This article is selected from the Guoxin Securities Research Daily, author Wang Jilin, this article PE, PB and other stock data are A-share data.
Guoxin Securities published a research report and pointed out that in recent years, the business model of the securities industry has gradually changed (the process of "heavy capitalization"), which has catalyzed the differentiation of securities firms, while the heavy asset model has opened the door to differential competition in the industry. Capital is the cashing form of the final profit, while assets are the core, and the acquisition of assets is one of the profit breakthroughs under the heavy asset model. At present, China's securities industry is subject to the regulatory system, the suppression of business demand, the lack of institutional investors and derivatives and other factors, the capital intermediary business is still scarce, the leverage level is still low.
Under the main tone of strict supervision, Guoxin Securities believes that large securities firms have strong capital strength and comparative advantages in risk control capabilities and business resources. in addition, supervision guides securities companies to further enhance their market competitiveness. regulatory resources are gradually tilted to high-quality securities firms. From the perspective of the competition pattern, the industry concentration is expected to increase, and the leading securities firms still have a lot of room for growth. Individual stocksHuatai (06886) and CITIC (06030) are recommended.
The traditional business model is gradually changing
Guoxin Securities believes that the capitalization of the brokerage model is a field worth studying. Under the traditional and channel business model, the brokerage has a single profit model, high cyclical attributes and weak anti-risk ability. in recent years, the gradual change of the business model promoted by the internal and external environment has also catalyzed the differentiation of securities firms.
1. The process of re-capitalization of securities firms
According to the different ways of profit formation, Guoxin Securities divides the securities business into "light asset business" and "asset heavy business".Light asset business refers to the business that mainly relies on securities firm licenses to achieve profits, including brokerage business, investment banking business and asset management business; heavy asset business refers to businesses that rely more on balance sheet expansion to make profits, such as proprietary, market-making, direct investment and capital intermediary business, and the acquisition of assets depends on liability expansion (bond financing) and capital replenishment. The capitalization of the brokerage model has brought about the transformation of the profit model, and the capitalization has enhanced the operating leverage of the securities firm, but reduced the level of ROA.
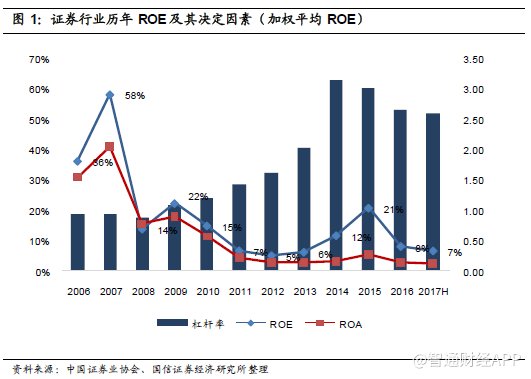
In the first half of 2017, the securities industry's ROE and leverage levels declined slightly, with ROE falling from 8.0% in 2016 to 6.5% (annualized), and leverage from 2.65 times to 2.59 times.
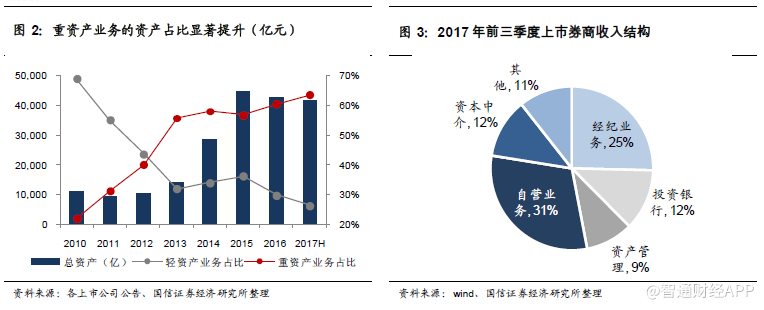
Capital intermediary business and investment business jointly drive the process of re-capitalization of securities firms.From 2010 to the first half of 2017, total assets of listed securities firms increased by 3.1 trillion, of which 72 per cent were driven by heavy asset business. Of the 3.1 trillion increase in total assets of listed securities firms during the statistical period, the brokerage business contributed only 300 billion, while the capital intermediary and investment business contributed 2.4 trillion. In other words, the brokerage business has contributed only 11% of the increase in the asset expansion of listed securities firms since 2010, while the asset-heavy business has contributed 78%.
The proportion of revenue from brokerage business has declined, and proprietary business has become the largest source of income.In the first three quarters of 2017, the income of listed securities brokers, investment banks, proprietors, capital intermediaries and asset management accounted for 25%, 12%, 31%, 12% and 9% respectively, and the investment income of proprietary business exceeded the income of brokerage business. Brokerages are putting a larger proportion of resources into proprietary business year by year, measuring the amount of resources occupied by proprietary business in terms of "proprietary fixed income securities / net assets", "proprietary equity securities and securities derivatives / net assets". The combined share of the two increased from 55% in 2008 to 115% and 114% in 2017H. Judging from the structural changes in recent years, the increase in the proportion of proprietary assets is mainly contributed by the increase in the proportion of fixed income bonds.

