Author: Jun, Bankless; Translation: Deng Tong, Jinse Finance
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has quietly become a cornerstone of blockchain development. It is not just a technology, but an ecosystem of developers, tools, and applications revolving around the technological advancement.
Today, many teams are rethinking Ethereum's design choices, enhancing the EVM to create a blockchain capable of processing billions of users and thousands of transactions per second. They leverage the advantages of EVM and break boundaries through new architectures and functionalities.
 This article focuses on projects that accelerate EVM to achieve scalability at a large scale and pave the way for future adoption of cryptocurrencies. Today, we will delve into Monad, MegaETH, Berachain, and Sei.
This article focuses on projects that accelerate EVM to achieve scalability at a large scale and pave the way for future adoption of cryptocurrencies. Today, we will delve into Monad, MegaETH, Berachain, and Sei.
Monad
First, let's talk about Monad.
Monad is an L1 blockchain that has raised 0.225 billion USD, enhancing the EVM by introducing optimistic parallel execution, aiming for a throughput of 10,000 transactions per second.
Parallel execution allows independent transactions to run simultaneously, significantly speeding up the processing speed. It can be imagined as using multiple washing machines simultaneously: no need to wait for each machine to finish, everything can be done faster while still appearing orderly.
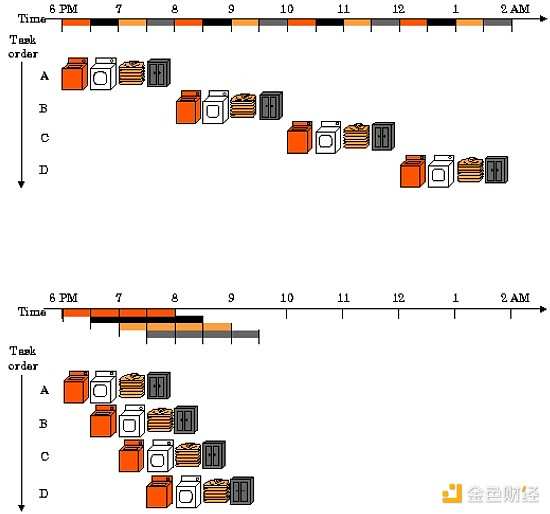
In addition to parallel execution, Monad also optimizes the performance of the entire stack.
Enhancing performance through its custom consensus mechanism MonadBFT, which can achieve faster trades with final determinations in a single time slot.
By separating processing from consensus through delayed execution, efficiency and block time are improved.
Its parallelized custom database MonadDB allows asynchronous state access, thereby speeding up data processing.
It is worth noting that Monad's architecture is optimized for consumer-grade hardware, making decentralization easier without the need for expensive validator setups.
MegaETH
Next is MegaETH.
MegaETH is Ethereum L2, which elevates Ethereum's security to a new performance level. Its goal is ambitious: to establish the first real-time blockchain capable of processing 100,000 transactions per second, relying on Ethereum and EigenDA to ensure security and data availability.
The key to MegaETH's throughput is specialization. Most blockchains require each node to perform the same tasks - verification, achieving consensus, and executing trades. MegaETH changes this by dividing roles.
Nodes are divided into three types: sequencers, verifiers, and full nodes. The sequencer handles transaction sequencing and execution. Full nodes only need to receive state updates to keep their local copy of the chain up to date. Verifiers work in the background, verifying everything with cryptographic proofs.
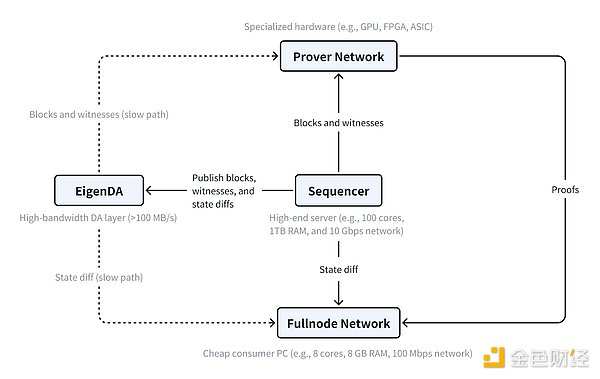
The main components of MegaETH and their interactions. Source: MegaETH Research
MegaETH also enhances the EVM through in-memory computation, where the sequencer keeps the entire EVM world state in memory. Compared to traditional systems, this improves state access speed by 1,000 times. Furthermore, improvements in block building algorithms and other updates allow MegaETH to address issues such as latency and throughput.
Berachain
Of course, we have to talk about Berachain.
Berachain is a high-performance L1 blockchain, similar to EVM, which means its execution layer mirrors the EVM runtime environment of the Ethereum mainnet. This enables the system to support all familiar tools and operations known to developers, but with additional advantages.
The core of these advantages is BeaconKit, a modular, EVM-centric consensus client framework on which Berachain is built. The main benefit of BeaconKit is the ability to integrate the functionality of the CometBFT consensus algorithm with the EVM execution environment. This effectively modularizes the stack, separating the consensus layer from the execution layer to enhance the overall Berachain experience.

