In recent times, global stock markets have been extremely turbulent.
The US stock market plummeted on Thursday, August 1st Eastern Time.$S&P 500 Index (.SPX.US)$dropping by 1.37%.$Nasdaq Composite Index (.IXIC.US)$The three major stock indexes in Europe fell across the board on Thursday.$UK FTSE100 Index (.FTSE.GB)$fell 1.01%,$German DAX30 Index (.GDAXI.DE)$fell 2.30%,$France CAC40 Index (.CAC.FR)$fell 2.14%.
The US stock market, especially the tech stocks, experienced a ruthless sell-off.$Meta Platforms (META.US)$Star tech stocks such as$NVIDIA (NVDA.US)$,$Apple (AAPL.US)$,$Amazon (AMZN.US)$also fell sharply, and its stock price plummeted 18.9% after-hours, becoming the focus of the market. $Intel (INTC.US)$Asian markets were not spared either, with indexes plummeting nearly 6000 points in just two days, a drop of nearly 15%, the biggest drop in nearly 16 years. This decline not only shocked investors, but also raised concerns about the global economic outlook.
One possible reason is the bursting of the AI bubble, which caused the collapse of tech stocks.$Nikkei 225 (.N225.JP)$Artificial intelligence (AI) technology was once the darling of the capital markets, but with the market's reassessment, the expectation of the bursting of the AI bubble has become an important reason for the collapse of tech stocks.
According to reports by US media, OpenAI can earn about $2 billion annually through ChatGPT and is expected to earn nearly $1 billion annually through large language models. OpenAI's total monthly revenue is about $0.283 billion, estimated to be between $3.5 billion and $4.5 billion in annual revenue. Therefore, OpenAI's loss for the year could be as high as $5 billion, and its cash flow may be exhausted within the next year.
Alphabet, Google's parent company, has intensified concerns with its second quarter financial report. The revenue growth of Google's cloud and search businesses (both related to AI) over the past year has not continued to show a steady upward trend.
According to reports from US media, Open AI is currently able to generate about 2 billion USD in revenue annually through ChatGPT and is expected to generate nearly 1 billion USD in revenue through its large language model charging service. The company's total monthly revenue is around 0.283 billion USD, and its estimated annual revenue is between 3.5 billion and 4.5 billion USD. Therefore, OpenAI could face a loss of up to 5 billion USD per year, and its cash flow could be depleted within the next year.
Alphabet, Google's parent company, released its second-quarter financial report, which has intensified concerns. The revenue growth of Google's cloud and search businesses (both of which are related to AI investment) in the past year has not continued to steadily rise.
As the "Red Clothes Leader" said in a short video, "Goldman Sachs, Sequoia and other institutions did the math, and the entire AI industry needs to earn $600 billion to justify the current hardware investment, but the result is that OpenAI only has income of $3 billion, and most of the industry's players are not making money."
Goldman Sachs emphasized that if important use cases don't become more apparent in the next 12-18 months, investors' enthusiasm may begin to wane.
Goldman Sachs believes that "tech giants plan to spend $1 trillion on AI capital expenditures in the coming years, but there is almost no substantive, visible result to prove that these investments are worthwhile". Goldman Sachs pointed out that the current situation is different from the early days of Internet technology applications. Even in the early days, Internet technology could use low-cost solutions to replace high-cost solutions. AI is now expensive and cannot provide cheaper alternatives.
Goldman Sachs also judged that the actual impact of AI on the economy in the next ten years will be very limited, and AI will only increase U.S. productivity by 0.5%, GDP will only increase by 0.9%, which will lead to a large amount of invested capital possibly being wasted, and the market value obtained by the "Big Seven Sisters" of the U.S. stock market may be the largest bubble in history.
This pessimistic expectation for the future of AI technology has led to a decline in investor confidence in technology stocks, and funds have begun to withdraw from this sector. At the same time, negative news from technology giants has further intensified the market's panic: for example, Intel's performance fell short of expectations; and Nvidia's stock price was affected by rumors of AI project delays, "a Hong Kong research institution called Aletheia Capital said that Blackwell volume production will be fully delayed until 25Q1".