two。 Compared with the United States: its net worth is slightly higher than that of the United States, and its total assets are only 22.8%.
The leverage level of the domestic securities industry is still low. The balance sheet of the securities industry has expanded rapidly in recent years. The net asset volume of China's securities industry is similar to that of the United States. At the end of 2016, the net assets of domestic securities firms were 1.64 trillion, net capital was 1.47 trillion, and total assets were 5.79 trillion. The growth rate of the US securities industry has been relatively stable over the past decade. According to the current exchange rate (1 US dollar = 6.6 yuan), the net assets of the US securities industry at the end of 2016 are about 1.57 trillion yuan, with total assets of about 25.45 trillion yuan. The net asset volume of the domestic securities industry is at the same level as that of the United States, but the total asset size is only 22.8% of that of the United States. Subject to the regulatory system, the suppression of business demand, the lack of institutional investors and derivatives and other factors, the domestic securities industry capital intermediary business is still scarce, the leverage level is still low.

Compared with overseas investment banks, Charles Schwab Corp and Goldman Sachs Group are typical models of light assets and heavy assets respectively.
a. Charles Schwab Corp accumulates customers through low commission rate, pays attention to the accumulation of customer assets, and gradually transforms into a comprehensive wealth management platform for retail customers, which is essentially a light asset model. In 2016, Charles Schwab Corp's share of asset management, net interest income and brokerage income was 41 per cent, 44 per cent and 11 per cent respectively.
b. Goldman Sachs Group has long focused on institutions and high net worth clients, focusing on big market making, capital intermediation, investment banking and wealth management business, while the advantage of institutionalization lies in more stable business demand and more derivative business, which is essentially an asset model. In 2016, Goldman Sachs Group accounted for 20 per cent, 18 per cent, 10 per cent, 32 per cent, 10 per cent and 8 per cent of investment banking, asset management, commissions and fees, market-making, proprietary income and interest income respectively.

Charles Schwab Corp maintains a high level of profitability and a high level of ROE, reaching 55% in 2007 and stabilizing at more than 10% in recent years. Under the light asset model, it has strong profitability and enjoys a higher valuation level. In the past 10 years, the average PE of Charles Schwab Corp is 20-30 times, and the average PB is 2.5-4 times, which is higher than that of traditional investment banks such as Goldman Sachs Group and Morgan Stanley.
4. There is no lack of growth, but the leverage is still low.
From the perspective of profit model, the direction of the future transformation of the securities industry is similar to that of the banking industry, that is, through leverage, the development of capital intermediary business to earn interest spreads. Banks have natural deposit liabilities and earn spreads plus intermediary business income. Brokerages do not aim at customers' liabilities, but more asset-side management, earning more asset management fees, as well as service income such as providing trading channels and matching financial products. The business structure of the domestic securities industry has gradually changed, with a significant decline in the proportion of brokerage and investment banking business, from 68 per cent in 2011 to 42 per cent in the first half of 2017. in addition, capital intermediaries such as margin financing and stock pledge repurchase have developed rapidly. However, compared with the banking industry, the capital intermediary business of the domestic securities industry is still scarce, the income of spread is relatively low, and the leverage is still on the low side.
The level of leverage in the banking sector is about 15 times. In the golden period of 2005-2013, leverage has been more than 15 times, with the corresponding ROE at about 15%, while the ROE of listed banks is relatively high, stable at about 20%, and has fallen to about 15% in recent years. In the golden age of banking development from 2005 to 2013, after-tax profits rose from 253.3 billion in 2005 to nearly 1.8 trillion in 2013, a sixfold increase.

