Source: national Economic Strategy
The population problem is far more serious than imagined.
In 2018, China's birth rate hit a 40-year low.This year, the number of people born in the country was 15.23 million, 2 million fewer than the previous year. The birth rate was only 10.94 per thousand, down two thousand points from the previous year and the lowest since 1978.
 This is the case in the whole country, and the problems in various provinces and cities are even more serious.
This is the case in the whole country, and the problems in various provinces and cities are even more serious.
Northeast China continues to be at the bottom, with the birth rate of developed provinces and cities such as Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai and Jiangsu and Zhejiang falling below the national average all the year round, and even Shandong, which has always been known as the "most daring", saw a sharp drop in the birth rate in 2018.
People in Shandong dare not give birth, Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai and Northeast China have been in the doldrums for a long time, and only Guangdong is relatively strong. What is the signal? What problems have been warned?
01
Ranking of birth rates:
Hainan and Qinghai are the highest, Shandong falls sharply, Beijing, Tianjin and Shanghai are depressed, and the northeast is at the bottom.
This is the highest birth rate in all provinces and cities in China in 2018:
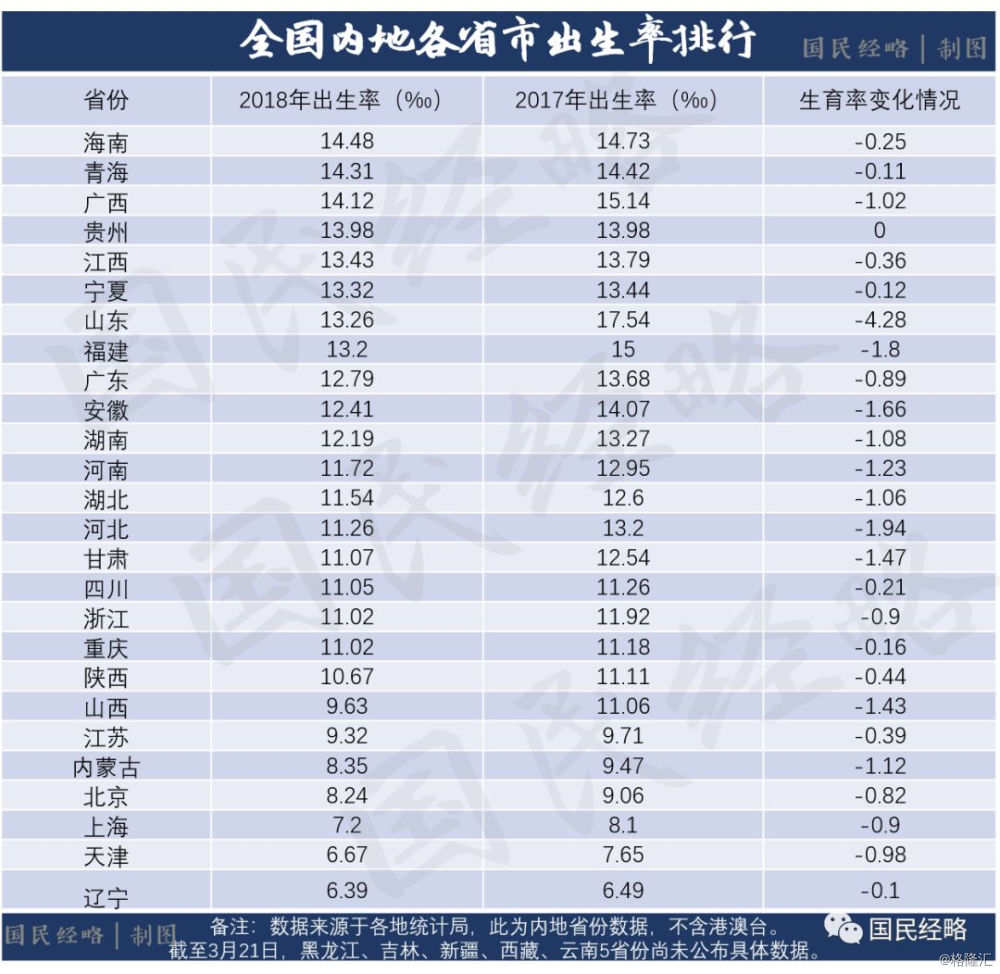
It is not difficult to see that, excluding Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, among the provinces that have published the relevant data,The birth rate in Hainan, Qinghai, Guangxi and other provinces is relatively high. Shandong, which ranked first last year, fell to the middle reaches, while developed areas such as Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai and Jiangsu and Zhejiang were relatively depressed, while the northeast continued to be at the bottom.。
At the same time, compared with 2017, the birth rate has declined not only in the whole country, but also in all provinces and cities.
