models that interact with humans through prompts in a directive manner, an AI Agent has the ability to think independently, plan autonomously, and utilize tools to gradually accomplish given objectives, making it goal-oriented.
Chart 1: Summary Analysis of AI Agent Perspectives.
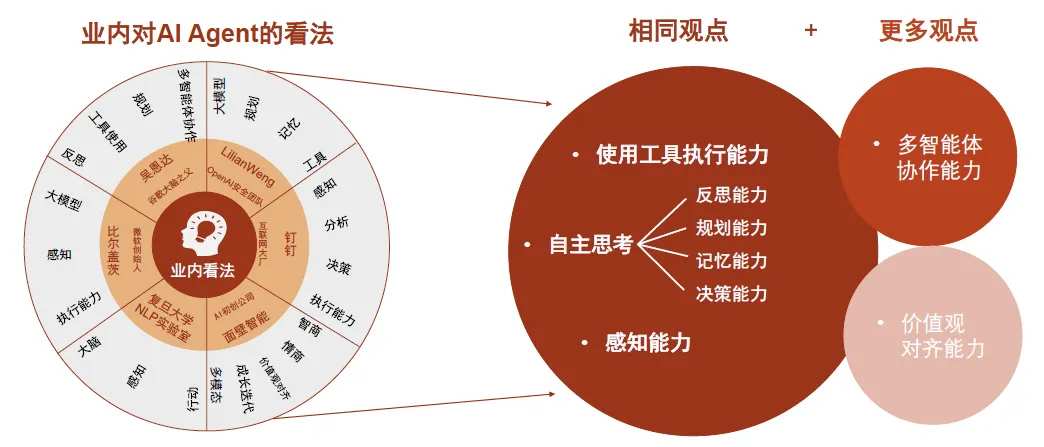
Evolution: Large models provide underlying technological breakthroughs for AI Agents, exploring the path to AGI.
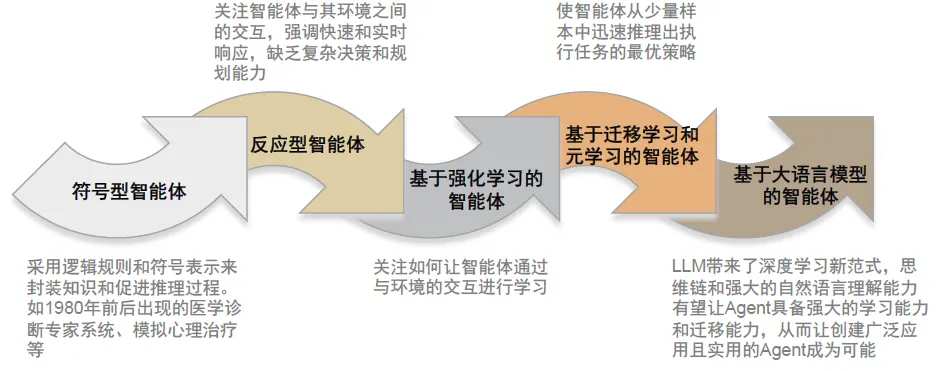
AI Agents have developed over 40 years, entering a new intelligent agent stage empowered by large models. In the 1980s, Wooldridge and others introduced agents into AI, and since then AI Agents have gone through four development stages: symbolic agents, reactive agents, reinforcement learning-based agents, and agents with transfer learning and meta-learning capabilities. Previous paradigms like reinforcement learning mainly focused on enhancing technical capabilities in specific areas, neglecting the development of general capabilities such as long-term planning, effective generalization, and knowledge memory. The natural language understanding capabilities, thinking chains, and emergent abilities of LLMs have endowed AI Agents with better learning and transfer capabilities, enhancing the generalization effect in problem-solving and pushing AI Agents into a new intelligent agent stage, becoming a major exploration path toward AGI.
Chart 2: Development history of AI Agents.
Industry Space: GMI estimates the global market size will reach 88.1 billion USD by 2032.
