In the first half of the year, 41 banks collectively experienced a decline in net interest margin, with 9 banks showing a decrease in the level of interest margin at 2% and above compared to the same period last year; the number of banks with negative growth in net income attributable to the parent company reached 12, an increase of 7 from the same period last year. Experts believe that the continued narrowing of the net interest margin has put pressure on the profit space of banks, and the possible recent lower interest rates on existing home loans will further challenge the interest margin of banks, increasing operational pressure.
On August 31, Cailian News published the half-year report coefficients of 42 listed banks in 2024. Cailian News reporters found that in the first half of this year, the overall performance pressure of listed banks further intensified, and profitability experienced a significant decline.
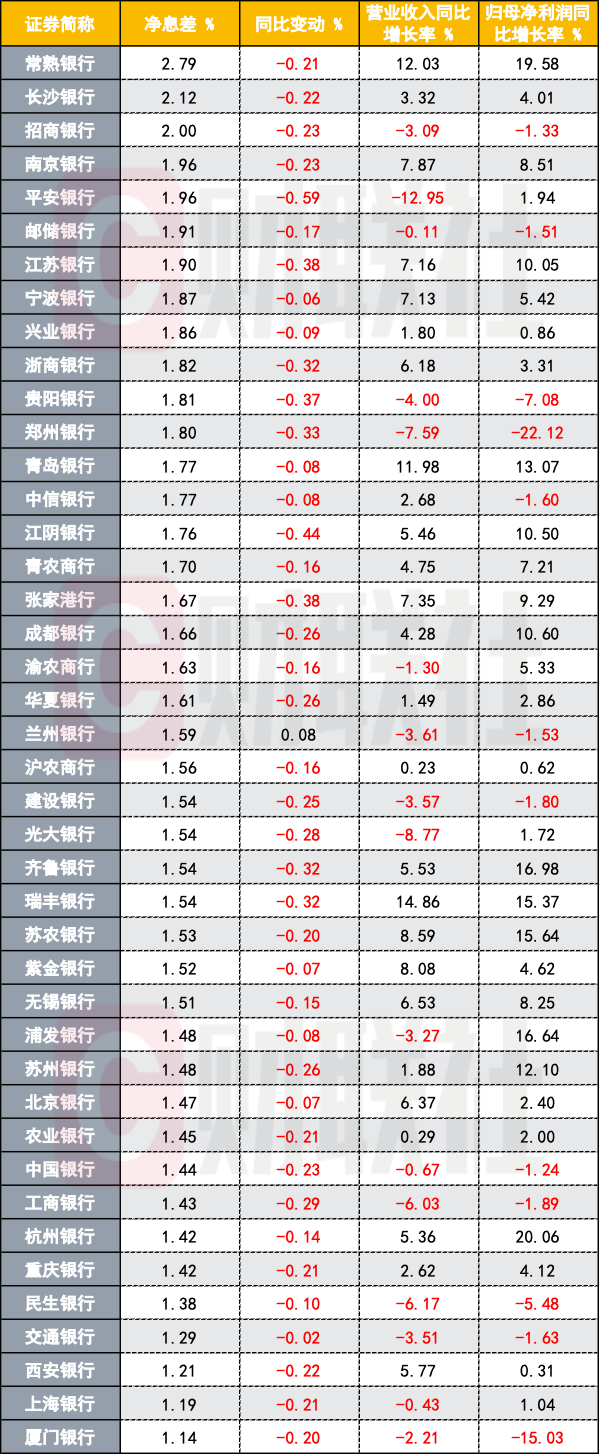
In terms of interest margin performance, except for Lanzhou Bank, the remaining 41 banks collectively experienced a decline in net interest margin, and the number of banks with an interest margin level at 2% and above decreased from 12 in the same period last year to 3. In terms of profitability, in the first half of this year, the number of banks with negative growth in net income attributable to the parent company reached 12, an increase of 7 from the same period last year.
In the view of industry experts, the continued narrowing of the net interest margin, even breaking new lows, has put pressure on the profit space of banks. At the same time, the possible recent lower interest rates on existing home loans will further challenge the interest margin of banks, increasing operational pressure. In the future, commercial banks need to actively explore new profit models to enhance their own competitiveness, optimize the adjustment of asset-liability structure, while appropriately giving up the pursuit of scale expansion, and seeking high-quality development.
Interest margins further declined, with 12 listed banks experiencing negative growth in net profit.
Since the beginning of this year, the level of interest margins in the banking industry has come under further pressure. Cailian News reporters found that in the first half of this year, among the A-share listed banks, only Lanzhou Bank saw a slight increase of 8 basis points, while the remaining 41 banks all experienced varying degrees of decline.
Specifically, in the first half of the year, only 3 banks, Changshu Bank, Changsha Bank, and CM Bank, maintained a net interest margin level of 2% and above, at 2.79%, 2.12%, and 2.00% respectively. It is worth noting that in the same period last year, among the 42 listed banks, there were as many as 12 banks with a net interest margin of over 2%.
Looking at the banks with lower interest margins, in the first half of this year, Bank of Shanghai and Xiamen Bank both fell below 1.2% on their net interest margins, at 1.19% and 1.14% respectively, becoming the two lowest ranking banks among the listed banks. In comparison, in the same period last year, even the lowest net interest margin among the 42 listed banks was still above 1.3%.
At the same time, with the continuous narrowing of interest rate spreads, the pressure on bank performance is gradually becoming evident, and even entering a downward profit channel.
In summary, in the first half of this year, 12 listed banks with negative growth in net profit attributable to shareholders have been added, compared with 7 more than the same period last year, including Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Bank of China, Bank of China, Bank of Communications, and Postal Savings Bank of China, the five state-owned major banks.
