Mitsui Chemicals Co., Ltd. (Location: Chuo-ku, Tokyo, President and CEO: Osamu Hashimoto, hereinafter referred to as 'Mitsui Chemicals') and Mitsui Chemicals' 100% subsidiary, Shimonoseki Mitsui Chemicals Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Shimonoseki City, Yamaguchi Prefecture, President and CEO: Naokazu Yokawa, hereinafter referred to as 'Shimonoseki Mitsui Chemicals'), have announced that they have embarked on the necessary technological development for converting phosphoric acid recovered from domestic untapped phosphorus resources into high-purity phosphorus materials with high added value, enabling recycling in the manufacturing sector.
This is a joint proposal accepted under the 'NEDO Lead Research Program/New Industrial and Innovative Technology Creation Lead Research Program' publicly solicited by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), together with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Yamashita Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., and Saga University.
■ Research and Development Background
High-purity phosphorus materials are essential materials for the formation of a decarbonized industrial society, including EV batteries, semiconductors, and renewable energy generation and storage batteries. These are manufactured using 'yellow phosphorus' produced from phosphate rock as a common raw material. However, production still relies on methods developed in the late 19th century, causing significant environmental impact.
 In addition, the current situation is that Japan is 100% dependent on imported phosphate rock and yellow phosphorus. Due to economic security risks associated with stable phosphate resource supply, phosphorus is designated as a specific important material.
In addition, the current situation is that Japan is 100% dependent on imported phosphate rock and yellow phosphorus. Due to economic security risks associated with stable phosphate resource supply, phosphorus is designated as a specific important material.
This research aims to establish a technology that converts waste containing phosphorus and by-products (untapped phosphorus resources) generated in the domestic manufacturing sector into high-purity phosphorus materials with high added value, purifies recovered phosphorus at the atomic and molecular levels, and enables wide-ranging recycling in various manufacturing sectors.
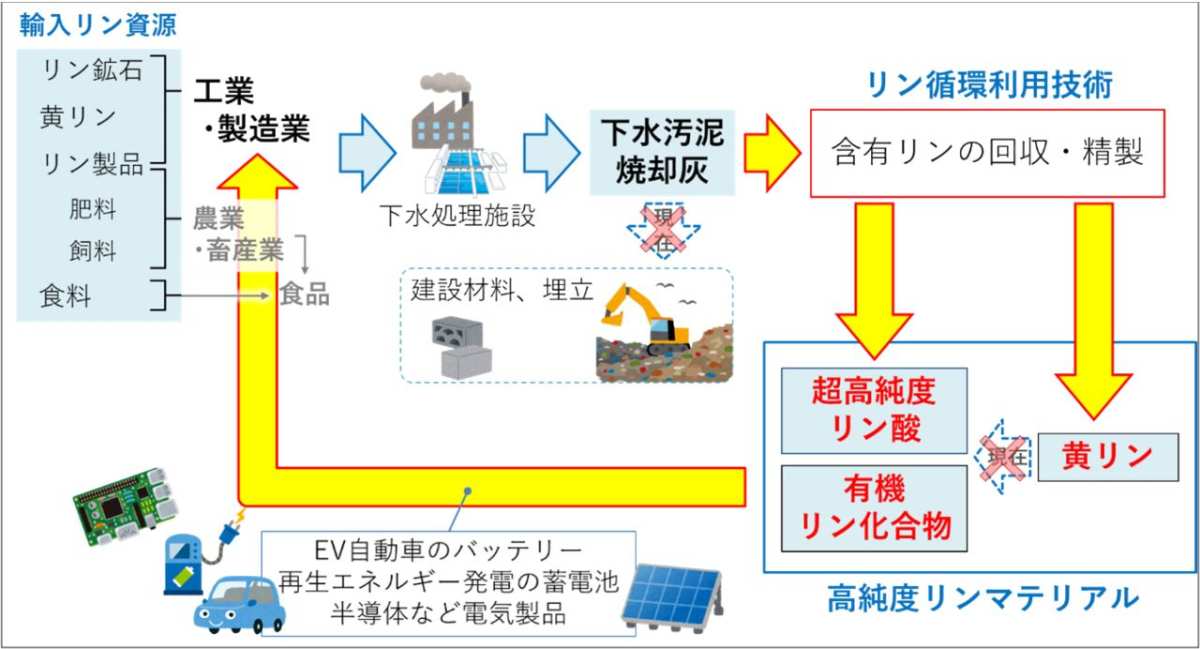 Image of technological development for the recycling of important high-purity phosphorus materials in the manufacturing sector
Image of technological development for the recycling of important high-purity phosphorus materials in the manufacturing sectorResearch and development contents, implementation structure, and the value of social implementation.