The continuous development of underlying cloud-side and edge-side large models is driving the growth of the AI Agent market size. Large models, as the core driving force of AI Agents, are expected to continue to promote the development of AI Agents through technological iterations and market growth. According to market.us, the global large model market size is expected to grow from 4.5 billion USD in 2023 to 82.1 billion USD by 2033, with a 10-year CAGR of 33.7%. Based on the different deployment methods of large models, AI Agent applications can be classified into cloud-side and edge-side categories.
► Cloud-side: The rapid development of cloud computing platforms creates favorable conditions for the incubation of AI Agent applications. According to IDC, the global public cloud market size is expected to grow by 22.4% year-on-year to 481.9 billion USD in 2023.
► Edge-side: Edge-side AI continues to penetrate, and the application of AI Agents at the edge is expected to become widespread: 1) In the AI smartphone sector, according to Counterpoint, shipments of Gen AI smartphones are expected to exceed 0.55 billion units by 2027, with a penetration rate of 43%; 2) In the AIPC sector, according to Canalys, global AI PC shipments reached 13.3 million units in Q3 2024, with a penetration rate of 20%; Canalys expects the global AIPC penetration rate to exceed 60% by 2027.
According to GMI data, the global AI Agent market size in 2023 is approximately 5.2 billion USD, with cloud-side applications accounting for about 64%. As companies accelerate the integration of AI into their operations to reduce costs and increase efficiency, and as AI Agents are embedded in end devices for consumers in the form of application services, GMI estimates that the global AI Agent market size will reach 88.1 billion USD by 2032, corresponding to a CAGR of over 36.5% from 2023 to 2032.
Chart 3: Growth forecast and driving factors for the Global AI Agent market size.
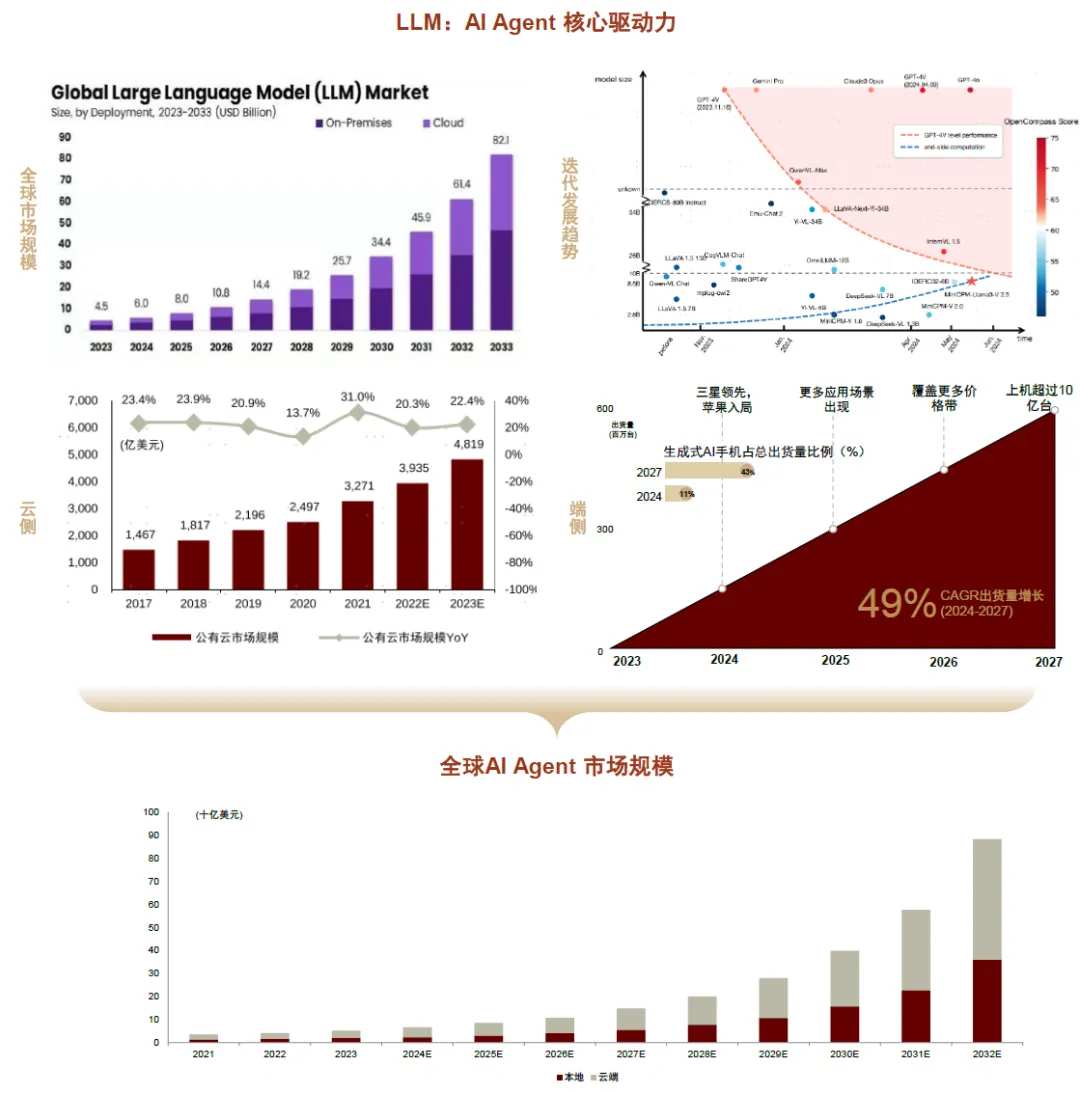
Note: The LLM market size estimation is from market.us; the public cloud market size estimation is from China Academy of Information and Communications Technology; the forecast for generative AI smartphone shipments is from Counterpoint; the AI Agent market size data is from GMI.
Infrastructure: From training to inference, continuous growth in computing power and diverse hardware demand.
AI Agents drive the emergence of more applications, increasing the demand for computing power, with multi-layer reasoning leading to exponential growth in computational load.
Since the release of GPT 3.5 in November 2022, we believe that the pricing standards for API input/output of millions of tokens set by large model vendors have shown a noticeable downward trend. We think that the business models of large model vendors are gradually entering an era of trade-off between price and volume, and the general decline in pricing standards is expected to attract more application developers and consumer users.
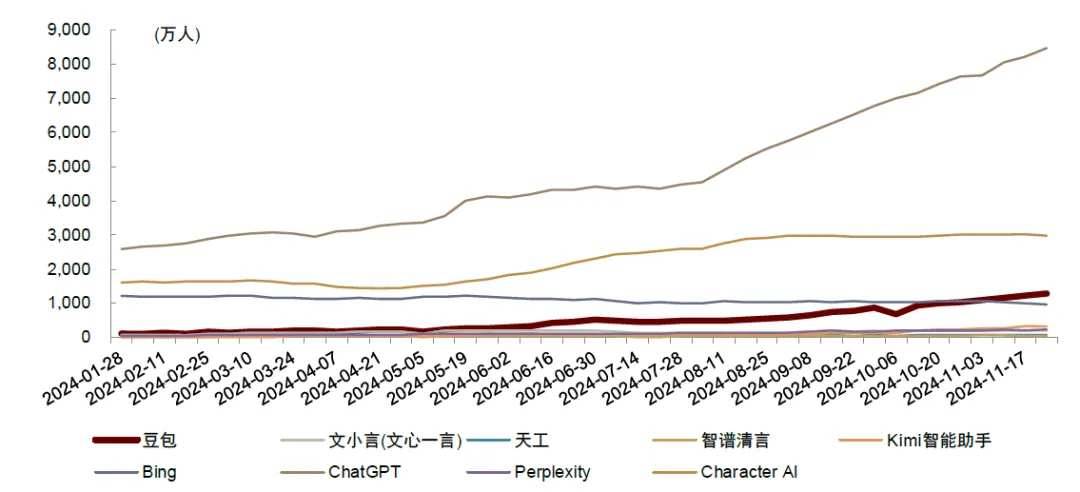
Chart 4: Daily active users of AI Agent apps like Zhipu Qingyan.
