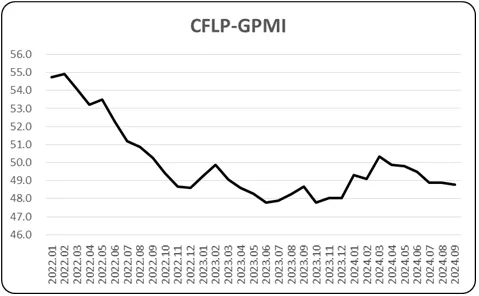
On October 6, the China Federation of Logistics and Purchasing announced that the global manufacturing PMI in September 2024 was 48.8%, a slight decrease of 0.1 percentage points from the previous month, lingering around 49% for the third consecutive month.
According to the Smart Financial APP, on October 6, the China Federation of Logistics and Purchasing announced that the global manufacturing PMI in September 2024 was 48.8%, a slight decrease of 0.1 percentage points from the previous month, lingering around 49%. By region, the PMI for manufacturing in Asia ended its continuous decline for 2 months, slightly rising from the previous month and staying above 50%; the PMI for manufacturing in Africa increased from the previous month to above 50%; the PMI for manufacturing in the Americas slightly increased from the previous month but remained below 50%; the PMI for manufacturing in Europe decreased from the previous month and continued to stay below 50%.
The comprehensive index changes showed a slight decrease in the global manufacturing recovery compared to the previous month, with the overall recovery still needing improvement. With the driving force of the improving Chinese economy, Asian manufacturing continues to be a stabilizer for global economic recovery. The recovery efforts in African manufacturing have improved, but stability still needs to be observed. Manufacturing in the Americas and Europe continues its weak operating trend. As major countries' monetary policies tend to ease and inflation pressure eases, the upward momentum of economic recovery is building, and forecasts from major world institutions are optimistic.
 Recently, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development released a report raising the 2024 economic growth forecast from 3.1% to 3.2%, and believes that the global economy is in a phase of stabilizing. The World Trade Organization's 'Goods Trade Barometer' shows a global goods trade index of 103, above the baseline of 100. Looking ahead to the fourth quarter, major countries still have room and reasons to continue easing monetary policies, with fiscal policies expected to continue to strengthen, leading to a positive global economic recovery. A more open and balanced global environment for cooperation is an important guarantee for accelerating the pace of global economic recovery.
Recently, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development released a report raising the 2024 economic growth forecast from 3.1% to 3.2%, and believes that the global economy is in a phase of stabilizing. The World Trade Organization's 'Goods Trade Barometer' shows a global goods trade index of 103, above the baseline of 100. Looking ahead to the fourth quarter, major countries still have room and reasons to continue easing monetary policies, with fiscal policies expected to continue to strengthen, leading to a positive global economic recovery. A more open and balanced global environment for cooperation is an important guarantee for accelerating the pace of global economic recovery.
Weakness in European manufacturing, with a slight decline in the PMI.
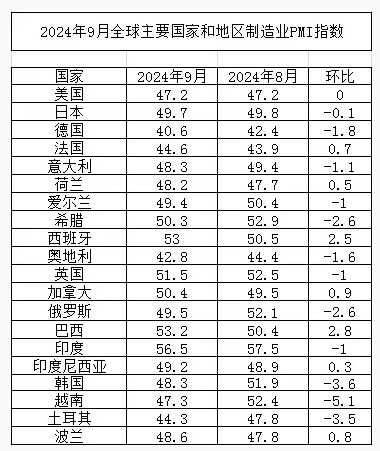
In September 2024, the PMI for European manufacturing was 47.3%, down 0.7 percentage points from the previous month, falling below 48%. Looking at major countries, the PMI for manufacturing in the United Kingdom decreased from the previous month but still remains above 51%; the PMI for manufacturing in Spain significantly increased from the previous month to 53%; the PMI for manufacturing in France slightly increased from the previous month but remains below 45%; the PMI for manufacturing in Germany and Italy both dropped by more than 1 percentage point from the previous month, both below 50% with Germany's PMI falling to around 40%.
From the trend of Europe's Manufacturing PMI, the foundation of Europe's economic recovery is not solid, and there are still downside risks. Europe's economy continues to face internal and external pressures from geopolitical conflicts and insufficient regional demand. The economic sentiment index for the Eurozone in September was 96.2, lower than the previous month's 96.6. Christine Lagarde, President of the European Central Bank, believes that the European economic recovery is facing resistance. To alleviate the downward pressure on the economy, the European Central Bank has already cut interest rates twice this year. In October, the probability of the European Central Bank continuing to cut interest rates remains high. Looking at inflation pressure, in September, the Eurozone's CPI decreased by 0.1 percentage points compared to the previous month, with a year-on-year CPI of 1.8%, also lower than the previous month's 2.2%, falling below the European Central Bank's target of 2%, indicating some relief in inflation pressure in the Eurozone, providing support for further interest rate cuts by the European Central Bank.
Manufacturing in the Americas continues to operate weakly, with a slight increase in the PMI.
In September 2024, the PMI for manufacturing in the Americas was 47.8%, up 0.2 percentage points from the previous month, but it has remained below 48% for three consecutive months, indicating that the weak trend in manufacturing in the Americas remains unchanged. Data from major countries show that Brazil and Canada saw varying degrees of increases in their manufacturing PMI compared to the previous month, both above 50%; U.S. manufacturing remained flat compared to the previous month, staying below 50%; Mexico's manufacturing PMI decreased from the previous month, also below 50%.