Compared with banks, there is no lack of growth in the domestic securities industry, the domestic securities market is not yet mature, and the asset securitization rate is on the low side. From the perspective of securitization rate and capital market volume, the domestic securities industry has broad growth space. In 2016, the securitization ratios (the ratio of total stock market capitalization to total GDP) in the US, Hong Kong, Japan and China were 147 per cent, 995 per cent, 100 per cent and 65 per cent respectively. Although the domestic securitization rate has increased rapidly since the 1990s, it is still on the low side compared with developed countries and regions.
The light asset model more reflects the "license value" of the business, while the heavy asset model more reflects the difference of capital strength and the choice of strategic direction of management.Guoxin Securities believes that the light asset business itself is easy to form a price war, the core of differentiation lies in the customer scale base and customer stickiness, while the heavy asset model has opened the door of industry differentiation competition. Capital is the cashing form of final profit, while assets are the core, and the acquisition of assets is one of the profit breakthroughs under the heavy asset model.
Business trend: acceleration of market-oriented transformation
1. Brokerage business: re-mining customer value and paying attention to cost advantage
Guoxin Securities believes that according to the commercial law, the price competition of homogenized business is inevitable, and the continuous reduction of commission rate also forces the industry to think about transformation, especially in the current stage when the characteristics of the "stock market" are more obvious. the re-exploration of customer value has become the core proposition of transformation.
When the market is weak, the power of commission war is insufficient, the downward trend of commission rate slows down, and the cost advantage of brokerage business should be paid attention to.The average daily stock-based turnover in the first three quarters of 2017 was 499.1 billion, down 12 per cent from 567.1 billion in 2016. The commission rate declined slightly in 2017, with the industry average commission rate of 3.4 per 10,000 in the first half of the year, compared with 0.4 per 10,000 at the end of 2016. When the market transaction is in the doldrums, the brokerages'"volume" momentum is insufficient after the commission reduction, so the commission war slows down. From the current profit margin of securities brokerage business, the current market commission rate is still far from the cost line, in the homogenization competition, price war is inevitable, Guoxin Securities believes that the cost advantage of securities firms is worth paying attention to.

The cost level of brokerage business is more important than the commission rate.In the process of market-oriented competition, securities firms with cost advantages will support companies to expand their customer base with price advantages, and have more leisurely space for intensive cultivation. Guoxin Securities constructs a "cost index" to reflect the brokerage business costs of various brokerages, expressed as "(brokerage business expenses + brokerage fees and commission expenses) / transaction volume" (2017H1). Among them, Oriental Fortune, Huatai and Guojin Securities have the lowest cost index of 1.84,2.80,3.03 respectively (Oriental Fortune Securities does not separately publish the cost information of brokerage business. Guoxin Securities is replaced by the full cost of Oriental Wealth Securities, and the three companies are all companies with characteristics in the application of Internet technology. Guoxin Securities believes that the commission rate is naturally suitable for price war, the operating costs of brokerage business are not the same, cost control is easier to reflect the operational skills of securities firms, and more sustainable.
Although the profit space at the commission end is compressed, the brokerage business is still the most "natural" contact with clients, with "import value". The "profit center" attribute of brokerage business may be weakened, and more reflect the "customer center", cut into interest income, asset management income and other value-added services, this is one of the future industry trends.

