Looking ahead to this year at the end of last year, many investors in the market think that under the forecast of a US recession in 2023, US stocks will be under pressure due to weakening fundamentals.
However, judging from the actual performance of US stocks, the S&P 500 rose 15.9% cumulatively in the first half of this year, and the NASDAQ rose as high as 31.7%, recording the best performance in the first half of nearly 40 years.
In a context of interest rate hikes, high inflation, and geopolitical tension, US stock hedge funds are shorting US stocks. US stocks soared, and the performance of local US hedge funds was poor. The overall yield of US hedge funds in the first half of this year was 3.45%, far outperforming major stock indexes.
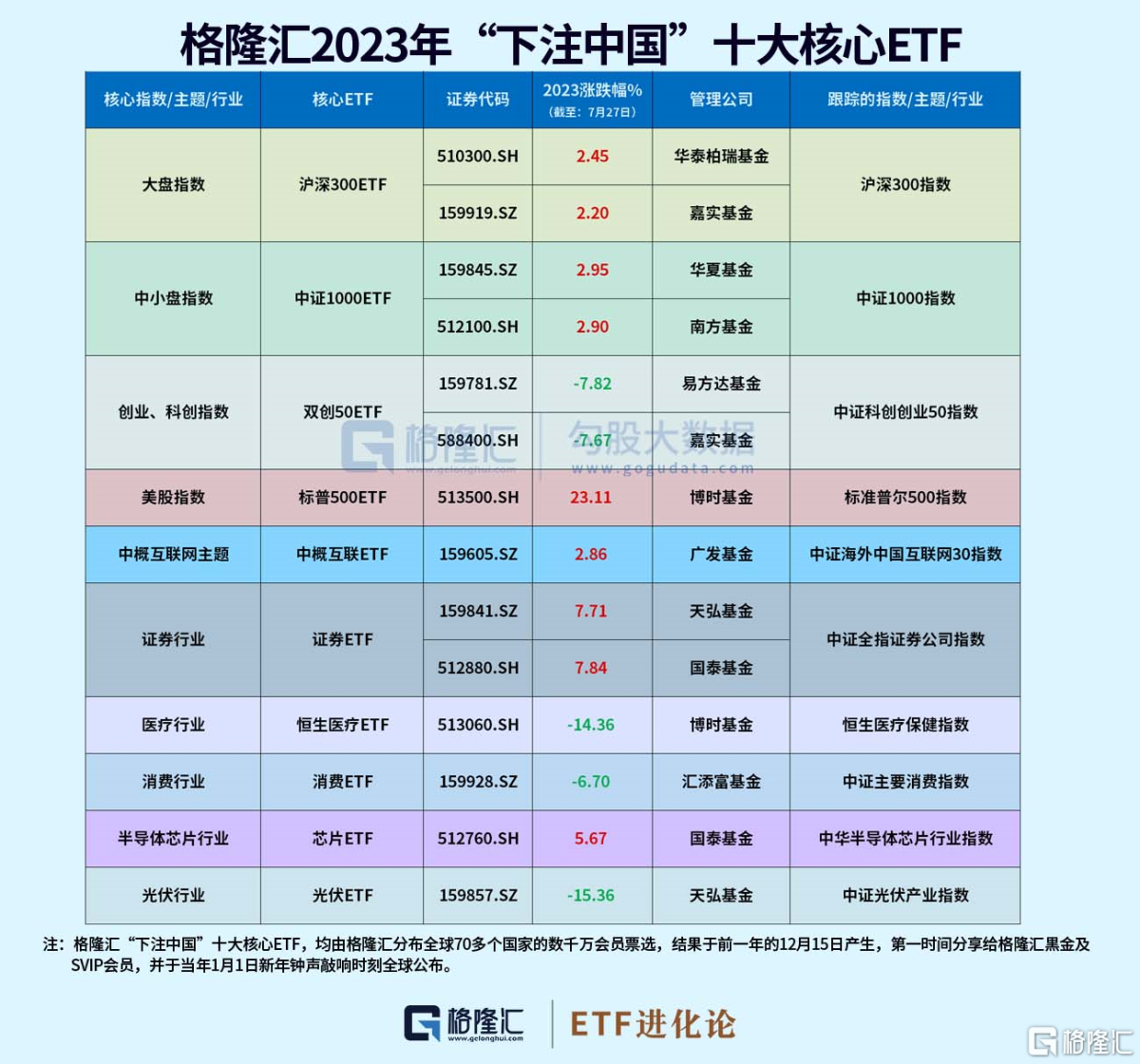
 In the A-share market, ETFs that track the NASDAQ index and the S&P 500 index have become “beautiful boys” this year.As of July 27, the “top ten core ETFs” have had an average increase of 0.41% since this year, and the S&P 500 is far ahead with an increase of 23.11%.