In addition, news of U.S. antitrust regulation has put pressure on technology stocks. These factors have combined to make technology stocks a major area of market selling.
Second, weak U.S. economic data sparks recession speculation.
Weak U.S. economic data is like a warning bell, ringing the market's worries about an economic recession. The U.S. July ISM Manufacturing PMI recorded 46.8, the largest contraction in eight months; while the number of initial jobless claims in the United States increased by 0.014 million to 0.249 million people last week, hitting a new high in nearly a year. These data not only show that the U.S. economy may be slowing down, but also raise concerns in the market about an economic recession.
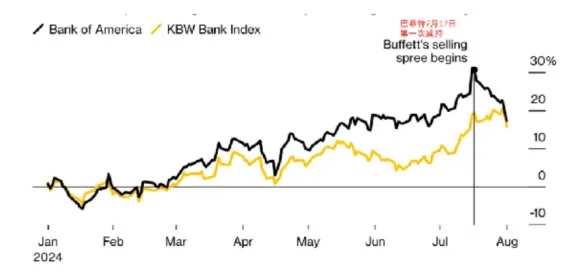
Buffett's sale behavior has also intensified the market's anxiety. Berkshire Hathaway has been reducing its holdings of Bank of America for 12 consecutive trading days since July 17. The Bank of America stocks in its holdings portfolio have decreased by 8.8%, and the total reduction amount has reached $3.8 billion.
The U.S. non-farm payroll data released at 8:30 p.m. Beijing time tonight showed that non-farm payrolls in July increased by 0.114 million, but this figure was far below the expected 0.175 million. The unemployment rate in the United States in July 2024 rose to 4.3%, setting a new high since October 2021 and higher than the previous 4.1%.
The rise in the unemployment rate to 4.3% means that the economic recession alarm of the Sam rule has been triggered, and this indicator has had 100% accuracy in predicting economic recessions since 1970. (According to the Sam rule, when the 3-month moving average of the unemployment rate rises by 0.5% or more compared to the lowest point in the previous 12 months, the U.S. economy will enter a recession).
Buffett's sale behavior above has also been interpreted by the market as a pessimistic expectation for the future of the U.S. economy. From the profit trend of bank stocks in history, high inflation and interest rates are good for bank stocks, but Buffett's choice to sell shares at this time indicates that he does not endorse the inflation narrative, and the Fed's upcoming interest rate cuts may be one of the logical reasons for Buffett's reduction of Bank of America stocks.$Bank of America (BAC.US)$Historical data provides us with valuable references. The period before and after the Fed cuts interest rates is often the beginning of a significant decline in U.S. stocks: from 1998, 2000, 2007 to 2019, the period before and after the Fed's interest rate cuts were accompanied by significant pullbacks in U.S. stocks.
Three months before the rate cut of October 1998, the S&P 500 fell 23%;
In the three months before the interest rate cut in December 2000, the chain reaction of the bursting of the Internet bubble began to appear, and the United States entered a 2.5-year economic recession, during which the S&P 500 fell by 50%;
One month after the interest rate cut in September 2007, the U.S. subprime mortgage crisis officially broke out, and the financial crisis swept the world, with the S&P 500 falling by as much as 58% in the following year and a half;
In October 2007, one month after the interest rate cut, the US subprime mortgage crisis officially erupted. The financial crisis swept the globe, and the S&P 500 fell by as much as -58% in the following year and a half.
During the first ten months of 2019 when affected by the Sino-US trade friction, the US stock plummeted in the fourth quarter of 2018, with the S&P 500 falling by 20%. However, six months after the rate cut, the 2020 Great Crash occurred.
Currently, the market generally expects the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates in September, "even if the US inflation rate rises again and the AI bubble causes a capital outflow of USD, the Federal Reserve will choose to cut interest rates to fill the gap of capital outflows".
