Source: Li Xunlei Finance and Investment
Author: Liang Zhonghua
In recent years, with regard to policy analysis and judgment, people increasingly rely on other sources of information, but most of the information available is unreliable, reliable information is often not available, and the effect is not obvious. In fact, in order to predict policies, the most important thing is not to look at short-term policy statements, but to judge the economic fundamentals of the future.
For example, after seeing the various statements made by the central bank last year, we judged that the central bank would cherish the room for regulation and control of monetary policy and would not cut interest rates. If this is the case, how to explain the 5BP reverse repo rate cut last year, how to explain the 10BP to cut interest rates even more this year? Policies can ignore fundamentals in the short term, but if you look at them for a long time, you have to follow them in the end. And the fundamental changes will not be transferred by people's will, but also the most honest. Last year, we were the first in the market to propose the opening of the interest rate cut cycle in China, which only depends on our analysis and judgment of fundamentals. It is based on the objective judgment of the fundamentals that the 2020 macro annual report released in December last year has become a rare macro report in the market that has not been "torn up".
Now, the epidemic has not changed the direction of economic downturn and policy relaxation, but only the slope of economic downturn and the speed of policy relaxation. The direction of asset allocation has not been changed by the epidemic. The market dominated by growth and bonds began last year. The logic behind investment is not economic stabilization, cyclical stabilization, but loose liquidity. The current epidemic has led to greater downward pressure on the economy, which has only accelerated the pace of policy relaxation and strengthened the logic of asset allocation. Looking forward, we think that we can imagine as much room for future policies as possible.
-Zhongtai Macro's Weekly thinking No. 62
Summary:
1、Interest rates are expected to hit a record low.In essence, the interest rate is not determined by the central bank, but by the rate of return on capital, and the central bank can only adjust the interest rate according to the change of the rate of return on capital to match the cost of capital with the change of return on capital. The arrival of the epidemic has increased the downward slope of the economy, and China's interest rate cut cycle will continue. Based on our calculation of the return on capital, looking ahead, the seven-day reverse repurchase policy interest rate in China is expected to fall below 2.25%, the one-year MLF is expected to fall below 2.85%, and the interest rate on 10-year government bonds is expected to fall to around 2.6%. However, when interest rates fall to a certain stage, they will encounter bottlenecks and the pressure on the exchange rate will also be reflected.
2、The deficit is expected to hit a record high.The financial pressure was already reflected last year. The growth rate of China's broad fiscal expenditure dropped from 12.7% in 2018 to 8.5% in 2019, and the rate of decline accelerated significantly in the last few months. We expect that the government will still make efforts to support infrastructure, and the fiscal deficit ratio may be raised to 3.5% or more in 2020, and the amount of special debt is expected to exceed 3 trillion yuan. We do not rule out the possibility of issuing special treasury bonds, and policy banks will also make some efforts. However, as hidden debt continues to be limited, infrastructure growth may pick up to about 8%.
3、Real estate relaxes or speeds up.Even without this epidemic, the regulation and control policy of real estate will be relaxed at the margin. Now after the epidemic comes, the sales pressure is greater, the cash flow of developers is also more tight, increasing the downward pressure on the economy, the pace of real estate policy relaxation may be accelerated. According to the experience of the last round of real estate relaxation, if the real estate regulation and control policy is relaxed again, it may give a boost to the core cities, but once the demand of small and medium-sized cities turns cold again, it may not be very effective just by relaxing regulation and money. It still needs a way similar to QE to create demand.
4、The policy market has long been on.Since November last year, growth equity assets and bonds have performed very brightly, suggesting that the logic that dominates the market is not the economic stabilisation or the opening of the inventory cycle, but more active policies in the downward pressure on the economy. in particular, the easing of monetary liquidity. The arrival of the epidemic accelerated the pace of loose policy, but strengthened the logic of asset allocation. Looking forward, we continue to be optimistic about the new economic assets in the growth direction and the logic of the downward bond yield, which is still the main allocation direction. With regard to the policy market in the future, we think we can have more room for imagination. No matter from the internal or external environment, the policy is already on the "fast lane". Please sit tight!
