Shen Wan said that after the risk of interest spreads was resolved, Japanese personal insurance companies still achieved a continuous positive contribution of three differences in the era of low interest rates. In comparison, reducing debt costs is China's main means of mitigating the risk of interest spreads; among them, lowering scheduled interest rates is the core gripper for reducing the cost of new debt.
In the era of low interest rates, personal insurance companies face challenges in operating. “Risk transformation” is a core issue in the insurance industry, and interest spread risk is a top priority in “risk conversion.”
In the August 16 report, Shenwan Hongyuan Securities analyzed Japan's interest rate difference risk mitigation plan and compared the differences in the insurance situation between China and Japan for reference.
 According to the Shen Wan Report, Japan's main means of mitigating the risk of interest spreads include: 1) reducing the scheduled interest rate (core); 2) optimizing the product structure (core); 3) increasing the allocation of foreign assets (core); 4) lengthening the longevity of government debt; 5) reducing operating costs; and 6) reducing stock allocation.
According to the Shen Wan Report, Japan's main means of mitigating the risk of interest spreads include: 1) reducing the scheduled interest rate (core); 2) optimizing the product structure (core); 3) increasing the allocation of foreign assets (core); 4) lengthening the longevity of government debt; 5) reducing operating costs; and 6) reducing stock allocation.
It is worth mentioning that after the risk of interest spreads was resolved, Japanese personal insurance companies still achieved a continuous positive contribution of three differences in the era of low interest rates. In this process, insurers take into account changes in customer demand under the aging trend, push the product structure towards the protection category, and further consolidate the positive contribution of death fee differences to profits.
What challenges do Japanese personal insurance companies experience?
In the early 90s of the last century, Japan's economic bubble burst, and the GDP growth rate declined markedly. Japan entered a period of low interest rates, and insurance companies faced pressure on the asset side, debt side, and business operations.
Shen Wan pointed out:
On the asset side:
1) Investment pressure: long-term interest rates declined steeply, the stock market fell sharply, dollar assets depreciated rapidly, and the yield center declined significantly;
2) Exposure to risk of stock assets: An increase in the non-performing loan ratio and a sharp drop in real estate prices further hamper investment performance.
On the debt side,
1) The premium growth rate weakened, and the number of insurance policies, payment amounts and insured amounts per household continued to decline;
2) The quality of insurance policies has declined significantly;
3) Increased risk aversion, changing customer needs,
In terms of business operations,
1) The risk of interest spreads and losses has been exposed, and profits have declined sharply;
2) Eight personal insurance companies went bankrupt, and mergers, acquisitions and restructuring became the main theme in the personal insurance industry.