Multi-layer reasoning drives a dramatic increase in computational power. In September 2024, Open AI officially released a preview of its next-generation generative AI model o1, which further enhances its reasoning performance by demonstrating the technology of Chains of Thought (CoT). We believe that the explicit demonstration of the Chain of Thought and the results obtained indicate that, to some extent, providing larger models with more computational power consumption can yield more intelligent results.
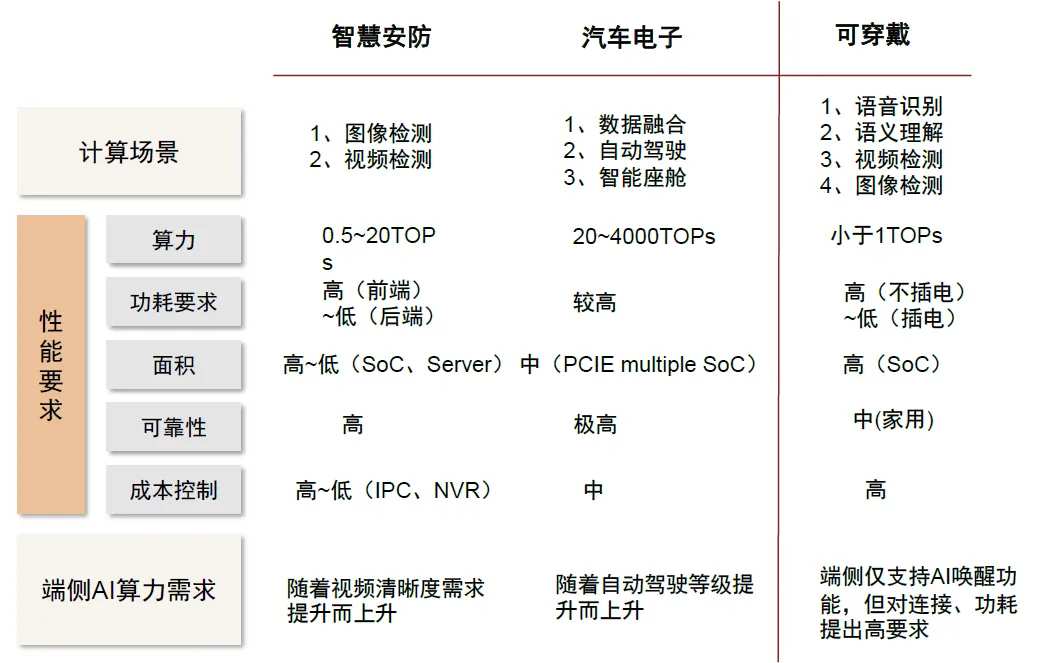
Domestic edge AI chips: Seeking a differentiated breakthrough.
Due to the extensive and diverse reasoning scenarios, the demand for customization and differentiation of AI chips has emerged. Although domestic companies are currently behind in terms of foundry processes and overall design capabilities, each has its strengths in niche areas. We believe that domestic edge AI chip companies are likely to solidify their positions in specific niches while expanding their foundational capabilities, gradually moving towards direct competition with overseas giants and making their mark on the international stage.
Chart 5: Performance Requirements of Downstream Terminal AI Chips.
Industry Landscape: C-end Hardware may become a Traffic Entry Point, B-end Production Tools to be Fully Upgraded.
C-end: AI Agent may change content distribution channels, Bullish on the development space of hardware traffic entry points.
Mobile terminals may become a new traffic entry point, profoundly impacting the business models of mobile manufacturers. In the Mobile Internet era, APPs have replaced web-based Search Engines, and various APPs have become the channels for people to obtain specialized information, highlighting the entry role corresponding to application stores (currently, mobile users mainly rely on manually downloading corresponding APP products from application stores; the APP itself undertakes the role of content screening, with different APPs providing different types of content products). In the Agent (APP-less) UI interaction model, APPs are weakened to be background service providers for Hardware. On one hand, the entry functions of APPs and application stores are diminished, possibly causing changes in the business models of mobile manufacturers' software ecosystems; on the other hand, AI Agent products, due to their high integration, high development barriers, and high compatibility requirements with mobile system-level Hardware, are more suitable for leading software and Hardware manufacturers such as mobile manufacturers, Cloud Computing Service providers, and major Internet companies. In this process, mobile manufacturers, having a natural grasp of mobile terminal hardware entrances, are expected to gain an advantage, thus participating more deeply in content distribution.
