The bond market suffered a sharp setback.
With a series of economic stimulus policies intensively introduced, the bond market suffered a sharp setback.
Starting on Tuesday this week, the central bank rolled out a comprehensive policy package, an unscheduled early convening of the political bureau meeting, a series of bullish policies immediately reversed the market's risk appetite, with equities and long-term bonds experiencing a seesaw effect. As the central bank officially implemented reserve requirement and interest rate cuts on Friday, the bond market continued to be under pressure for a correction.
 According to market analysts, in addition to the stock-bond seesaw effect, the wide monetary signal released by the interest rate and reserve requirement cuts also led to the concentrated realization of the wide monetary expectation in the bond market. Considering the significant trading around interest rate cuts in the bond market previously, in an environment where the bullish trend has exhausted, market profit-taking sentiments are escalating.
According to market analysts, in addition to the stock-bond seesaw effect, the wide monetary signal released by the interest rate and reserve requirement cuts also led to the concentrated realization of the wide monetary expectation in the bond market. Considering the significant trading around interest rate cuts in the bond market previously, in an environment where the bullish trend has exhausted, market profit-taking sentiments are escalating.
On Friday, the 30-year treasury bond yield rose above the 2.3% level, with all maturity treasury bond futures experiencing their largest single-day historical decline. Today, the pullback in treasury bond cash markets continues to deepen.
During the morning trading session, the interbank medium and long-term interest rate bonds experienced a rapid decline. The active 10-year treasury bond cash bond (240011) saw its yield rise by 7.25 basis points to 2.25% intraday; the active 30-year treasury bond cash bond (230023) had its yield rise by 9.5 basis points to 2.425%.
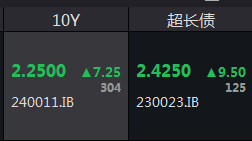
Since the low point on September 24th, based on intraday prices, the yield of the 10-year treasury bond has accumulated a rise of over 22 basis points, and the 30-year treasury bond yield has accumulated a rise of over 26 basis points.
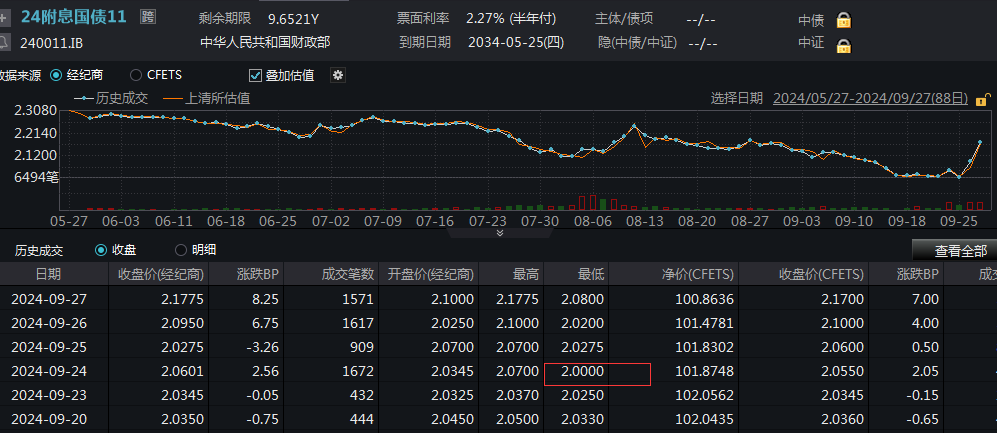
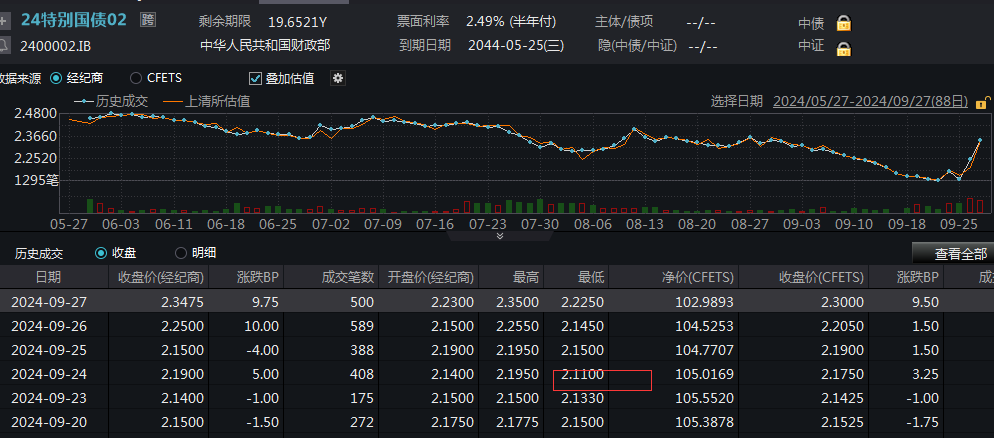
Multiple funds and wealth management products experienced significant withdrawals.
As the bond market correction deepens, the net asset value of the top financial products also experiences significant fluctuations.
Wind data shows that as of Friday, the mid-to-long-term pure bond fund index has accumulated a weekly decline of 0.22%, with the largest single-day decline of 0.24% on the 27th.
Choice data shows that as of Friday, out of over 6600 bond funds in the market (calculated separately by different share classes), nearly 300 products have interval unit net value declines of over 1%, approximately 4500 products have negative interval unit net value growth rates. In terms of fund types, the significant decline in bond funds is mostly pure bond funds.