Source: BeaconKit - a modular framework for building EVM consensus clients.
BeaconKit can also be paired with any EVM execution client, allowing each upgrade of EVM (such as Dencun) to be automatically applied to Berachain. This means that Berachain not only retains the same status as EVM, but also speeds up its performance, expands it, and increases its composability without losing compatibility. For example, with BeaconKit, Berachin can achieve finality in a single time slot, which means blocks are immediately finalized, instead of waiting 12-15 minutes or more as on Ethereum.
Sei
Finally, let's delve into Sei.
Sei combines the EVM environment with parallel execution to achieve faster and cheaper transactions while leveraging existing tools and developer communities. Its parallel execution allows multiple transactions to occur simultaneously, significantly increasing throughput, and supplemented by SeiDB to achieve rapid state updates.

The novelty of Sei lies in its "Twin Turbo" consensus mechanism, which speeds up block time to just 400 milliseconds. It achieves this goal by eliminating two key technologies common inefficiencies in consensus protocols:
Intelligent block propagation - accelerating block creation, reducing validators' waiting time, and ultimately decreasing latency.
Optimistic block processing - validators start processing transactions immediately upon receiving a block proposal, speeding up finality.
In addition, Sei also integrates features such as interoperability between EVM and CosmWasm, opening the door for the Cosmos ecosystem.
However, Sei does indeed sacrifice some decentralization between nodes, as these features introduce quadratic communication complexity. This means that with more validators joining, the number of messages will significantly increase, making network scaling more difficult.
Conclusion
These ambitious projects aim to build on Ethereum's achievements, scaling throughput to thousands of transactions per second. Most are still in early stages; three out of four have not yet launched on the mainnet. Only time will prove their success in scaling, driving adoption, and enabling efficient application development.
What does this mean for Ethereum?
The initial hope is that some of these high-performance chains are L2 chains, aligning with Ethereum's aggregation-centric scaling roadmap. Another positive aspect is that they all are compatible with EMV, building on existing tools while enhancing them in unique ways to promote EVM adoption.
This is also a critical moment for the Ethereum community, as many are questioning why there is not more focus on extending Ethereum itself to L1. Vitalik seems to be in "war mode," constantly publishing blogs about Ethereum's potential future. The key is that Ethereum has multiple paths to increase throughput on Ethereum L1, and importantly, all paths are under discussion and exploration.


 本文重点介绍了加速 EVM 实现大规模可扩展性并为未来加密货币采用铺平道路的项目。今天,我们将深入探讨 Monad、MegaETH、Berachain 和 Sei。
本文重点介绍了加速 EVM 实现大规模可扩展性并为未来加密货币采用铺平道路的项目。今天,我们将深入探讨 Monad、MegaETH、Berachain 和 Sei。