In the A-share market, ETFs that track the NASDAQ index and the S&P 500 index have become “beautiful boys” this year.As of July 27, the “top ten core ETFs” have had an average increase of 0.41% since this year, and the S&P 500 is far ahead with an increase of 23.11%.
Looking at the macro level, the current macro-micro fundamentals of US stocks are unspeakably strong, and the supporting effect on the rise in the stock market is not obvious. At the macro level, the good employment data in the US this year made some investors think that the current US economy is still strong. Judging from various economic indicators, the US may have now entered a “structural recession.”
According to data tracked by Haitong Securities, when discerning whether the US economy has fallen into recession, the market currently mostly refers to the economic cycle defined by the US Bureau of Economic Research (NBER). Unlike simply judging the strength or weakness of the economy through GDP trends, the US Bureau of Economic Research weighs a series of actual economic activities. The reference indicators include six items, including the number of households employed, non-farm employment, personal income, personal consumption, manufacturing and trade sales, and industrial production. The current trend decline in the indicators described above defines the US economy as a recession.
At present, some US economic indicators have shown obvious signs of weakening. For example, in April 2023, the growth rate of US manufacturing and trade sales fell to 0.3%, in the historical ranking of low to 21% since 2000. In May, the growth rate of industrial output fell to 0.2%, at the 31% historical level. Furthermore, the growth rate of US personal consumption and personal income indicators in May was also at a low level in history. Looking at all disaggregated data, the NBER composite index has now fallen to 1.4% year on year, and is only in the historical ranking of 34% since 2000.
In the segment of personal consumption in the US, service consumption is currently still clearly recovering, while the scale of commodity consumption has continued to level off over the past few months. From a micro perspective, the S&P 500 EPS in the first quarter of this year was still negative year on year. According to S&P expectations, the second quarter may continue the negative year-on-year growth trend, that is, the micro profits of US listed companies also did not provide significant support for stock market performance.
The rise in US stocks this year was mainly driven by valuations, stemming from a recovery in risk appetite. Currently, the supporting factors from fundamentals in the US stock market are not strong. Looking at the valuation dimension of US stocks, the PE (TTM) of the S&P 500 has risen 19.2% from 18.1 times at the beginning of the year to 21.6 times now. By splitting the valuation profit contribution of rising US stocks, it can be seen that the rise in US stocks this year is mainly driven by the valuation side. The S&P 500 rose 15.9% in the first half of the year, and the increase in valuation contributions was about 22%. Instead, the profit side contributed a negative contribution.
Since the increase in stock market valuations may be due to a decline in risk-free interest rates, it may also be due to a decrease in risk premiums due to sentiment recovery.
Starting from the liquidity dimension, the US macro-liquidity background is still tight this year. The Federal Reserve continued to raise policy interest rates to 5% to 5.25% in the first half of the year, compared to only 4.25% to 4.5% at the end of last year.
On July 26, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 25 basis points as scheduled, raising the target range of the federal funds rate to 5.25% to 5.50%, the highest since January 2001. The Federal Reserve has raised interest rates 11 times, with a cumulative increase of 525 basis points. The FOMC statement shows that economic activity is expanding at a moderate pace; employment growth is strong, and the unemployment rate remains low. Federal Reserve Chairman Powell said at the press conference that future interest rate hikes will still depend on data. It is possible that interest rates will be raised or not raised in September; the Federal Reserve did not decide to raise interest rates every other meeting. Interest rates will not be cut this year. Some FOMC members say they expect interest rates to be cut next year. Powell believes inflation can be reduced without significant damage to the economy; Fed staff no longer predict a recession this year. The inflation rate is not expected to fall back to 2% until around 2025.
The continued rise in benchmark interest rates and market expectations have made the current interest rate on US bonds remain high. The overall interest rate on US bonds has remained high in the 3.3% to 4.1% range for 10 years from the beginning of the year. It can be seen from this that the probability of liquidity is not the main driving force for raising the valuation of US stocks; that is, the valuation repair of US stocks may mainly come from a recovery in risk appetite.