Charles Schwab Corp embodies this direction of transformation. Schwab has cultivated a number of sticky clients with a low commission strategy, and grasped their investment preferences through transaction information. After launching the asset management business, various financial products and one-to-one financial consultant consulting services have smoothly increased customer stickiness, and the focus of income has also shifted to the commission income obtained by providing value-added investment services for customers. Today, asset management fee income has replaced the traditional commission income (figure 7) to become Charles Schwab Corp's highest proportion of business income. In addition, brokerage business drives the growth of interest income, and the first three drivers of interest income growth are assets held to maturity, financial assets available for sale, and assets related to brokerage business. Charles Schwab Corp is essentially a light asset model and enjoys a higher valuation than traditional overseas investment banks.
two。 Proprietary business: earnings volatility increases under IFRS9
In March 2017, after the announcement of IFRS9, the Ministry of Finance revised the accounting standards related to financial instruments. According to the requirements of the Ministry of Finance, H-share listed companies and "A shares" listed companies need to implement the new standards from January 1, 2018, while other A-share listed companies will be implemented on January 1, 2019.
IFRS9 (2014) IFRS 9-Financial Instruments classifies financial assets into three categories around the business model of contractual cash flow and assets: (1) financial assets measured at fair value and their changes are included in current profits and losses (FVTPL); (2) financial assets measured at fair value and their changes are included in other comprehensive income (FVTOCI); and (3) financial assets measured according to the amortized cost method (AC). In IFRS9 (2014), financial assets within the scope of IFRS9 (2014) are classified mainly according to three conditions with logical order.

The four categories of financial assets under the IAS39 criterion should be transformed into the three categories under IFRS9. Under the assumption that the purpose and intention of the company holding assets remain unchanged, Guoxin Securities is the most likely to correspond. A more specific corresponding result needs to be judged in combination with the logical conditions in the above figure, and adjusted to the final most likely situation, as shown in the following figure:

Guoxin Securities believes that the impact of the new standards on securities firms will be mainly reflected in the following points:
(1) the volatility of performance increases.If equity available-for-sale financial assets are reclassified as "assets measured at fair value and the changes are included in the profits and losses of the current period" (FVTPL), changes in fair value and dividends are recognized as profits and losses of the current period, and the performance volatility increases.
(2) the maneuverability of earnings management through AFS is reduced.Available-for-sale financial assets are the most "fuzzy" range in IAS39, which has become a safe haven for companies to cushion profits. Under the original IAS39 criteria, there are many kinds of financial assets available for sale, including bonds, funds, stocks, securities company financial products, bank financial products, trust plans and so on. However, the subject of available-for-sale financial assets has been abolished under IFRS9, and the classification is clearer.
(3) the division of FVTOCI subjects is more cautious.If non-transactional equity instruments are classified as FVTOCI, changes in fair value are included in other comprehensive income, and other comprehensive income arising from changes in fair value cannot be transferred to current profits or losses even if financial assets are transferred, and asset impairment losses are not included in current profits or losses. The treatment of this kind of financial assets is the most different from the available-for-sale financial assets (equity category) in IAS39. No matter whether the fluctuation of fair value is positive or negative, it will no longer affect the profit, and it will not be transferred to profit when it is sold, but directly into retained earnings, which will reduce the fluctuation of profit and, of course, reduce the opportunity of using such financial assets for earnings management; if debt instruments are classified as FVTOCI, changes in fair value will be included in other comprehensive income and may be included in the current profit or loss at the time of termination of recognition.
(4) another significant change of the old and new criteria is that the impairment method of financial assets has changed from the previous "incurred loss model" to the "expected loss model", which may increase the amount of loss reserve.The concept of impairment of financial assets is more aimed at AC and FVTOCI. For AC, the accounting is basically the same; for FVTOCI (creditor's rights), the expected profit and loss is included in the current profit and loss, which is not much different from the original IAS39; for FVTOCI (equity) impairment loss can not be included in the current profit and loss, while the original IAS39 available-for-sale equity impairment loss is included in the current profit and loss, which changes greatly.
In the short term, as the new IFRS9 (2014) will have to be implemented by the listed brokerages on January 1, 2018, if the available-for-sale financial assets are not sold, the previous buoyancy will not be reflected in the income statement, so some of the AFS will float or be cashed at the end of the year.
3. Investment banking: refinancing and bond underwriting are expected to pick up.
The overall release speed of IPO accelerated in 2017, with 30-40 monthly IPO batches. Although the recent review is more stringent and the number will be reduced, the regulators only strictly check. In the context of increasing the proportion of direct financing, the approval speed may slow down in the future, but it is expected that the overall high-speed issuance situation of IPO will not be changed.
Under the influence of the new rules on refinancing at the beginning of the year, the new rules on the reduction of holdings in May and the prudent supervision of mergers and acquisitions, the scale of equity refinancing has declined sharply. at present, the effect of encouraging funds to "get out of the void into reality" through strict supervision has initially appeared. and recently, the CSRC has repeatedly stated that "M & A has become an important way for the capital market to support the development of the real economy", encourage the increase in the proportion of direct financing, and the scale of refinancing is expected to pick up gradually in 2018.