1、Interest rates are expected to hit a record low
Although on the surface, the interest rate is determined by the central bank, but from the decision-making mechanism, the interest rate is essentially determined by the rate of return on capital.When the macroeconomic growth rate declines, the investment return of the whole society will often decrease, if the capital cost of enterprises is not reduced at this time, then the investment behavior of enterprises will be more unprofitable, so it is necessary to cut interest rates to stabilize investment demand. When the macro-economy is in an upward cycle, the return on investment will also increase, when the central bank needs to raise interest rates to raise the cost of capital and prevent the economy from overheating.So the central bank needs to regulate interest rates according to changes in economic fundamentals, especially the rate of return on capital.
In fact, it is not the central bank that determines macroeconomic growth and return on capital, but is often determined by factors of production such as population and technology.Just like China's monetary, fiscal and real estate policies continue to underpin the economy in the past decade, but the economic growth rate is still all the way downwards. In the final analysis, the growth rate of China's working-age population is declining and the demographic dividend is gradually fading. Just like Japan and Europe have been hoping for money to stimulate the economy, but in the end, the economy is still depressed, mainly because the aging population is very serious. Therefore, last year, the governor of the Central Bank of China also emphasized in his article that monetary policy cannot solve the problem of long-term economic growth.
So in essence, the interest rate is not determined by the central bank, but by the rate of return on capital, and the central bank can only adjust the interest rate according to the change of the rate of return on capital to match the change of the cost of capital and the return on capital.For example, both Japan and Europe have negative interest rates, not because their central banks do not cherish the room for monetary policy regulation, but because the return on capital determined by long-term factors is so low that central banks have to follow fundamentals to reduce financing costs for the real economy.
Conversely, central banks cannot operate against economic fundamentals for a long time.For example, when the economy was in a downward channel in 2018, if monetary policy was tightened and interest rates were raised, fundamentals would fall faster, and in the end, the central bank chose to ease money. This time is similar, although the policy statement a few months ago also stressed the need to cherish the room for interest rate cuts, but after cutting interest rates by 5BP in the fourth quarter of last year, it recently cut 10BP.
This is because the central bank's decision-making is passive, can only follow the fundamental decision-making, cherish the space for interest rate means to regulate and control monetary policy, and mainly rely on "reform" rather than the central bank. Only by improving the efficiency of economic growth and the return on capital through reform can the downward trend of interest rates be stopped, otherwise the central bank will have to follow the trend.
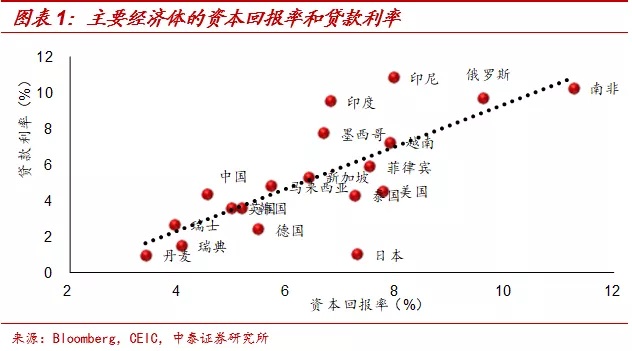
We have repeatedly stressed in previous reports that even without this outbreak, there would be downward pressure on the economy. In particular, the return of the average value of the real estate market has led to great macroeconomic pressure this year and next year. The arrival of the epidemic has only increased the downward slope of the economy and advanced the downward pace.Therefore, the fundamentals will continue to fall in the future, and China's interest rate reduction cycle will continue.
With regard to the room for interest rate cuts, we believe that this round of major interest rate indicators are likely to break through the lows of 2015-2016 and create new lows.According to our previous estimates, the rate of return on after-tax capital in China has not changed much compared with 2016. The macro-economy continues to weaken in 2019, and the return on capital is likely to continue to fall, that is, lower than in 2016. The rate of return on capital is an important variable to determine the interest rate, which means that China's interest rate center is expected to break through the last round of low.