Chart 6: Changes in Content Distribution Channels
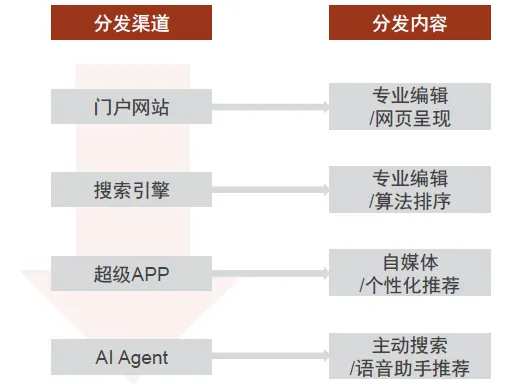
Chart 7: AI Agents Help Improve Distribution Efficiency

B-end: AI Agents may drive a new round of industrial investment, fully upgrading production tools.
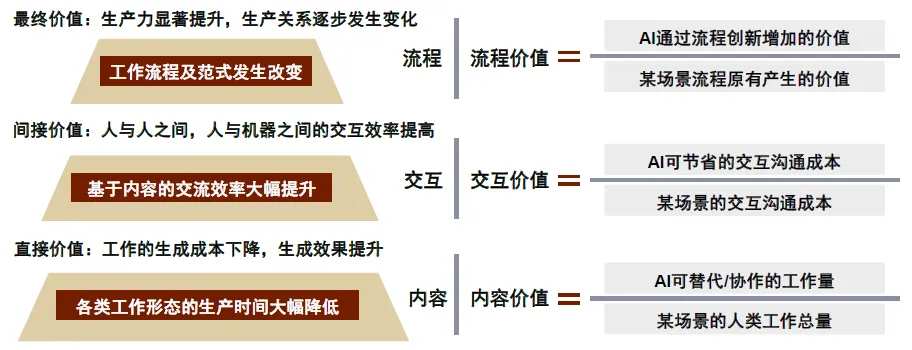
AI Agents are expected to leverage specialized knowledge to penetrate the B-end market, achieving cost reduction and efficiency improvement for enterprises. Compared to individual users, enterprise users typically face more complex and diverse business needs and possess clearer business scenarios, business logic, a wealth of contextual industry data, and accumulated industry knowledge cases, allowing for the effective utilization of the autonomy, perception and understanding of the environment, decision-making and execution, interaction, and tool usage advantages of AI Agents. The B-end market has accumulated massive contextual datasets, expected to deepen the scene experience and the coupling of models through model training and fine-tuning, facilitating the integration of AI Agents into enterprise client workflows and carrying business logic. It is believed that AI Agents will gradually release the core value of AI in the B-end, achieve cost reduction and efficiency enhancement, optimize human-machine and inter-person interactions, and lead the transformation of production relations.
Chart 8: The Value of AI Agents in B-end Implementation, Enhancing B-end Production Efficiency
The arrival of the intelligent robot era empowered by AI Agents.
The development of traditional robots has become relatively mature, and AI Agents are expected to drive new vitality in the robot industry, with embodied intelligence becoming a future development direction. Robots have already been implemented in many scenarios such as Autos, electronics manufacturing, and logistics, but commercialized industrial and service robots are mostly designed to perform specific tasks. Embodied intelligence consists of "Ontology" (physical entities) and "Agents" (AI Agents), capable of perceiving and understanding the surrounding environment, executing specific tasks in the physical environment, and learning and evolving through environmental interactions. It is believed that with the decline in the proportion of the labor force, rising costs, and increasingly complex and unstructured task scenarios, more versatile embodied intelligence is expected to become a future development direction of the robot industry.
Chart 9: Embodied intelligence is an AI system that can interact with the physical environment and learn from those interactions.

AI Agents bestow intelligence upon robots, opening up vast application spaces.