Under the influence of rising interest rates and strict supervision of real estate financing, the scale of corporate bond and corporate bond underwriting fell sharply in 2017. However, since the third quarter, the scale of corporate bond and corporate bond underwriting has stabilized and rebounded. Under the background that interest rates will not rise quickly and substantially, the rebound in bond underwriting in 2018 is expected to continue.

4. Asset Management Business: active Management is the Future Direction
In the first half of 2017, regulators conveyed a strict regulatory attitude on channel business and capital pool business. In fact, last year's regulatory documents also passed on strict supervision of channel business, non-standard, and capital pool business, including eight bottom lines and an overall increase in the proportion of venture capital provisions required for directional channel business in the risk control index management measures of securities companies. At present, the effect of active management transformation is beginning to bear fruit. The scale of channel business has declined for two consecutive quarters, falling by 600 billion in the second quarter and 700 billion in the third quarter.
On November 17, 2017, the central bank, CBRC, CSRC, CIRC and safe jointly issued the guidance on standardizing the Asset Management Business of Financial institutions (draft for soliciting opinions), which formulated unified regulatory standards for asset management products and maximized the elimination of regulatory arbitrage space. The impact on the asset management of securities firms is mainly reflected in:
(1) the fund pool business is explicitly prohibited.Since May, regulators have inspected the capital pool business, requiring securities firms to carry out rectification and reform, requiring that they are not allowed to be added, and the scale has gradually decreased. At present, the management of securities firms has gradually adapted to the new regulatory regulations.
(2) for multi-layer nesting and channels:It is clear that asset management products can invest in one layer of asset management products, and the invested asset management products shall not invest in other asset management products (except investment public securities investment funds). It also requires financial institutions not to provide access services for the asset management products of other financial institutions to evade the regulatory requirements such as investment scope and leverage constraints. The general direction of securities firms' asset management in the future is the transformation of active management. under this regulatory background, the scale of channel business is expected to gradually decrease.
(3) to break the rigid payment of asset management products:It requires the transformation of asset management products to net value. At present, most of the asset management products are still expected income products, and the specific implementation rules have not yet been issued, but they will promote the transformation of expected income products to net products and truly achieve "sellers' due diligence and buyers' responsibility". It is in line with the original intention of returning to the origin of the asset management business.
(4) for the level of leverage:The debt ratio (total assets / net assets) of public offerings and private offerings shall be capped at 140% and 200% respectively; in addition, for scalable private offerings, the classification ratio of fixed income, equity, commodities and financial derivatives and mixed products shall not exceed 3, 1 and 2 times, respectively.
The new regulatory regulations, the overall rise in the proportion of venture capital reserves, and classified evaluation indicators all restrict the channel business.It is expected that the size of the channel business will still shrink in 2018. In the long run, it is a general trend for asset management to return to the origin of active management, which is conducive to business development in the long run.
4. Capital intermediary business: the two financial institutions fluctuate with the market, and stock pledge repurchase continues to grow.
The business of financing and financing is greatly affected by the market, and the scale of the business fluctuates with the market. The highest level of the bull market in 2015 was 2.27 trillion. In the third quarter, the overall market risk appetite and the balance of financing increased.
The periodicity of the stock pledge repurchase market is weaker than that of the two financial services. since the stock pledge repurchase pilot project in 2013, the business has gradually matured, and the scale growth is relatively stable. In September, the Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange jointly issued the "Stock Pledge repo Trading and Registration and settlement Business measures (2017 draft)" to amend the stock pledge repo trading rules and guide "getting rid of the emptiness into reality". To modify the use of funds and the upper limit of stock pledge rate. The new regulations further strengthen risk management and standardize business operation, and the negative impact is expected to be limited. Stock pledge repurchase business, as one of the cash flow control channels of listed companies, is still rising, and the scale is expected to continue to grow.
The leading effect appears.
1. Regulatory resources tend to high-quality securities firms
