Source: CICC Commentary Author: Zhang Jundong, Fan Li, Zhang Wenlang With the expectation of a basic stable market and interest rate cuts in September [1], trading style has changed. After the June CPI and retail sales data were released, large-cap growth stocks led by AI concepts have clearly pulled back, while gold, small-cap stocks, and real estate, consumer, manufacturing, and bank-related stocks in the Dow have performed relatively well. The trading main line behind seems uncertain, and there has been a large discrepancy in the market's judgment on whether the US economy will have a "soft landing" or a "hard landing" after interest rate cuts. Is the market currently experiencing a short-term cut in style or a long-term change in style? We believe that with the basic expectation of interest rate cuts being largely fulfilled, the space for interest rate cut trading ("buying on expectations") may be significantly squeezed, while the "cyclical trading" after interest rate cuts is gaining momentum (see "All kinds of interest rate cut trading are the same, but the trading logic after interest rate cuts is different"). Unlike interest rate cut trading, cyclical trading mainly prices the recovery of terminal demand and the restart of the economic cycle after interest rate cutting. Its supporting logic is the resilience of US household demand, large fiscal and re-industrialization, and more deeply, the "realization from empty to real" of the total scale and structural resilience of the US economy. Under the support of total-scale resilience of the economy, the interest rate cut may be relatively limited (that is, a "shallow" interest rate cut), which is more beneficial to the real economy, especially profitable-supporting enterprises, and has a relatively limited boost to valuation. In terms of pace, Trump Trade 2.0 may accelerate the arrival of cyclical trading, given the increasing probability of Trump's recent election victory, stronger fiscal dominance (monetary coordination), industrial return, and potential weak US dollar in his policy ideology. At the same time, we also remind that due to the uncertainty caused by the election results, US stocks may enter a relatively high volatility period in the July-October of each election year; and after the uncertainty of the election dissipates, US stocks and bond rates often rise, and on average, value stocks perform better than growth stocks after the election (see "Major asset classes in US election years: seeking certainty in uncertainty").
In the second quarter of 2024, Hong Kong stocks experienced a strong rebound, with an increase of nearly 20% in one month. However, as the risk premium quickly repaired to a low level, the upward momentum slowed down, and it weakened again in late May, which is consistent with our judgment of the first stage goal of the Hang Seng Index of 19,000-20,000 points. Despite the market fluctuations, the Southbound capital has maintained a steady inflow trend since the beginning of the year, with only three days of net outflow in the second quarter. As an important participant in the Southbound capital, how are domestic public funds holding Hong Kong stocks and how has the industry allocation changed? We answer these questions by reviewing the Hong Kong stock holdings of public fund semi-annual reports.$Hang Seng Index (800000.HK)$Hong Kong stocks experienced a strong rebound in the second quarter of 2024, with an increase of nearly 20% in one month. However, as the risk premium quickly repaired to a low level, the upward momentum slowed down, and it weakened again in late May, which is consistent with our judgment of the first stage goal of the Hang Seng Index of 19,000-20,000 points.

As the Southbound capital has maintained its steady inflow trend since the beginning of the year, and with only three days of net outflow in the second quarter, we examine how the Southbound capital's domestic public mutual funds holdings in Hong Kong stocks have changed, including its industry allocation. This will be done by analyzing the public fund semi-annual reports.
Overall trend: public fund holdings in Hong Kong stocks increased to the highest since 2021, and the proportion of public funds to Southbound capital also increased.