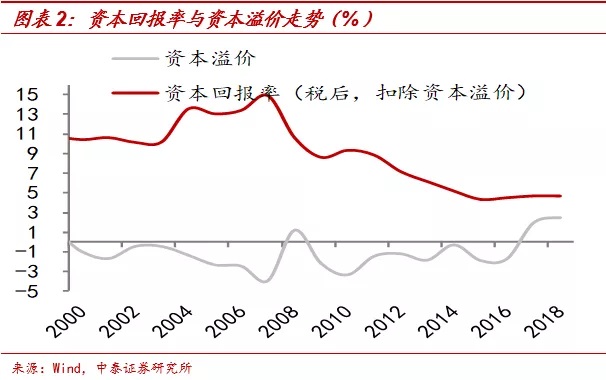
Looking ahead, the seven-day reverse repo policy rate is expected to fall below 2.25 per cent, the one-year MLF to below 2.85 per cent and the 10-year Treasury rate to around 2.6 per cent.So the reverse repo rate still has room to cut interest rates above 15BP, and there is room for interest rates to be cut above 40BP in MLF. The risk of adjustment in the bond market is small, and interest rates are expected to continue to decline.
However, when interest rates fall to a certain stage, they will also encounter bottlenecks, just as interest rates in Europe and Japan cannot be negative too much even if they can break through zero, otherwise savers will hold their own cash.As an emerging economy, if the interest rate is low, the pressure on the exchange rate will also be reflected.Therefore, looking forward, I am afraid that the depreciation pressure on the exchange rate is not small.

2、The deficit is expected to hit a record high
Financial pressure has been reflected in the past year.Considering public financial expenditure, government fund expenditure, urban investment standard bond, policy bank expenditure, railway debt and so on, we measure the growth of broad finance in our country. The results show that the growth rate of China's broad fiscal expenditure dropped to 8.5% in 2019 from 12.7% in 2018, and the rate of decline accelerated significantly in the last few months.
Economic growth is slowing down, tax revenue and land transfer revenue are significantly weaker, and the reduction of the income end is the main constraint of the slowdown in the growth of fiscal expenditure.

In addition to the apparent debt, the hidden debt of local government has also increased for two consecutive years.We counted the interest-bearing liabilities of more than 2000 urban investment companies, and the size of local hidden liabilities rose slightly to 40.11 trillion by the first half of 2019, an increase of only 1.37 trillion from the end of 2018. If the swap debt is taken into account, the debt increase is only 2.03 trillion, down from nearly 9 trillion at its peak.
If the increase in interest is taken into account, the local hidden debt has hardly increased.If we estimate that the average interest rate on stock city investment bonds is 5.7 per cent, the interest rate on urban investment company debt alone (excluding swap debt) has increased by 1.1 trillion, accounting for more than 80 per cent of the net debt increase in the first half of 2019. Considering that the interest rate for non-standard financing may be much higher than 5.7%, the actual interest expense may be higher. So after deducting interest, there has been almost no increase in local hidden liabilities this year.
In the past, whenever the economy went down, the hidden debt of the local government was often the focus of efforts and became an important support for the steady growth of infrastructure.However, under the premise of the lifelong accountability system, the debt expansion of the financing platform is obviously limited, and the support for infrastructure is also greatly weakened.

Under the downward pressure of the economy, we expect that finance will still make efforts to support infrastructure, but it is more likely to be achieved through the increase of special debt lines, the increase of budget deficit ratio, and the support of policy banks, while the regulation of local hidden liabilities may not be greatly relaxed.It is estimated that in 2020, the fiscal deficit ratio may be raised to 3.5% or more, and the amount of special debt is expected to exceed 3 trillion yuan. We cannot rule out the issue of special treasury bonds, and policy banks will also play a role, but due to the continued limitation of hidden debt, infrastructure growth has rebounded to about 8%.