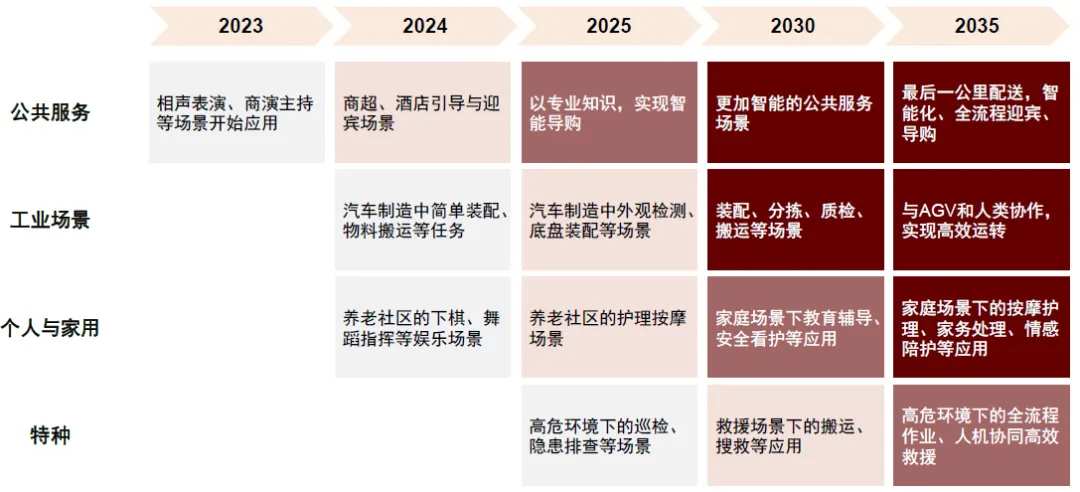
The emergence of large models provides an opportunity to move towards general AI. Since the release of Google's Transformer neural network architecture, many researchers have found that Transformer-based pre-trained language models also perform well in non-language tasks, demonstrating strong generalization capabilities. Subsequently, large models were introduced to the field of embodied intelligence, such as Google's PaLM-E model released in 2023, which is based on the Transformer neural network and developed as an embodied multimodal large language model, capable of guiding robots to achieve long sequence, one-shot, and zero-shot operation tasks. AI Agents based on large models are expected to enhance the wisdom of embodied intelligence systems in human-machine interaction, motion control, and perceptual interaction. Embodied intelligence algorithms no longer only target specific tasks but are able to generalize to unknown tasks. It is believed that this will likely reduce future development costs, accelerate iteration speed, and thus speed up the commercialization of embodied intelligence. Looking to the future, it is believed that with declining costs and increased social acceptance, the penetration rate of humanoid robots is expected to rise rapidly. It is estimated that China's humanoid robot shipment volume may reach 0.35 million units by 2030, with the market space expected to reach 58.1 billion yuan by 2030, maintaining a high growth trend.
Chart 10: The application progress rhythm of humanoid robots in four types of scenarios.
Risk Warning
The downturn in the macro economy affects consumer demand: macro factors such as exchange rate fluctuations, CSI Commodity Equity Index prices, and inflation impact consumer demand for discretionary consumer goods.
Technological iterations are not meeting expectations: the iteration of AI agents and large models is slowing down, or facing insurmountable technical challenges in end-side adaptation.
AI commercialization is not meeting expectations: there are differences in customer willingness to pay for AI and usage habits; if there is a lack of motivation for continued use, AI products are unlikely to become necessities in life, which may lead to insufficient user stickiness and hinder commercialization capabilities.
Computing power supply is below expectations: the high demand for inference computing power from AI agents makes computing power supply critical. If domestic research and development and supply progress are below expectations, or if geopolitical risks limit the supply of imported computing power products, it may affect the promotion and implementation of AI agents.
The risk of tightening data security regulations: the widespread application of data may raise data security concerns, and if regulatory policies tighten further, it will constrain corporate data processing and AI model training.
The risk of intensified industry competition: increased competition among industry companies will impact profitability and enhance uncertainty in the industry.
编辑/jayden

