Source: Wall Street View, Author: Zhao Ying
If the improvement of the supply chain no longer drives the decline in inflation, the only downward pressure may come from economic recession. And if there is no recession, more patience will be needed to wait for inflation to return to 2%, which will take some time.
The "last mile" of anti-inflation is a long way to go, and the time required may exceed market expectations.
According to media reports on Wednesday, Randal Verbrugge, senior economist at the Cleveland branch of the Federal Reserve, said that due to the intrinsic characteristics of inflation, falling to the 2% target may take several years.
Verbrugge's model shows:
By the second quarter of 2025, the inflation rate will still be higher than the target, reaching 2.7%; by mid-2027, the inflation rate will be close to but still slightly higher than 2%.
When explaining why inflation's "last half-mile" is so stubborn, Verbrugge pointed out that there are three main forces driving inflation: economic recession, economic overheating, and supply chain pressure. In the absence of these external factors, inflation usually has persistent "intrinsic characteristics", and it will be slow to fall to 2% without external impetus.
"Since April 2023, inflation has been declining relatively quickly, but since inflation is still positive, most adjustments are also positive. The question is how much will it continue to rise?"
This Friday will announce the Federal Reserve's "most favored" core indicator-the core PCE indicator. The consistent prediction of top analysts reflected in blue chip economic indicators since this year is that the PCE inflation rate will be close to 2% in 2025, far earlier than Verbrugge's model prediction. However, Powell admitted earlier this month that it may take longer to bring the inflation rate down to 2%.
Verbrugge explained why companies may continue to raise prices when expected inflation declines:
The inherent sustainability of inflation is based on people's way of forming expectations for the future and the way prices are set in the economy.
Since April 2023, inflation has been declining relatively quickly, but since inflation is still positive, most adjustments are also positive. The question is how much will it continue to rise? Wages are one part of it, and if companies suddenly have to pay higher wages, it will reduce profit margins, and companies may try to raise prices to avoid squeezed profits.
Therefore, Verbrugge believes that unless there are external forces or unconventional internal forces to push, inflation will not quickly return to 2%, but will slowly fall back.
Historical experience has also proven that this is true, especially from 2012 to 2019, the trimmed mean of the PCE inflation rate for 12 months has only changed by half a percentage point, which took about six years. The trimmed mean is another way of observing core inflation rates, excluding the components with the fastest and slowest monthly growth.
Overall, Verbrugge's model implies that if the improvement of the supply chain no longer drives inflation down, the only downward pressure that can be brought is economic recession. And if there is no economic recession, then it takes at least three years for inflation to fall. In addition, Verbrugge added that economic recession will help companies decide. They can slowly raise prices or wages over time instead of raising them by 4% or 3.5% this year.
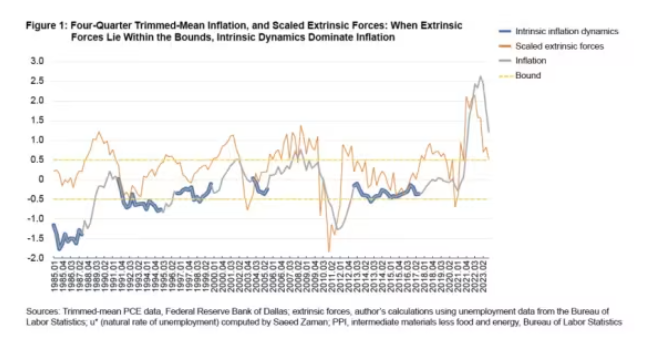
Overall, Verbrugge's model implies that if the improvement of the supply chain no longer drives inflation down, the only downward pressure that can be brought is economic recession. And if there is no economic recession, it will take patience to bring inflation down, which will take at least 3 years.
In addition, Verbrugge explained why companies may continue to raise prices when expected inflation declines: the inherent sustainability of inflation is based on people's way of forming expectations for the future and the way prices are set in the economy.
Editor/Lambor