The total size of investable public funds in Hong Kong stocks remained stable, with new fund sizes accelerating compared to the previous quarter. In general, as of the end of the second quarter of this year, there were a total of 3594 investable public funds in Hong Kong stocks (excluding QDII), with a total of 2.2 trillion yuan in assets. While the number of funds increased slightly compared to the first quarter, the scale slightly decreased by 4.1 billion yuan, accounting for 29.1% and 13.3% of the total number of 12,369 non-money market funds and the total scale of 17.9 trillion yuan, respectively. Among them, 1,980 are active equity funds (with a total scale of 1.45 trillion yuan), and the scale also decreased by 28.4 billion yuan compared with the first quarter. In terms of issuance, the number of investable public funds in Hong Kong stocks that were newly issued in the second quarter was the same as that in the first quarter, with an average of 35 new funds per month. However, the new scale increased significantly, reaching 63.1 billion yuan (compared to 39 new funds and 42.9 billion yuan in the first quarter). The same is true for active equity funds, with a steady issue rate of 21 per month in the first quarter and a new scale increase of 24.5 billion yuan (13.4 billion yuan in the first quarter).
Public funds held or actively increased their holdings in Hong Kong stocks, accounting for a slightly higher proportion of Southbound capital. Of the 3,594 public funds mentioned above, the market value of Hong Kong stocks held by the funds increased by 23.0% to 375.7 billion yuan from 305.5 billion yuan in the first quarter. Taking into account that the Hang Seng Index and the MSCI China Index increased by 7.1% and 5.8%, respectively, in the second quarter of this year, and the Hang Seng Technology only increased by 2.2%, it indicates that public funds may have active equity behavior. At present, the proportion of Hong Kong stock holdings is 24.1%, higher than the 19.0% in the first quarter. Looking further at the active equity fund, the market value of Hong Kong stocks they hold increased significantly from 222.6 billion yuan in the first quarter to 271.1 billion yuan in the second quarter (+21.8%), with holdings accounting for 21.7%, the highest since the end of 2021. However, the increase in the stock holdings of public funds in the Southbound capital stock exchange-traded funds is not as obvious, with an increase of only 0.4 percentage points from 13.6% to 14.0%, which also indicates that other types of investors (such as insurance funds) are equally enthusiastic about buying Hong Kong stocks.
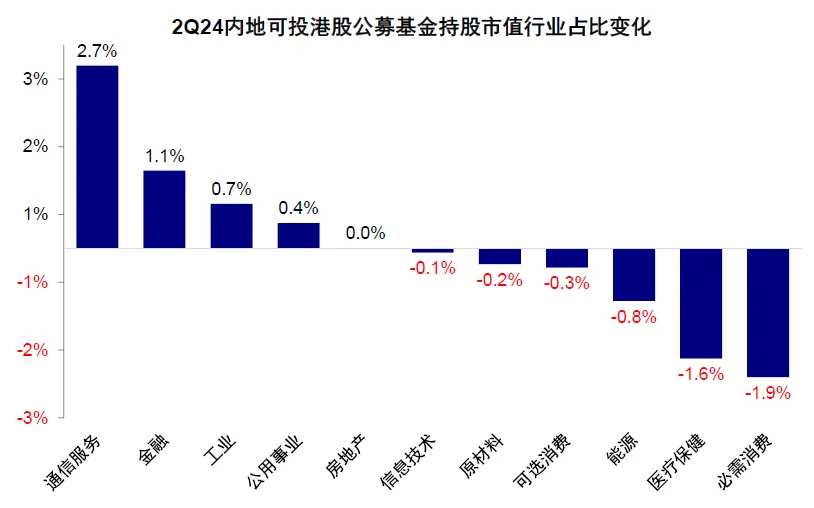
Industry allocation: holdings in new economy and high dividend shares increased, media and entertainment, banks and communication services increased the most, and biomedical, food and beverage, automotive and auto parts, and energy decreased significantly.
Media and entertainment, banks, and communication services have increased the most, while biomedical, food and beverage, automotive and auto parts, and energy have declined. Overall, the proportion of new economy holdings has decreased from 62.8% in the first quarter to 61.6%, while the proportion of old economy has increased to 40%, the highest since 2019. In terms of sub-industries, media and entertainment, banks, communication services, and technology hardware have seen the largest increase in holdings. Conversely, biomedical, food and beverage, automotive and auto parts, and energy have seen the largest decrease. Compared with their own historical levels, communication services, banks, transportation, and raw materials are already at historical highs, while biomedical, automotive and auto parts, real estate, and food and beverage are at historical lows.