Among them, the largest decline was in Shandong, falling from 17.54 ‰ to 13.26 ‰, a decline of 4.28 per thousand points.
On the whole, the regional distribution of the birth rate shows two extremely distinct characteristics:
First, the more developed the economy is, the lower the birth rate is.Most of the provinces with the lowest birth rate belong to developed areas, including Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and so on.
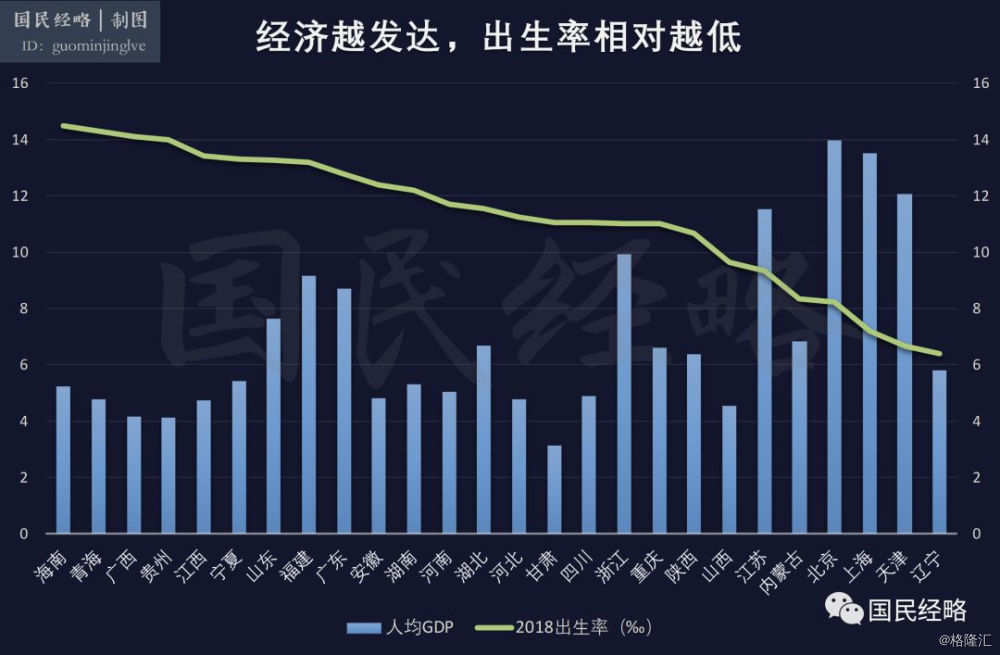
The explanation behind this is that the more developed the economy is, the higher the level of education is, the more progressive the concept is, the more developed the social security system is, and the less necessary it is to raise children to prevent old age. At the same time, the cost of giving birth in developed areas is too high, so parents tend to have fewer children and spend more on existing children.
This rule is true all over the world, and countries such as Japan, South Korea, Europe and the United States are deeply trapped by falling fertility rates.
Second, in the areas where the family planning policy was strictly implemented in the past, the birth rate was relatively low.Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing, Jiangsu and Sichuan are all areas with the strictest implementation of the one-child policy in the past, and their birth rates are all lower than the national level.
As for Xinjiang, Tibet and other provinces, due to the existence of ethnic policies, their birth rate has been maintained at a relatively high level.
02
Why are the people of Shandong afraid to give birth?
The birth rate of provinces and cities across the country, the most serious decline is the populous province of Shandong.
