 |  | |
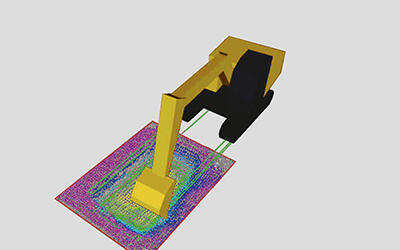
| Demonstration test situation. | Topographical sensing results after trench excavation by lidar. |
Kawasaki Heavy Industries has developed the 'Excavator Autonomous Construction System' (hereinafter referred to as this system), achieving autonomous trench excavation by excavator. This enables the 'autonomization' of trench excavation by excavators traditionally carried out by skilled workers in the construction civil engineering site.
This system, controlled by the excavator-mounted controller, plans efficient excavation operations based on input 3D design data and topographical sensing results from lidar, and autonomously determines the excavation volume while performing excavation and dump loading. In our verification test, we confirmed the system's ability to autonomously construct a 2m wide, 0.6m deep, and 10m long trench. Additionally, we have confirmed that besides excavation work, autonomous operations such as leveling the trench floor horizontally and compacting it can also be performed autonomously.
Currently, the shortage of labor due to decreasing population is becoming more pronounced, and in the construction civil engineering industry, training skilled workers and securing talent has become a major challenge. Furthermore, with a strong demand for improving working conditions and increasing productivity, the need for 'autonomization' of work at construction civil engineering sites is expected to increase further. Towards the practical application of this system, we will continue to work on system development to achieve stable autonomous excavation under various soil conditions.
 By combining our advanced hydraulic control technology developed over the years and industrial robot control technology, this system has achieved our unique excavator autonomous control as well as high responsiveness, high precision, and high efficiency. Aimed at bringing innovation to the construction civil engineering industry, we will continue to advance further development with our technology and challenges.
By combining our advanced hydraulic control technology developed over the years and industrial robot control technology, this system has achieved our unique excavator autonomous control as well as high responsiveness, high precision, and high efficiency. Aimed at bringing innovation to the construction civil engineering industry, we will continue to advance further development with our technology and challenges.
 | - | It generates a continuous path from simple point instructions and performs a smooth path following like a robot. |
 | - | Based on the 3D design data input by the controller mounted on the shovel and the data obtained by terrain sensing, it plans excavation operations. |
| - | Sensing technology and soil estimation technology enable efficient and highly robust excavation. |
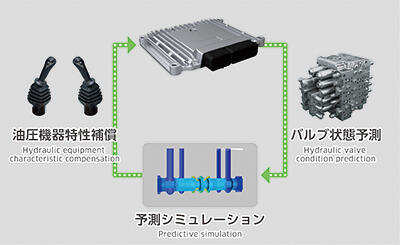 | - | Advanced hydraulic control technology allows for precise, flow-following commands to achieve high-precision and smooth operation. |
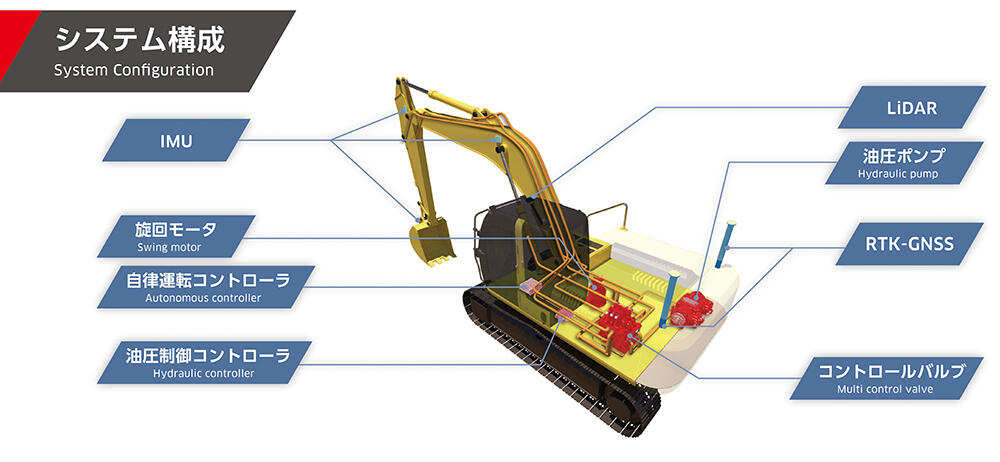
| ※1. | LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging): A technology that measures the distance and shape of objects based on the reflected light information from laser light. In this system, the ground shape is measured using LiDAR. | |
| ※2. | The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is a device that detects three-dimensional inertial motion (translational motion along three orthogonal axes and rotational motion). In this system, IMU is installed in buckets, etc., to measure the orientation. | |
| Bullet point 3. | Real Time Kinematic-Global Navigation Satellite System (RTK-GNSS) enables centimeter-level positioning by utilizing carrier phase information of satellite signals in addition to location information. This system uses two RTK-GNSS receivers to measure the position and orientation of the excavator. |
[Reference Link]
Hydraulic equipment for hydraulic excavators:

 本システムは、当社が長年培ってきた高度な油圧制御技術と産業用ロボットの制御技術を融合することで、当社独自のショベルの自律制御はもとより、高応答、高精度、高効率な動作を実現しました。建設土木業界に革新をもたらすソリューションとなることを目指し、当社の技術と挑戦で、さらなる開発を進めてまいります。
本システムは、当社が長年培ってきた高度な油圧制御技術と産業用ロボットの制御技術を融合することで、当社独自のショベルの自律制御はもとより、高応答、高精度、高効率な動作を実現しました。建設土木業界に革新をもたらすソリューションとなることを目指し、当社の技術と挑戦で、さらなる開発を進めてまいります。