At the individual stock level, holdings in new economy and high dividend shares increased, and Tencent and Meituan had the most heavily weighted positions. In the second quarter, mainland public funds continued to hold on to leading stocks.$TENCENT (00700.HK)$,$CNOOC (00883.HK)$,$MEITUAN-W (03690.HK)$with$CHINA MOBILE (00941.HK)$They continue to invest in leading companies. Similar to the first quarter of this year, the above-mentioned leading companies (Tencent, Meituan, CNOOC, and China Mobile) ranked the top four in terms of holding market value, while Li Auto Inc had the highest market value decrease. Xiaomi Group and$CHINA RES BEER (00291.HK)$,$YANKUANG ENERGY (01171.HK)$with$LI AUTO-W (02015.HK)$replaced Ideal Auto, and entered the top ten weighted stock ranks.$SMIC (00981.HK)$with$CCB (00939.HK)$Compared with the first quarter, holdings of Tencent, Meituan, and$CMOC (03993.HK)$And.$GIANT BIOGENE (02367.HK)$in the leading stocks
increased the most.$CGN POWER (01816.HK)$The number of funds holding Li Auto Inc. and CMOC Group Limited has decreased significantly, although the number of funds has increased. In addition, the concentration of top-heavy stocks has increased significantly. The top three heavy stocks account for 41.9% of the market value of the top 100 heavy stocks, an increase of 6.3 percentage points from the first quarter. The top 10 heavy stocks also increased from 53.5% in the first quarter to 58.0%. Prospect: The market is approaching the support level, and the Fed's interest rate cuts provide short-term resilience. However, domestic policy initiatives are still key to the trend. $GENSCRIPT BIO (01548.HK)$and $CMOC Group Limited (603993.SH)$In addition, the concentration of top-heavy stocks has increased significantly. The top three heavy stocks account for 41.9% of the market value of the top 100 heavy stocks, an increase of 6.3 percentage points from the first quarter. The top 10 heavy stocks also increased from 53.5% in the first quarter to 58.0%.
Prospect: The market is approaching the support level, and the Fed's interest rate cuts provide short-term resilience. However, domestic policy initiatives are still key to the trend.
After the strong and rapid rise of the Hong Kong stock market at the end of April, the rebound driven mainly by the recovery of the funds and risk preferences reached its end in late May, and has continued to decline in the past two months. The market's callback and the continued outflow of overseas funds have also confirmed our previous judgment that the main force behind the market's previous rebound was trading funds and some regional rebalancing funds, and the expected long-term value investment funds have not yet formed a trend of return. In the third quarter, driven by the expectation of a Fed interest rate cut, the Hong Kong stock market rebounded for a while, but this rebound failed to continue. Under the condition that the expectation of a interest rate cut did not change significantly, it weakened again, and the Hang Seng Index fell back to the key level of 17,000 points. This trend is consistent with our previous tips, that is, the impact of the Fed's interest rate cut to the Chinese market including AH is more through affecting domestic policies and then transmitting to the market. Therefore, skipping the intermediate links to look directly at the market's impact is not only meaningless, but may also cause misleading, such as the rapid decline of US bond yields in October last year and the Fed's interest rate cuts from July to September 2019, the Hong Kong stock market maintained weakness or even fell. From a short-term technical indicator perspective, the Hang Seng Index is close to the key support level of around 17,000 points. The risk premium rose to the highest level since late April, exceeding the historical average of 1.5 standard deviations, and the short selling ratio rose to the highest level since early April of 19%. Therefore, unless there are new unexpected events, we expect some support in the short term.