Under the main tone of strict supervision, large securities firms have strong capital strength and comparative advantages in risk control ability and business resources.Since the beginning of this year, regulators have expressed a strong regulatory attitude towards channel business and capital pool business. on the one hand, regulators have reiterated that they must not carry out or participate in asset management business with the nature of capital pools, and strictly control the scale of products, which should decline month by month. On the other hand, securities fund management institutions engaged in asset management business should adhere to the origin, prudently and diligently perform the duties of managers, there should be no channel business to transfer management responsibilities, and the scale of the channel should be gradually reduced. In November 2017, the draft for soliciting opinions on the new regulations on asset management was launched to unify the regulatory standards for similar asset management products. With the tightening of supervision, the differences between securities firms in risk control, business and performance are gradually widening.
Regulatory resources tend to high-quality securities firms.In July 2017, the CSRC revised the classification and rating measures for securities companies to pay more attention to capital adequacy indicators and comprehensive risk management, and the net capital bonus standard was raised from 1 billion to 2 billion. In addition, the indicators such as compliance, risk control and market competitiveness are strengthened in addition and minus points, and the evaluation indicators are skewed towards quality, such as introducing the average brokerage income ranking of the business department, paying attention to the active management scale and the quality of underwriting projects, and guiding securities companies to further enhance their market competitiveness.
In 2017, major securities firms fully returned to double A ratings, with improvements in business operation, risk control indicators and protection fund contributions. (1) the business operation is linked to the classification of securities firms, which is conducive to the development of high-quality securities firms.For example, in mid-June 2017, the CSSA issued a decision on revising the measures for the Administration of Securities issuance and underwriting to various securities firms, stipulating that the qualification of underwriters of corporate creditors should be linked to the results of classified ratings (in the last two years, the rating is above A for at least one year), and the underwriting qualification of corporate creditors of non-Category A brokers is linked to the industry ranking of the amount of corporate bonds underwritten (top 20). In addition, in September 2017, the Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges issued the measures for Stock Pledge repo Trading and Registration and settlement (draft for soliciting opinions in 2017), which stipulates that securities companies should link pledge business with classified evaluation (the financing balance of self-owned funds of category A, B and C securities companies shall not exceed 150%, 100% and 50% of the company's net capital, respectively). (2) the CSRC directly applies the classified evaluation results, and the calculation proportion of venture capital of securities companies with different ratings is different; (3) according to the classified rating results of securities companies, the China Securities Investor Protection Fund Company pays the fund according to 0.5% of its operating income, the lower the rating, the higher the proportion of the company's contribution.
two。 Industry concentration is expected to increase
In the previous pure channel business-based model, the differentiation between securities firms is difficult to reflect, and the price competition is fierce. In 2017, the commission rate and transaction volume showed a downward trend, and the proportion of brokerage income decreased further. Large securities firms have advantages in investment banking business, asset management business and credit business, and their business is more balanced, which makes their performance have more comparative advantages. Judging from the performance in the first three quarters, the performance of large securities firms as a whole is better than that of small ones.

Large securities firms have advantages in investment banking business, asset management business and credit business, which makes their performance have more comparative advantages.
a. In terms of investment banking business, under the strict regulatory environment, large securities firms have more advantages in dealing with policy adjustments and compliance risk control.The concentration of the industry has increased, and in terms of the scale of equity financing, the market share of the top 10 in the industry has increased from 48% in 2015 to 68% now. In September 2017, the CSRC issued the guidelines on Internal Control of Investment Banking Business of Securities companies (draft for soliciting opinions). In view of the common requirements for internal control of investment banking business in the industry, such as "emphasizing development, neglecting quality", "emphasizing scale and neglecting risk", high-quality securities firms that focus on project quality and risk control will be more competitive after the introduction of internal control guidelines for investment banks.

