Source: Wall Street News
Japan's core inflation in April remained above the Bank of Japan's 2% inflation target. People are worried that the recent depreciation of the yen will increase cost-driven inflationary pressure in the future.
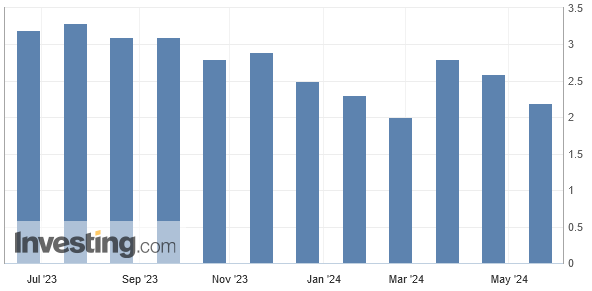
Japan's core inflation rate has cooled for the second month in a row, but remains above the Bank of Japan's 2% inflation target. The recent depreciation of the yen has heightened concerns that cost-driven inflationary pressure may continue.
On Friday, Japan's Ministry of Home Affairs announced the April price index, which is generally in line with expectations.
CPI rose 2.5% year on year in April, and is expected to rise 2.4%.
Core CPI rose 2.2% year on year in April, in line with market expectations.
In April, the CPI excluding fresh food and energy rose 2.4% year over year, in line with market expectations.
Among them, the core CPI has been declining for 2 consecutive months, but it remains above the Bank of Japan's 2% inflation target.
As the new fiscal year begins in April, many companies will take the opportunity to adjust prices for products and services. Japanese companies are increasingly having to weigh whether to raise prices in order to pass on the rising costs caused by the depreciation of the yen.
According to estimates by analysts at the NLI Research Institute, the impact of price adjustment measures on Japan's inflation rate is much smaller, and the impact on price increases is around 0.1%.
Some analysts believe that the current inflation data is unlikely to shake the Bank of Japan's determination to normalize policy. The Bank of Japan is confident of maintaining a virtuous wage-price cycle and steadily increasing inflation in the future.
Bank of Japan officials are also increasingly pointing out the risk of early interest rate hikes. Even after the Japanese government suspected two previous interventions to support the yen exchange rate, the yen exchange rate remained near a 34-year low.
Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda said on Thursday that the poor start of the Japanese economy this year will not take the central bank off the path of raising interest rates. So far, the pace of economic recovery is within expectations, and the overall situation has not changed.
The Bank of Japan has always emphasized that service sector prices are a key factor in interest rate policy considerations, and service prices rose 1.7% year on year in April, which is a slight decrease from 2.1% in March.
Although consumer spending is still lackluster, as real wages continue to fall, shoppers' spending tendencies have declined, and household spending has been falling for 13 consecutive months.
Japan's GDP contracted in the first quarter of this year, showing zero or negative growth for three consecutive quarters. The key factor affecting the contraction of GDP is personal expenditure. Japan's personal expenditure has declined for the fourth consecutive quarter.
Editor/jayden