Looking forward, the Fed's "probable" interest rate cut in September will play a certain role in supporting the market, but the impact is indirect, such as opening up some domestic interest rate reduction space, supporting the denominator liquidity, and boosting some long-term board sectors (such as technology hardware, biotechnology, etc.). We estimate that if the yield on 10-year US Treasuries reaches 3.8%, the corresponding space for the Hang Seng Index is about 18,500-19,000. Therefore, the greater upward space still comes from domestic policies supporting the fundamentals, especially the speed and strength of fiscal policy efforts to counterbalance the downward private credit cycle. Since the beginning of the year, the pulse of fiscal deficit has obviously declined, partly explaining the weakness of demand and the market's callback since the second quarter. Recently, the central bank cut interest rates by 10bp[1] and arranged about 300 billion yuan of ultra-long-term special national bonds to support equipment updating and replacement [2], which are positive signals. We believe that the central bank's interest rate cut (financing cost) and fiscal policy (improving investment return rate and expectation) are both in the right direction and are undoubtedly positive, but in the context of weak short-term growth, the intensity and strength of policy stimulus still need to be strengthened. The Politburo meeting at the end of July emphasized that macro policies should "continue to exert force and be more powerful" and "firmly and unswervingly complete the annual economic and social development goals and tasks"[3], indicating that policies attach great importance to short-term growth pressure, and there is hope for more policy support in the short term. We believe that if policy efforts (we focus on the monthly changes of government financing and fiscal deficit pulses in social financing) are faster, the support will be provided. Based on various internal and external constraints, we expect policy to have support in the benchmark scenario, but the expectation of strong stimulus is still unrealistic, and more presents a state of "stabilizing leverage", so there is support at the bottom of the market, but more will still be a pattern of shock and structural market. At the configuration level, we still recommend investors to focus on three directions under the structural market: overall return decline (high dividends and high repurchases of stable returns, that is, "cash cows" with ample cash flow), partial leverage (especially related to the new quality production supported by the third plenary session policy and still vibrant technology growth), and partial price increase (natural monopoly sectors, upstream and public utilities). At the same time, we believe that the recent pullback in the dividend style does not mean that this factor has "gone out", but more due to the decline of the cycle and energy prices. In the background of no significant opening of the credit cycle and the downward expectation of long-term growth, providing stable returns to hedge the dividend factor of the downward return rate still has investment value.
From a short-term technical indicator perspective, the Hang Seng Index is close to the key support of around 17,000 points. The risk premium has risen to the highest level since late April, exceeding the historical average of 1.5 standard deviations, and the short selling ratio has risen to the highest level since early April, at 19%. Therefore, unless there are new unexpected events, we expect some support in the short term. Looking forward, the Fed's "probable" interest rate cut in September will play a certain role in supporting the market, but the impact is indirect, such as opening up some domestic interest rate reduction space, supporting the denominator liquidity, and boosting some long-term board sectors (such as technology hardware, biotechnology, etc.). We estimate that if the yield on 10-year US Treasuries reaches 3.8%, the corresponding space for the Hang Seng Index is about 18,500-19,000.
Based on various internal and external constraints, we expect policy to have support in the benchmark scenario, but the expectation of strong stimulus is still unrealistic, and more presents a state of "stabilizing leverage", so there is support at the bottom of the market, but more will still be a pattern of shock and structural market. At the configuration level, we still recommend investors to focus on three directions under the structural market: overall return decline (high dividends and high repurchases of stable returns, that is, "cash cows" with ample cash flow), partial leverage (especially related to the new quality production supported by the third plenary session policy and still vibrant technology growth), and partial price increase (natural monopoly sectors, upstream and public utilities). At the same time, we believe that the recent pullback in the dividend style does not mean that this factor has "gone out", but more due to the decline of the cycle and energy prices. In the background of no significant opening of the credit cycle and the downward expectation of long-term growth, providing stable returns to hedge the dividend factor of the downward return rate still has investment value.

Editor/new