In 2017, Shandong's birth rate reached 17.54 per thousand, the highest in the country and about three times that of Heilongjiang, which ranks lowest.For a time, Shandong was called the "most daring" province in the country.。
In 2018, however, the situation took a sharp turn. The birth rate in Shandong dropped from 17.54 per thousand to 13.26 per thousand, a drop of more than four thousand points.
Be affected by thisIn 2018, the number of people born in Shandong fell directly from 1.7498 million to 1.3295 million, a full 420000 less. The decline is far greater than in other provinces.
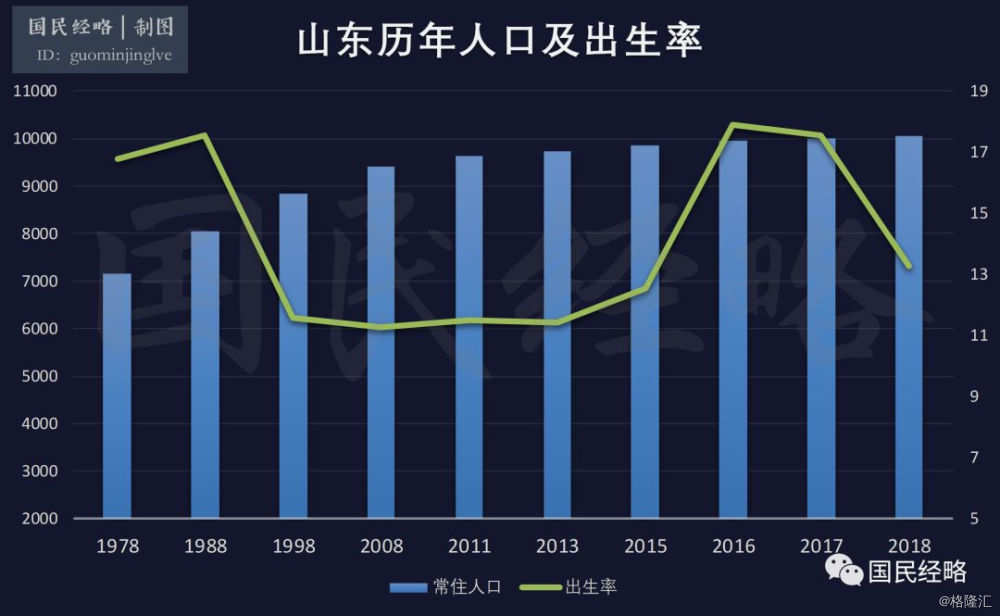
The reason is that in the past, the implementation of family planning in Shandong was relatively strict. With the release of the full second child in 2016,Shandong is the first to bear the brunt of the pent-up desire to have children.
However, by 2018, as the desire to have children was released, the number of second-child births in many places in Shandong dropped sharply, halving directly in some cities, which led to a sharp decline in the number of births in Shandong.
Even so, Shandong's birth rate of 12.36 per thousand is still higher than that of most provinces in the country.In another populous province bordering Shandong, the birth rate in Henan is only 11.72 per thousand, while in Jiangsu, which is not far from Shandong, the birth rate is less than 10 per thousand, only 9.32 per thousand, lower than the national level.
Of course, this has something to do with the economy and culture of Shandong.
On the one hand, Shandong is deeply influenced by traditional Confucian culture.Raise children to guard against old age and have both childrenThere is a great market for the concept of
On the other hand, ShandongRegionEconomicsRelatively developed, relatively balanced economic development, housing prices compared with other coastal areas are more reasonable, fertility costs are relatively reasonable.
Even so, the sharp decline in fertility in Shandong is an important microcosm of the decline in fertility across the country.
03
Why is Guangdong so strong?
Generally speaking, the stronger the economic development, the lower the desire to have children.
Guangdong is an exception in this respect.
In 2018, the birth rate in Guangdong was as high as 12.79 per thousand, surpassing not only Henan, Sichuan and other traditional populous provinces, but also Jiangsu, which belongs to the same economic level, which is only 9.32 per thousand.