Multiple fixed-income financial products also experienced significant pullbacks. Wind data shows that in the past week, a total of 741 fixed-income financial products experienced net value pullbacks, with 25 products having pullback rates exceeding 1%, and nearly 30% having pullback rates exceeding 0.01%. This includes several top financial subsidiary companies such as CMB Wealth Management, CIB Wealth Management, and China Post Wealth Management.
Feng Lin, Department Director of Research and Development at East Money, believes:
"In the medium to long term, the trend still needs to observe the policy effects. Until the policy effects are evident and drive a reversal in fundamental expectations, it will be difficult for the bond market trend to fundamentally reverse, which will also constrain the short-term downside space in the market."
Some analysts point out that in the short term, the bond market is undergoing adjustments, causing certain disturbances in the performance of financial products' net asset values. This has a greater impact on financial companies with higher proportions of fixed-income financial products in their portfolios. "Particularly, some products that achieve high returns through leverage are more sensitive to interest rate changes, and should be vigilant about potential risks of breaking the net asset value."
Has the market responded appropriately?
Looking from the current perspective, has the market response been adequate?
Guotou Securities analysts Yin Ruizhe and Liu Dong analyze that how this round of bond market adjustment will unfold also depends on the subsequent performance of the fundamentals.
The report divides the bond market's decline since 2016 into two common patterns: micro overheating type and macro-driven type:
During micro overheating adjustments, the interest rate increase is generally around 20 basis points, and the duration usually does not exceed 2 months.
In the macro-driven decline, credit spreads generally widen significantly, while in the micro overheating decline, credit spreads instead narrow slightly.

Looking at the current pullback magnitude, the adjustment of 20 basis points is already close to the previous 'micro overheating' adjustment magnitude, but the adjustment time is still relatively short. Whether it will evolve into 'macro-driven type' in the future still requires patient waiting for the validation of the fundamentals.
Guotou Securities believes that the following three sets of fundamental indicators are worth paying attention to: whether the fundamental high-frequency indicators stop falling; whether the growth rate of medium and long-term corporate loans stops declining; and whether the real estate market stabilizes.
Guotou Securities points out that since the incremental policies have not been fully implemented, there is still high market expectations for fiscal policy, and the current market feedback on this round of growth-stabilizing policies may not have yet entered the 'waiting for validation' phase.
Huaxi Securities believes that from a theoretical perspective, the price center of the 10-year government bond yield spread is 2.10%, and the 30-year government bond is 2.30%; from the market expectation perspective, the market consensus range of the 10-year government bond yield may be 1.97%-2.10%, while the range for the 30-year government bond is 2.16%-2.30%.
What other incremental fiscal measures may be introduced?
With successive supportive policies from central institutions and signals of potential policy intensification released by the Political Bureau meeting, market expectations for incremental policies are gradually increasing.
Xiong Ruijian, a bond futures researcher at GF Futures, believes that today's bond market decline includes two drivers, besides the quick rise in the stock market pushing up market risk appetite, another significant factor is the expectation of incremental policies after the Political Bureau meeting.
Some industry insiders point out that with the issuance of an additional 3.8 trillion local special bonds and 300 billion super long-term special national bonds, the expected funding gap is still around 1 trillion compared to the beginning of the year. Against the backdrop of promoting the stabilization and recovery of the domestic economy growth rate, this provides space and conditions for issuing government bonds and other incremental fiscal policies.
Huaxi Securities stated that the fiscal tools that may be used currently are divided into several categories: first, tools that do not require approval from the National People's Congress, such as using the remaining quota of government bonds, and the balance limit of government bonds. Second, for additional fiscal tools with a scale exceeding 1 trillion, new quotas that may require approval from the National People's Congress.
Therefore, the report points out that if there is an increase in government bond issuance, the timing of implementation may be after the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress in late October, between November and December, while October may accelerate the issuance of the remaining quota for the year, leaving room for future issuances.
Based on this, Huaxi Securities believes that the subsequent impact on the bond market will mainly manifest in three aspects:
First, government bond payments form government deposits, absorbing market liquidity, which temporarily impacts the fund side, but we expect this impact to be relatively controllable. However, against the backdrop of the central bank's expansion of required reserve ratio, we expect that there will not be a clear tight state in liquidity.
Second, it affects the market's expectations on the economic fundamentals. If 1-2 trillion government bonds are issued in the fourth quarter, firstly, they will be directly included in social financing, with a year-on-year pull effect on the annual social financing stock of about 0.3-0.6%. Secondly, in terms of GDP pull effect, the direction of the funds needs to be considered. If the increased issuance of national debt is used for debt conversion purposes, it may not necessarily lead to additional output.
Third, is the direct supply pressure, which may mainly depend on the supply term. If short-term government bonds account for a larger proportion, the impact may be relatively small because of the central bank's bond purchases, leading to a significant increase in the demand of major banks for short-term government bonds. However, if they are all super long-term government bonds, concentrated supply shocks may bring certain pressures.
Editor/ping

 据市场人士分析,除了股债“跷跷板”效应的因素之外,降息降准释放的宽货币信号也带来了债市宽货币预期的集中兑现,考虑到围绕降息债市此前已较多交易,利多出尽环境下市场止盈情绪发酵。
据市场人士分析,除了股债“跷跷板”效应的因素之外,降息降准释放的宽货币信号也带来了债市宽货币预期的集中兑现,考虑到围绕降息债市此前已较多交易,利多出尽环境下市场止盈情绪发酵。