Specifically, the net profit attributable to shareholders of Bank of Zhengzhou and Xiamen Bank in the first half of the year both decreased by more than 20%, with a year-on-year decrease of 22.12% and 15.03% respectively; Bank of Guiyang and Minsheng Bank followed closely, with a year-on-year decrease of 7.08% and 5.48% respectively; the net profit attributable to shareholders of the remaining 8 banks decreased by more than 1%.
In addition, among the banks that achieved positive growth in net profit attributable to shareholders in the first half of the year, there were only 11 banks with a growth rate of more than 10%, a decrease of 9 compared with the same period last year.
The narrowing interest rate spread further squeezes profits, and a new round of downward adjustment of the stock housing loan interest rate opens the window.
In the view of Ming Ming, Chief Economist of CITIC Securities, the continuous decline in net interest margin of many banks is mainly due to the continuous decline of LPR and actual loan interest rates, the concentrated repricing at the beginning of the year, and the increased efforts of banks to reduce fees and benefit the real economy, which have increased the operating pressure on banks. At the same time, the decline in bank profits may also be related to the lingering pressure on economic growth, weakened demand for credit, and reduced loan interest rates.
"The level of interest rate spread of banks is an important indicator of their profitability and interest rate risk management." Zheng Jiawei, Chief Analyst of Yongxing Securities Fixed Income, told Cailian News that the current central bank is increasing the intensity of countercyclical adjustments, guiding LPR downward through OMO, guiding the overall financing cost for real economy financing to stabilize and decrease, and promoting commercial banks to give benefits to the real economy. Therefore, the net interest margin of listed banks continues to decline, and the net interest margin of many banks has reached a new low, resulting in certain pressure on bank profit space. In addition, the recent possible downward adjustment of the interest rate on stock housing loans will further challenge the interest rate spread of banks.
It is worth mentioning that China is considering further lowering the interest rates on existing housing loans, allowing existing housing loans with a scale of up to 38 trillion yuan to seek 'refinancing', in order to reduce the debt burden of residents and stimulate consumption. Industry insiders generally believe that there is a high possibility of lowering interest rates on existing housing loans, which will further compress the profit margins of banks.
The window for a new round of interest rate cuts on existing housing loans has opened. Li Yu-jia, chief researcher of the Housing Policy Research Center of the Guangdong Province Urban and Rural Planning Institute, analyzes that on the one hand, the recent significant reduction in deposit interest rates has greatly reduced the cost of funds for banks, and the adjustment in the medium and long term is even greater, with the intention of reducing the preference for residents' fixed-term deposits. On the other hand, the central bank's open market operation interest rates are also being cut, resulting in a rapid reduction in the cost of funds for commercial banks, opening the window for another round of interest rate cuts on housing loans.
According to data monitored by the Rong 360 Digital Technology Research Institute, in July 2024, the average interest rates for 3-month and 6-month fixed-term deposits in banks were 1.481% and 1.689% respectively. The average interest rates for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year fixed-term deposits were 1.817%, 1.94%, and 2.339% respectively, while the average interest rate for a 5-year fixed-term deposit was 2.295%.
In Li Yu-jia's view, although this move may lower the interest rates on bank housing loans, it can slow down the trend of early repayment and reluctance to borrow, as well as alleviate the decline in sales of commercial housing. At the same time, for banks, the decline in funding costs will enable them to increase their loan volume, even if the interest rates are lower, their total profits will remain unchanged.
Forcing banks to explore new models, experts suggest abandoning scale expansion and turning to high-quality development.
Zeng Gang, Director of the Shanghai Institute of Finance and Development, analyzed to Cailian Press reporters that if the interest rates on existing loans are significantly higher than the current rates, residents may also achieve the so-called 'refinancing' through other implicit means, replacing the original loans with loans at lower interest rates.
If the interest rates on existing loans are directly adjusted, it means that long-term pressure is being converted into short-term release. For banks, the yield on loan assets will further decline. If the decline in funding costs does not match, the interest spread will be further compressed, putting great pressure on revenue and profit.
At the same time, Ming Ming also believes that if the interest rates on existing housing loans are lowered, it will reduce banks' interest income and further compress their net interest spread, increasing operational pressure. Faced with the challenges of narrowing interest spreads and negative profit growth, banks may need to take various measures to optimize their asset-liability structure, improve risk management capabilities, reduce operating costs, and find new sources of profit growth.
In Zhang Jiawei's view, the interest rate spread is further under pressure, which also forces commercial banks to actively explore new profit models to enhance their competitiveness. This can be achieved by strengthening product innovation, expanding intermediary business income, and increasing the proportion of non-interest income, thus reducing their dependence on interest rate spreads. At the same time, commercial banks also need to continuously optimize their asset-liability structure, improve risk management capabilities, and strengthen cost control to cope with the downward pressure on interest rate spreads.
"The operation of large banks is relatively stable, while the pressure on some small and medium-sized banks is increasing. Industry differentiation will intensify." Zeng Gang suggested that, overall, banks need to strengthen risk management and disposal. On a prudent basis, they should further reduce the cost of liabilities, adjust the asset structure, and maximize income as much as possible. At the same time, they can consider abandoning the pursuit of scale expansion to a certain extent, control a reasonable development speed, and seek high-quality development.
"Principally speaking, this is a normal situation in the process of economic adjustment and transformation, and it is within a controllable range. In the long run, as the real economy gradually recovers, the space for the interest rate spread, profits, and scale expansion of the banking industry will also be restored." Zeng Gang further stated.