In fact, if we use the risk premium ratio index to describe the risk appetite of US stocks, we can see that the risk premium rate of the S&P 500 has continued to decline since this year. Currently, it is only 0.83%, which has reached a new low since 2010. It can be seen that the sentiment in the US stock market has clearly recovered this year, which in turn has become the main factor driving the rise in the market.
Structurally, from an industry perspective, the rise in US stocks this year was actually mainly contributed by the technology industry. Seven major technology companies have contributed 70% of the increase in US stocks since this year. The seven companies are: Apple, Microsoft, Nvidia, Amazon, Meta, Alphabet, and Tesla.
Although the S&P 500 rose as high as 17.5% this year, the overall increase in the remaining components of the S&P 500 after excluding all technology stocks was only 2.1%. It can be seen that there is a clear differentiation between the US stock technology industry and other industries this year.
The current round of strengthening of the US stock technology industry is mainly due to the superposition of the US technology innovation cycle and profit expectations. In terms of the technology cycle, the rise of ChatGPT since the end of last year has triggered a new wave of technology led by artificial intelligence. At the same time, the huge user base of US artificial intelligence companies and innovation in paid business models have rapidly stimulated investment activity in the capital market.
Judging from profit expectations, the market's fundamental expectations for US technology stocks are clearly picking up. Bloomberg data shows that the market's EPS expectations for the Nasdaq index in 2023 have been revised from the annual low of 437.9 US dollars/share to the current 460.1 dollars/share. In contrast, profit expectations for the S&P 500 have continued to decline.
From the perspective of individual stocks, technology leaders contributed most of the gains in the US stock index. Seven leading tech stocks, including Nvidia, Meta, Tesla, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, and Google, have all performed very strongly since this year (up to 2023/7/21). The first three have risen by 203.2%, 144.5%, and 111.1% respectively. Google also had the lowest increase of 36.1%, and the total market value of these companies in the S&P 500 component is as high as 30.8%. These high-weight technology stocks contributed most of the rise in the US stock index. For example, Nvidia's stock contributed a 2.8% increase in the S&P 500 index this year. The seven leading technology stocks mentioned above contributed a cumulative increase of 12.8% points, accounting for 73.2% of the overall increase of the S&P 500. If we compare all US stocks horizontally, we can find that out of all 6,209 US stock companies (excluding OTC), 39% of individual stocks have recorded a decline since the beginning of the year, and 61% of individual stocks have risen. Of these, only 29% of individual stocks have risen above the S&P 500; judging from the overall performance of the US stock market, the simple arithmetic average of all individual stock increases is 10.4%, and the median is only 4.0%, that is, the overall performance of US stocks is clearly inferior to the broad-based index.
The Haitong Research Institute further counted the differences in the rise and fall rates of individual stocks in various market capitalization ranges and found that the largest market capitalization leaders with a market capitalization of more than 200 billion US dollars rose the most clearly, with an average increase of 27.1%. These large market capitalization leaders accounted for 39.9% of the total market capitalization market capitalization in the total market capitalization.
In summary, the overall performance of the US stock market this year has actually not been as strong as the broad-based index. Behind the overall rise in the market market is a clear rise in a few technology stocks and leading stocks.
From a performance perspective, as of July 27, Tesla, Microsoft, and Alphabet of the seven tech giants mentioned above announced their financial data for the 2nd quarter.
US tech giants Microsoft and Google's parent company Alphabet announced results for the second quarter of natural year 2023. Microsoft's financial report shows that in the three months ending June 30 this year, revenue reached 56.189 billion US dollars, up 8% year on year, higher than market expectations but lower than 12% of the same period last year; operating profit increased 18% year on year to 24.254 billion US dollars; net profit increased 20% year on year to 20.081 billion US dollars; and the current quarter's capital expenditure that the market is concerned about reached 8.94 billion US dollars, higher than market expectations. Among them, Windows operating system revenue fell 12% year over year; Surface hardware device revenue fell 20% year over year.
Compared to Microsoft, Google performed slightly better. Alphabet's second-quarter revenue was US$74.64 billion, up 7% year over year, higher than market expectations; operating profit was US$21,838 billion, up 12.3% year over year; of these, Google's total service revenue increased about 5.5% year over year, and Google search revenue increased about 4.8%.