III. Yen carry trade unwinding wave
The yen/dollar exchange rate rose 1% to 148.51 on Thursday. The yen/dollar exchange rate soared nearly 1.9% on Wednesday, expanding the monthly gain to more than 7%.
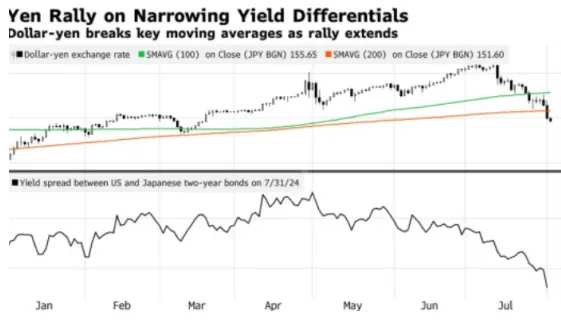
Strategists at Oriental Faith and DT Securities believe that the yen-dollar exchange rate could reach as high as 140 yen to the US dollar. The strategist at Macquarie also said, "the significant rise of the yen has just begun." By the end of this year, the USD/JPY rate could be close to 140, and it could reach 125 by December 2025. This will bring the yen exchange rate back to the level it was at the beginning of 2022 when the Federal Reserve had just started raising interest rates.
The rise of the yen against the US dollar led to a wave of arbitrage trading closures globally, pushing down currencies such as the Mexican peso, Australian dollar, and New Zealand dollar.
The so-called yen carry trade refers to investors borrowing low-interest yen and then investing in high-interest asset-based currencies such as US Treasury bonds to make a profit. However, as the US Federal Reserve continues to raise interest rates and US dollar liquidity tightens, the cost of borrowing US dollars has increased, while the locking-in cost of the yen against the US dollar has also increased. This means that the return on investment from the yen carry trade no longer matches the cost, causing many investors to unwind, that is, selling the previously invested assets and withdrawing funds.
This closing behavior has had a certain impact on the global financial market. First, high-yield assets such as US Treasuries face selling pressure, which puts upward pressure on US bond yields in the short term.
Second, due to the suspension of the carry trade, the buying power of US Treasury bonds has weakened, which may put pressure on global asset valuation and increase downward pressure on the stock and bond markets.
In addition, the suspension of the yen carry trade also means a reduction in short yen positions, which may have an impact on the yen exchange rate.
IV. Technical bear market test for Japanese stocks
Following a 2.49% drop on August 1, the Nikkei 225 index suffered a more than 5% intraday drop on August 2. Since the high-point correction in July, the Nikkei 225 index has fallen by nearly 6,000 points, with a maximum cumulative decline of close to 15%. If the Nikkei 225 index falls by more than 5% again, it will face a technical bear market test.
The trigger for this drop in the Japanese stock market was the Bank of Japan's introduction of a "rate hike + balance sheet contraction" combo. Although Japan's short-term interest rates have only been raised to 0.25%, the magnitude of this interest rate hike is not large. However, considering that Japan has long been in a state of negative interest rates, this "rate hike + balance sheet contraction" measure has had a greater impact on the market's risk preference for funds. This policy change, combined with the abnormally high yen appreciation, has led to capital outflows from the stock market, further fueling the decline of the Japanese stock market.
"The trend of the yen's appreciation and the stock market's decline may continue, inevitably affecting corporate performance," analysts pointed out. "There is an obvious reverse relationship between the yen and the Japanese stock market, that is, the continuous appreciation of the yen has caused a capital outflow effect on the Japanese stock market."
V. Summary
In this wave of decline, the declines in the Hong Kong and A-share markets are relatively small. Since October 2022, the US stock market has surged and the Chinese capital market has continued to fall. At present, it appears that this seesaw effect of funds may move in the opposite direction. China's real economy is performing well and the interest rate cut policy of the People's Bank of China has provided further support for the stock market. It is expected that in the process of global fund reallocation, the undervalued advantage of China's stock market will attract global capital attention.
Editor/Emily