b. In terms of asset management business, the active management ability of large securities firms is outstanding.According to the Securities Investment Fund Industry Association, the top 20 listed securities firms with monthly average assets under management at the end of the second quarter include Citic, Guojun, Huatai, Shen Wanhongyuan, Everbright, Orient, China Merchants and Yangtze River. the average monthly asset management scale of other securities firms is in the top 20, of which Everbright, Guojun and CITIC account for more than 30%. The return of asset management to the origin of active management is a long-term trend, and the active management ability of large securities firms is in the lead, which is conducive to the development of their business.

c. In terms of credit business, large securities firms have strong comparative advantages in terms of capital strength and debt channels.At present, the financing interest rate of margin trading business is basically around 8%, while in the domestic high interest rate environment, financing costs rise and interest spreads decline, while securities firms with advantages in debt channels will benefit more.
Since 2016, the industry has entered a new regulatory cycle and channel dividends have been weakened. in this environment, large securities firms with clear strategic positioning, sufficient capital strength and balanced business layout are showing their advantages. In addition, supervision guides securities companies to further enhance their market competitiveness, and regulatory resources are gradually tilted to high-quality securities firms. From the perspective of the competition pattern, the industry concentration is expected to increase, and the leading securities firms still have a lot of room for growth.
Focus on investment opportunities under marginal improvement
1. It is predicted that 2018 will be the turning point of profit
Under the neutral assumption of wide volatility in the market, the core indicators are assumed: 1) the average daily stock-based turnover of the market is 520 billion, and the average commission rate is 3.2 / 10,000; 2) the financing size of IPO is 220 billion, the size of equity refinancing is 1.2 trillion, and the scale of bond underwriting is 4.2 trillion; 3) the average daily balance of margin trading is 1.1 trillion.
Under the neutral assumption, performance is expected to grow by 5 per cent year-on-year in 2018, corresponding to a ROE of 6.5 per cent and 7 per cent. Market trading sentiment is expected to improve, but the commission rate is expected to decline slightly, and brokerage revenue is expected to decline 7% in 2018 compared with the same period last year; thanks to the increase in the proportion of direct financing, the scale of stock and bond underwriting is expected to increase, and investment banking revenue is expected to increase by 29% compared with the same period last year; for capital intermediary business, the scale of financing and financing fluctuates with the market, the scale of stock pledge repurchase continues to grow, and capital intermediary business is expected to grow by 12% year on year. It is expected that the growth rates of asset management business and proprietary business are-15% and 10% respectively.

two。 The risk-return ratio of the plate increases
Financial deleveraging into the second half, the maximum marginal pressure has passed. Since the second half of 2016, a number of policies of "one bank and three meetings" have enabled investors to be pessimistic about the securities sector, including the "new eight bottom lines" issued by the Securities Regulatory Commission, the draft for soliciting opinions on the new financial management rules of the CBRC, and the new rules on capital management of the central bank. In 2017, under the principle of "legal supervision, strict supervision and comprehensive supervision", the supervision system of the business chain of the securities industry has been gradually improved, and the risk control and governance capabilities of securities firms have been greatly improved. At present, strong regulatory sentiment has been fully expected by the market, the marginal impact of follow-up policies on the market is expected to weaken.
At present, the industry ROE is at the pre-bull market level. The current ROE is 6.52%. The industry ROE is between 5% and 8% in the first half of 2011-2014; the current industry leverage is 2.59 times, and the industry leverage is between 1.4-2.2 times in the first half of 2011-2014. Industry leverage has increased, but leveraged funds are mainly invested in capital intermediary business and proprietary business. On the whole, capital intermediary assets have the characteristics of good liquidity, low risk, sufficient guarantee ratio and small risk exposure; in addition, in terms of proprietary business, most securities firms have achieved positive comprehensive investment returns (including investment income, fair value changes in profit and loss, and other comprehensive income), indicating that the investment style of securities firms is sound and their risk exposure is controllable.

On the recommendation of individual stocks, recommend Huatai (showing the cost advantage of brokerage business, accelerating the transformation of wealth management, and replenishing capital), CITIC (the capital strength ranks first in the industry, the sustained development of international business, the obvious advantage in the layout of institutional business, and the leading ability of comprehensive financial services). (editor: Jiang Yu)
