On December 16, 2024, Guangdong Hec Technology Holding Co., Ltd. and Hangzhou Guangdong Hec Technology Holding Co., Ltd. received the "Notice of Approval for Clinical Trial of Drugs" issued by the National Medical Products Administration, approving the clinical trial of the Class 1 new drug HEC169584 capsules for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
According to Zhitong Finance APP, on December 16, 2024, Guangdong Hec Technology Holding Co., Ltd. and Hangzhou Guangdong Hec Technology Holding Co., Ltd. received the "Notice of Approval for Clinical Trial of Drugs" issued by the National Medical Products Administration, approving the clinical trial of the Class 1 new drug HEC169584 capsules for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
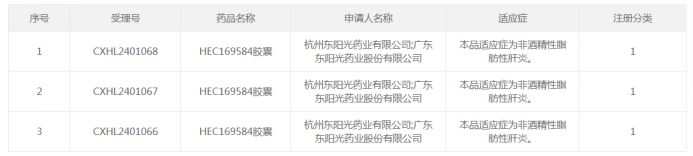
Screenshot from: CDE official website.
 Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, also known as metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease or MASH) is a complex chronic metabolic disease with a complicated pathogenesis. It is a severe type of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, also known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease or MASLD). As it progresses, it may evolve into liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. In recent years, due to changes in diet and lifestyle, as well as rising obesity rates, the number of NASH patients in China has dramatically increased. According to Frost & Sullivan's report, the number of NASH patients in China reached 42.5 million in 2023 and is expected to reach 54.9 million by 2030. In March 2024, Resmetirom obtained FDA approval for market introduction. This drug is an oral thyroid hormone receptor (THR)-β agonist and became the first FDA-approved treatment for adult NASH associated with moderate to severe liver fibrosis. However, as of now, there are no approved drugs for the treatment of NASH in China and Europe, leaving a significant market potential and unmet clinical needs in the NASH field.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, also known as metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease or MASH) is a complex chronic metabolic disease with a complicated pathogenesis. It is a severe type of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, also known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease or MASLD). As it progresses, it may evolve into liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. In recent years, due to changes in diet and lifestyle, as well as rising obesity rates, the number of NASH patients in China has dramatically increased. According to Frost & Sullivan's report, the number of NASH patients in China reached 42.5 million in 2023 and is expected to reach 54.9 million by 2030. In March 2024, Resmetirom obtained FDA approval for market introduction. This drug is an oral thyroid hormone receptor (THR)-β agonist and became the first FDA-approved treatment for adult NASH associated with moderate to severe liver fibrosis. However, as of now, there are no approved drugs for the treatment of NASH in China and Europe, leaving a significant market potential and unmet clinical needs in the NASH field.
HEC169584 is the first candidate drug obtained by Guangdong Hec through its AI-driven small molecule drug design platform. The team utilized the HEC-GEN model (a molecular fragment generation model based on sparse graph attention neural networks) to generate a large number of structurally diverse ligand small molecules based on the THR-β target pocket and evaluated their affinity with the target protein through molecular docking technology. Using the aforementioned AI techniques, the company ultimately selected the candidate drug HEC169584, which demonstrated good efficacy, drug-like properties, and safety both in vitro and in vivo. Preclinical research results indicate that HEC169584 has high in vitro activity against THR-β cells; it has strong liver targeting, with a liver-to-blood ratio of 24.5 (AUC ratio), which can reduce impacts on the thyroid axis, heart, and other tissues; in the NASH with liver fibrosis mouse model, it has shown efficacy in improving liver function, blood lipids, liver lipids, liver inflammation, liver NAFLD activity score, and liver fibrosis. Currently, there are no similar drugs on the market domestically, and HEC169584 is expected to accelerate clinical progression, bringing new treatment options for patients.
The pathogenesis of NASH is complex, and combination therapy targeting different points has become a new trend in clinical research and development. In the field of NASH, Guangdong Hec has adopted a proactive strategic deployment, addressing mainstream targets for NASH drug development, including GLP-1/FGF21 dual-target agonists, FXR agonists, THR-β agonists, ACC inhibitors, and other drugs under research, which have entered clinical stages successively, anticipating new breakthroughs in the combination treatment of NASH.

 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH,又称为代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝炎或MASH)是一种发病机制复杂的慢性代谢疾病,是非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD,又称为代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝病或MASLD)的一种严重类型,随着其进展,可能演变为肝脏纤维化、肝硬化及肝癌。近年来,由于膳食及生活习惯转变、肥胖率升高等因素,中国NASH患者人数大幅增长,根据弗若斯特沙利文报告,2023年中国NASH患者人数达4250万人,预计2030年将达到5490万人。2024年3月,瑞司美替罗(Resmetirom)获得FDA批准上市,该药是一款口服甲状腺激素受体(THR)-β激动剂,成为FDA批准的首款治疗成人NASH伴中晚期肝纤维化的药物。但截至目前,中国及欧洲尚无获批治疗NASH的药物,NASH领域仍存在巨大的市场空间和未满足的临床需求。
非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH,又称为代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝炎或MASH)是一种发病机制复杂的慢性代谢疾病,是非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD,又称为代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝病或MASLD)的一种严重类型,随着其进展,可能演变为肝脏纤维化、肝硬化及肝癌。近年来,由于膳食及生活习惯转变、肥胖率升高等因素,中国NASH患者人数大幅增长,根据弗若斯特沙利文报告,2023年中国NASH患者人数达4250万人,预计2030年将达到5490万人。2024年3月,瑞司美替罗(Resmetirom)获得FDA批准上市,该药是一款口服甲状腺激素受体(THR)-β激动剂,成为FDA批准的首款治疗成人NASH伴中晚期肝纤维化的药物。但截至目前,中国及欧洲尚无获批治疗NASH的药物,NASH领域仍存在巨大的市场空间和未满足的临床需求。