On July 20, Tesla released financial results for the second quarter of 2023. According to the data, Tesla's revenue for the second quarter of this year was 24.927 billion US dollars, up 47% year on year, reaching a new high; net profit was 2,703 billion US dollars, up 20% year on year, higher than market expectations.
Meanwhile, at the second-quarter results briefing, Tesla CEO Elon Musk announced the latest developments in the much-publicized Tesla humanoid robot Optimus.Musk said that Tesla has produced 10 humanoid robots. The walking test is expected to be carried out in November this year, and the utility test is planned to be carried out at the Tesla factory next year.
Regarding the next market for US stocks, Anxin Securities believes that overall, interest rate hikes are nearing the end, and the market is gradually shifting its focus to economic recovery. Recent macro data are generally improving, reflecting the strength of the US economy. The probability of a recession will be relatively slight, and the impact on corporate profit recovery is limited. Although corporate profit expectations for the 2nd to 4th quarter are in the downward revision, the margin is slight. As corporate profits rise from the track in the second half of the year, stock index performance can be expected. In the first half of the year, the S&P 500 increased by about 13%. According to our 33-year historical data, if the increase in the first half of the year was more than 10%, the average increase in the second half of the year was 10.6%, and there was no negative return in one year; in the years where the S&P 500 showed negative returns in the second half of the year, usually the first half of that year was cowhide or already had negative returns, which is optimistic about the performance of US stocks in the second half of the year.
Wan Qiong, fund manager of the Bosch S&P 500 ETF, said that in the 2nd quarter of 2023, US inflation continued to decline and economic indicators improved. In terms of economic fundamentals, demand has recovered beyond expectations, and consumption is driving economic growth. The US GDP in the first quarter of 2023 is equivalent to 2% month-on-month, up 0.7% from previously published data, exceeding market expectations of 1.4%, mainly driven by consumer goods, especially automobile and parts sales. Inflation continues to decline, but core inflation remains stubborn. Under the influence of last year's high base, overall US inflation declined rapidly in May. CPI fell sharply from 4.9% year on year to 4%, but the core CPI fell only slightly from 5.5% to 5.3% year on year. The US PCE price index rose 3.8% year on year in May, in line with expectations, lower than the previous value of 4.4%. The core PCE price index rose 4.6% year on year, down 0.1% from the previous value. The level of inflation improved marginally, but it was still significantly above the 2% inflation target. The Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 25 bps in May and suspended interest rate hikes in June. In the second quarter, the S&P 500 index rose 8.30%, and the Nasdaq 100 index rose 15.16%.
Looking ahead to the third quarter of 2023, overseas economies may slowly decline. The negative impact of the continued tightening of monetary authorities in overseas countries will continue to drive the US and European economies downward. According to short-term interest rates leading the manufacturing PMI, the global economy may bottom out near the end of this year. The differentiation between the service industry and manufacturing industry between the US and Europe will continue. Since this year, travel between the US and Europe has remained strong (returning to the level of 19), and the high boom in the service industry has provided some support for employment. The effects of the US credit contraction will begin to accelerate in the 3rd quarter, becoming the main driving force to suppress demand, but the slow release of excess savings will prevent demand from falling excessively, and consumer demand is still resilient. Fighting inflation is still the core task of the Federal Reserve. It is expected that there will still be an interest rate hike in July. The path after September and the magnitude after restarting interest rate hikes are even more important. Currently, it seems that interest rate cuts are still far away, and overseas liquidity may continue to fluctuate greatly in the 3rd quarter.
The Guangfa Fund predicts that US inflation will remain high in the second half of the year, including industrial chain reconstruction and service sector recovery, which are expected to support employment at a high level. The US economy is expected to maintain a moderate recovery trend, but under higher interest rates on US Treasury bonds, uncertainty about US economic recovery is expected to increase, and the possibility that the Fed's monetary policy will shift to stopping interest rate hikes or even cutting interest rates will gradually rise; benefiting from the scientific and technological innovation dividends brought about by artificial intelligence, it is expected that the performance of the US market will still be worth looking forward to.

 A股市场,跟踪纳斯达克指数、标普500指数的ETF今年成为“靓仔”。截止7月27日,“十大核心ETF”今年以来平均涨幅0.41%,标普500以23.11%的涨幅遥遥领先。
A股市场,跟踪纳斯达克指数、标普500指数的ETF今年成为“靓仔”。截止7月27日,“十大核心ETF”今年以来平均涨幅0.41%,标普500以23.11%的涨幅遥遥领先。