In Japan, various institutions such as Shimonoseki Mitsui Chemicals and Mitsui Chemicals, which are proficient in wet process phosphoric acid production and catalytic chemistry, have the knowledge and technological expertise in phosphoric acid, and by working together, they will contribute to the expansion of the recycling applications of recovered phosphorus from mainly agricultural fertilizers, which were traditionally limited to fertilizer uses in the agriculture sector.
Research and development theme: Development of technology for the recycling of high-purity phosphorus materials, which are important in the manufacturing sector.
1. Development of sea technology for recovering phosphoric acid from unused resources and purifying it to ultra-high purity at the molecular level (Research Item A)
2. Development of technology to purify phosphorus at the atomic level to ultra-high purity (Research Item B)
3. Development of technology to produce organic phosphorus compounds at ultra-high purity (Research Item C)
Research performing companies and institutions | Research items | |
|---|---|---|
Shimonoseki Mitsui Chemicals Co., Ltd. | A-1 | Development of artificial phosphorite and ultra-high-purity phosphoric acid manufacturing method using sewage sludge incineration ash |
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology | A-2 | Development of a process to purify crude phosphoric acid and crude metaphosphoric acid from phosphorus-containing waste |
Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. (Subcontract) National University Corporation Muroran Institute of Technology | B-1 | Development of technology for producing hypophosphorus acid by catalytic reduction of phosphoric acid using hydrogen |
Yoneyama Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Subcontract) National Institute of Technology, Kagawa College, an independent administrative agency | B-2 | Technology for producing yellow phosphorus by reduction of phosphoric acid to hypophosphorus acid with hydrogen radicals and disproportionation reaction |
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology | B-3 | Continuous reaction process technology for condensed phosphoric acid using reducing agents. |
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. | C-1 | Purification technology for the synthesis of phosphoric acid and phosphorous acid esters as key reagents for silicon compounds. |
National University Corporation Saga University. | C-2 | Efficient purification of phosphorus materials by organic phosphoric acid esterification. |
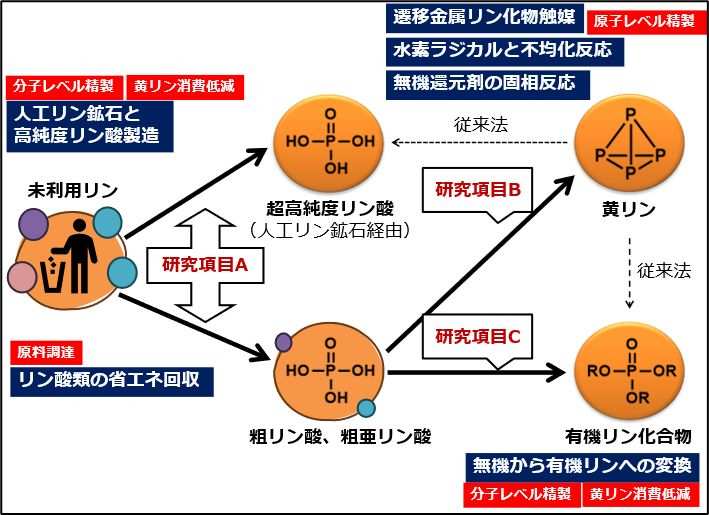 Technology development for the recycling of high-purity phosphorus materials from unused phosphorus resources - solution methods and approaches.
Technology development for the recycling of high-purity phosphorus materials from unused phosphorus resources - solution methods and approaches. * Regarding the decision on the implementation structure of the 2024 NEDO Leading Research Program/New Technology Leading Research Program | NEDO
Above.

 また日本で使われるリン鉱石および黄リンは、海外輸入に100%依存しているのが現状です。リン資源の安定供給には経済安全保障上のリスクもあることから、リンは特定重要物資に指定されています。
また日本で使われるリン鉱石および黄リンは、海外輸入に100%依存しているのが現状です。リン資源の安定供給には経済安全保障上のリスクもあることから、リンは特定重要物資に指定されています。