3、Real estate relaxes or speeds up
Even without this epidemic, the regulation and control policy of real estate will be relaxed at the margin.According to our estimates, 60% to 70% of China's residents' wealth is allocated to real estate-related fields; the economic growth driven by real estate is still more than 20%; economic and financial risks are highly related to changes in the real estate market; and most importantly, land transfer is still an important source of revenue. So the policy does not want the real estate market to soar, but in fact it does not want to bring economic and financial risks because of the decline in the real estate market.
Therefore, last year's Central Economic work Conference again mentioned "three stability" and stressed that "housing should not be speculated." at the same time, it also stressed that "policies should be implemented because of the city," and the subsequent policy adjustments in some cities have also proved that once the real estate market goes down more, it will inevitably lead to the marginal relaxation of regulation and control policies.
Now that the epidemic has come, the pace of real estate policy relaxation may be accelerated.In the case of the tightened financing environment, the cash flow of real estate enterprises is more dependent on sales rebates, and deposit and personal mortgage loans account for nearly 50% of the sources of real estate development funds. According to the pace of previous years, after the Spring Festival Golden week, real estate sales will gradually pick up, and this time affected by the epidemic, Golden week has been more than half a month, sales are still hovering at a low level.
Real estate sales itself is facing greater downward pressure, and now the sales pressure is even greater. This will lead to more tight cash flow of developers, do not rule out the possibility that more real estate development enterprises will go bankrupt. The shortage of cash flow will also affect the development progress of projects under construction and increase the downward pressure on the economy. These factors are bound to lead to the relaxation of real estate regulation and control policies more quickly.

We believe that if the real estate regulation policy is relaxed again, it may give a boost to the core cities, but the effect on the vast majority of small and medium-sized cities is limited.We have a detailed analysis on this point in the previous topic.The last round of real estate deregulation began in 2014, when monetary policy was also loosened sharply, but in effect, the real estate market in big cities quickly stabilized and rebounded, while the real estate market in smaller cities did not recover quickly. It was not until the monetization policy was increased that the small cities gradually stabilized and rebounded.
The reason behind it isThe real estate market in the core cities is supported by demand, which has been suppressed by policy tightening before, but once the policy is liberalized, demand will rise again. However, the real estate market in small and medium-sized cities is facing the problem of insufficient demand, and the monetization of shed reform creates demand, which drives the market.
In the past few years, China's real estate market has maintained an annual sales area of 1.7 billion square meters, and a large part of the demand has been overdrawn.Therefore, if the demand of small and medium-sized cities turns cold again, it may not be very effective just by relaxing regulation and money, but it still needs a way similar to QE to create demand.


4、The policy market has already started.
The epidemic has not changed the direction of asset allocation.Since November last year, growth equity assets and bonds have performed very brightly, indicating that the logic that dominates the market is not the economic stabilization or the opening of the inventory cycle, but more active policies in the downward pressure on the economy. in particular, the easing of monetary liquidity.
The arrival of the epidemic accelerated the pace of loose policy, but strengthened the logic of asset allocation.Originally, monetary policy was also loose, but the pace was relatively reserved, but now the epidemic has a greater impact on the economy, and in order to achieve the growth target, the pace of monetary easing will certainly be greatly accelerated. So instead of breaking the logic of easy liquidity, it has been strengthened.
Looking forward, we continue to be optimistic about the new economic assets in the growth direction and the logic of the downward bond yield, which is still the main allocation direction. The cycle still faces a decline in short-term earnings and long-term pessimistic expectations, so it is difficult to perform well. Consumption is overvalued and needs to be adjusted before opportunities can be seen.
With regard to the policy market in the future, we think we can have more room for imagination.No matter from the internal or external environment, the policy is already on the "fast lane". Please sit tight!
Risk tips: epidemic spread, trade problems, economic downturn.
Edit / Jeffy