According to the ISM report, in September, the PMI for U.S. manufacturing was 47.2%, unchanged from the previous month, remaining below 48% for three consecutive months. Changes in sub-indices show that the manufacturing production index and new orders index saw varying degrees of increases compared to the previous month but remained below 50%, indicating some relief in supply-demand pressure in U.S. manufacturing compared to the previous month but still maintaining a weak trend.
Manufacturing in the United States continues to operate weakly, indicating that even after the Federal Reserve decided to start cutting interest rates, the risk of an economic recession in the United States has not been completely eliminated. Recently, the Bloomberg Economics Research Institute predicted that the likelihood of the U.S. economy already being or soon to be in a recession is as high as 70%. Consumer confidence in the United States has also weakened. Data released by the World Economic Forum showed that the U.S. consumer confidence index dropped by 6.9 points to 98.7 in September, the largest decline since August 2021. Against this backdrop, the necessity for the Federal Reserve to continue cutting interest rates to stimulate the economy becomes more pronounced. Recent data related to inflation also support the continued interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. The annual rate of inflation for personal consumption expenditures in the United States slowed to 2.2% in August, the lowest level since March 2021. In September, the increase in non-farm payrolls in the United States did not change the market's expectation for the Federal Reserve to continue reducing interest rates, but there was an adjustment in the expected magnitude. Seasonally adjusted non-farm payrolls in the United States increased by 0.254 million people in September, exceeding the market's expected 0.15 million people and the revised 0.159 million people from the previous month. Based on the data changes, U.S. banks adjusted their expectations for a November Fed rate cut from 50 basis points to 25 basis points.
Manufacturing in Africa accelerated its recovery compared to the previous month, with the PMI rising to above 50%.
In September 2024, the PMI for manufacturing in Africa was 50.3%, up 1.9 percentage points from the previous month. Looking at major countries, the rapid recovery in South Africa's manufacturing sector was the main factor contributing to the faster recovery in African manufacturing. South Africa's manufacturing PMI increased from around 43% the previous month to over 52%; Nigeria's manufacturing PMI remained relatively stable, slightly below 50% for two consecutive months; Egypt's manufacturing saw a slight decrease compared to the previous month, falling below 50%.
Although manufacturing in Africa accelerated its recovery compared to the previous month, the monthly trend in PMI often fluctuates around 50%, indicating that the stability of Africa's manufacturing recovery still needs to be observed. Tapping into Africa's economic potential requires increased foundational investments in a relatively stable political environment to achieve sustainable industrial development. The construction of the African Continental Free Trade Area, propelled by the African Union, is progressing rapidly to enhance Africa's manufacturing competitiveness through economies of scale and strengthened regional cooperation. Additionally, artificial intelligence and the digital economy are gradually becoming crucial areas of support for economic development in various African countries.
Asian manufacturing continues to operate steadily, with a slight increase in the PMI.
In September 2024, the PMI of Asian manufacturing was 50.7%, ending the trend of continuous decline for 2 consecutive months, with a slight increase of 0.1 percentage point compared to the previous month, staying above 50% for 9 consecutive months. Looking at the main countries, the PMI of manufacturing in China was 49.8%, a 0.7 percentage point increase from the previous month; while the PMI of manufacturing in India decreased from the previous month, still above 56%; among the major ASEAN countries, the Philippines' manufacturing PMI increased significantly from the previous month, rising to above 53%; Thailand's manufacturing PMI decreased from the previous month but remained above 50%; manufacturing PMI in Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, and Vietnam had varying increases and decreases compared to the previous month, but all remained below 50%; the PMI of manufacturing in Japan and South Korea both declined to varying degrees from the previous month and remained below 50%.
From the perspective of index changes, driven by the positive recovery of manufacturing in China, the PMI of Asian manufacturing continues to maintain stable growth. With the continued fermentation of China's fiscal and monetary policy effects, in the fourth quarter, China's economic recovery momentum will continue to strengthen, potentially driving the recovery momentum of the Asian economy to further increase. The Asian Development Bank recently released a report, stating that emerging economies in Asia maintained the vitality of economic growth in the first half of 2024, and raised the economic growth forecast for emerging economies in the Asia-Pacific region in 2024. It is expected that the emerging economies in the Asia-Pacific region will grow by 5.0% in 2024, an increase of 0.1 percentage points from the forecast value of 4.9% in April. At the same time, it is expected that the inflation rate of emerging economies in the Asia-Pacific region will further slow to 2.8%, a decrease of 0.4 percentage points from the previous expectation of 3.2%.

 近期,经济合作与发展组织发布的最新报告将2024年经济增长预期由3.1%上调至3.2%,并认为全球经济正处于企稳阶段。世界贸易组织发布《货物贸易晴雨表》显示,全球货物贸易景气指数为103,高于基准点100。展望四季度,世界主要国家货币政策仍有继续宽松的空间和理由,财政政策也有望继续发力,全球经济有望向好恢复。更加开放和均衡的全球化合作环境是全球经济加快复苏节奏的重要保障。
近期,经济合作与发展组织发布的最新报告将2024年经济增长预期由3.1%上调至3.2%,并认为全球经济正处于企稳阶段。世界贸易组织发布《货物贸易晴雨表》显示,全球货物贸易景气指数为103,高于基准点100。展望四季度,世界主要国家货币政策仍有继续宽松的空间和理由,财政政策也有望继续发力,全球经济有望向好恢复。更加开放和均衡的全球化合作环境是全球经济加快复苏节奏的重要保障。