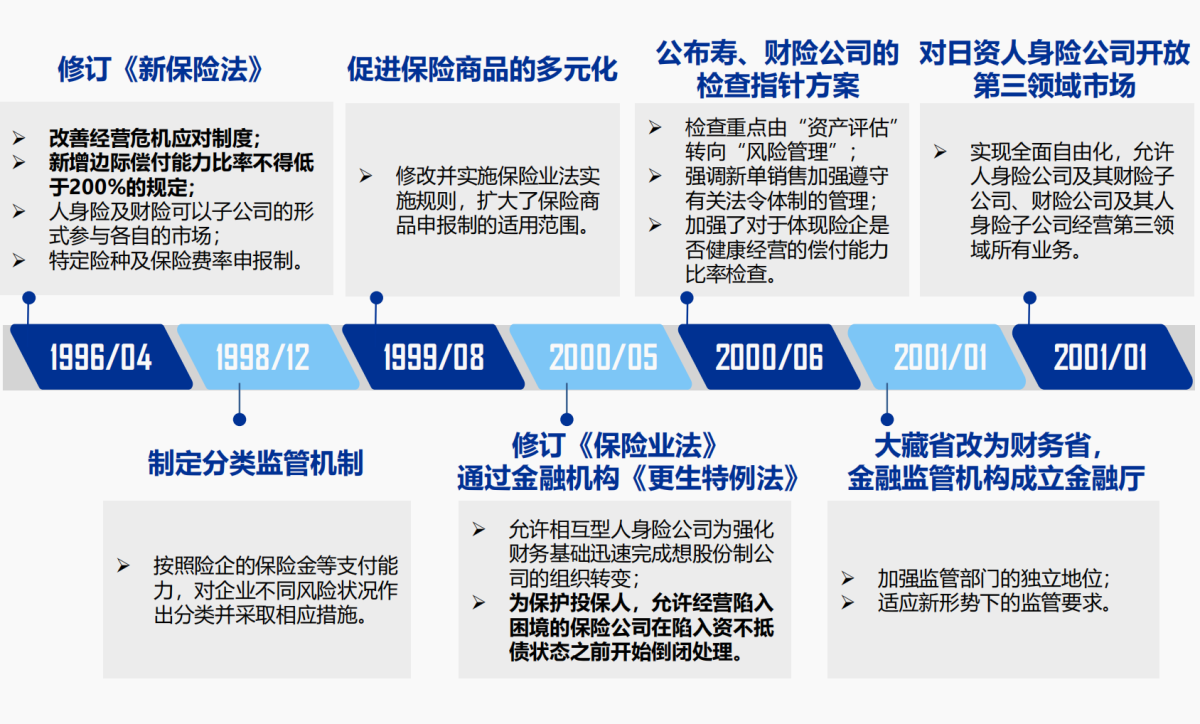
How can Japan mitigate the risk of interest differences?
Japan's main means of mitigating the risk of interest spreads include: 1) reducing the scheduled interest rate (core); 2) optimizing the product structure (core); 3) increasing the allocation of overseas assets (core); 4) lengthening the longevity of government bonds; 5) reducing operating costs; and 6) reducing stock allocation.
Shenwan Securities pointed out that
The asset allocation structure of Japanese personal insurance companies has been drastically adjusted, and the share of overseas securities has increased significantly. The Japanese personal insurance industry has expanded its share of overseas investment, using overseas high-interest assets to make up for the lack of high-yield local assets. Foreign securities accounted for 13.07% of Japanese personal insurance investments in 1990, rose to 26.57% in 2021, and fell in stages to 23.8% in 2022.
Overseas securities allocations continue to contribute to excess earnings. From 2009 to 2022, the average return on investment in Japanese personal insurance general accounts was 2.12%, and the average return on investment in overseas securities during the same period was 3.33%, higher than 1.21pct for general accounts; in 2017 and 2019 alone, the yield on overseas securities was lower than 0.40pct and 0.26pct for general accounts, and the rest of the year contributed significantly to excess income.
The core gripper on the debt side, on the other hand, is to reduce the scheduled interest rate+optimize the product structure:
Continuously optimize the product structure and increase the proportion of guaranteed products and interest rate sensitive products. As the population ages, demand for death insurance has declined, and demand for medical insurance continues to rise. Japan's health insurance products have driven premium growth, and the business share rose from 8% in 1985 to 34% in 2015.
Under the influence of changes in product structure, the dead margin partially offsets the profit margin loss. From 1990 to the beginning of 2000, the ratio of death difference income in the Japanese personal insurance industry to the total benefit of the three differences increased by 17 pct (personal insurance companies used a more conservative life table when designing products, the death margin was higher, and the value ratio was 2-3 times that of death insurance).
Furthermore, Japan
It is worth mentioning that
After getting out of the interest spread crisis, Japanese personal insurance companies still achieved a continuous positive contribution of three differences in a low interest rate environment. Japanese personal insurance companies use dead spreads and fee spreads as the main source of profit, optimize the profit structure by increasing the share of insured products, improve the financial stability and profitability of the entire industry, and maintain a stable profit level in a long-term low interest rate environment;
Under the influence of changes in customer demand+optimization of profit structures by insurers, build a product structure with guarantee products as the main focus;

 申万报告指出,日本化解利差损风险的主要手段包括
申万报告指出,日本化解利差损风险的主要手段包括