Compared with Beijing, Shanghai and Tianjin, the birth rate in Guangdong is much higher. In 2018, the birth rate was only 8.24 per thousand in Beijing, 7.2 per thousand in Shanghai and 6.67 per thousand in Tianjin, only about half of that in Guangdong.
What is the reason behind this?
One reason is that Guangdong has a developed economy and a relatively large number of young immigrants.The existence of these young people not only makes Guangdong's aging rate the lowest in the country, but also increases Guangdong's birth rate.
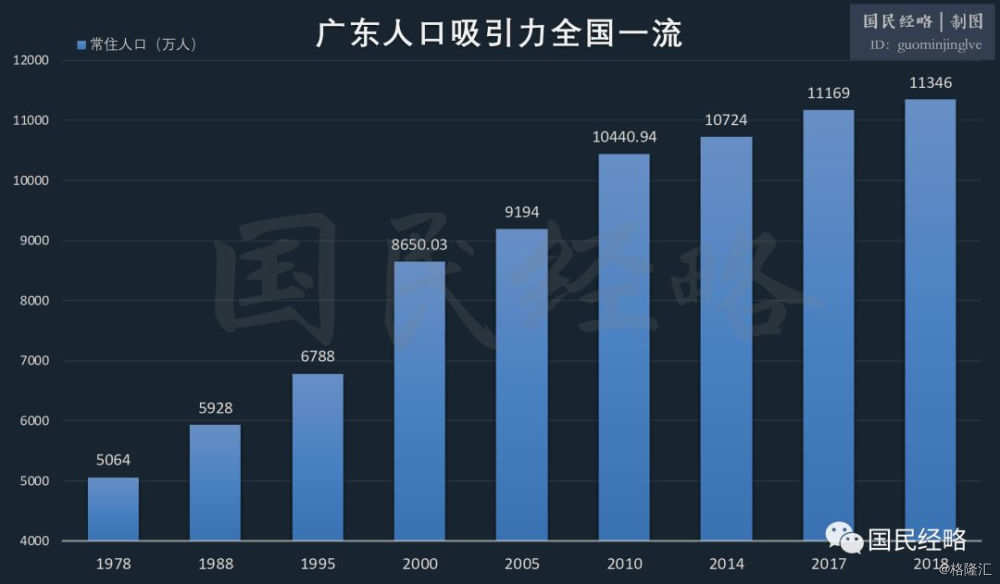
Another reason is that eastern Guangdong, represented by Chaoshan, has always had a strong fertility tradition.Coupled with the relatively complete preservation of the clan system, this increases the flexibility of the local fertility policy.
Therefore, for a long time, the birth rate in Guangdong is higher than the national average, and it also forms a distinct correspondence with other developed areas.
The strong birth rate, coupled with the strong attractiveness of foreign population, has made Guangdong one of the healthiest areas in the country in population structure, with the pension wealth steadily ranking first in the country, and the aging rate at the bottom of the country, which provides a strong support for the economy.
This is the most benign development model.
04
Northeast: oftenSex is at the bottom
Compared with Guangdong, the three northeastern provinces are typical at the other end.
These three provinces, not only the level of economic growth continues to be at the bottom of the country, but also the population continues to flow out, aging leaps to the highest level in the country, and the long-term economic development will inevitably be affected.
To make matters worse, the birth rate of these three provinces is among the lowest in the country.
In 2017, the birth rates of Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang provinces were 6.49 ‰, 6.76 ‰ and 6.22 ‰ respectively, all of which were the lowest in the country and only about 60% of the national birth rate. The 2018 data have not been fully released, but Liaoning has dropped from 6.49 ‰ to 6.39 ‰, and other provinces may not be optimistic.
There are many contradictions in the northeast. It not only has the characteristics of developed areas, such as high urbanization rate, high proportion of population education, but also has the characteristics of backward areas, such as economic downturn and population outflow.
In Northeast China, the degree of urbanization is relatively high.This is determined by the history of its old industrial base. In the past, there were many state-owned enterprises in Northeast China, and the proportion of education and urbanization was relatively high. Naturally, the implementation of family planning policies in these places was relatively strict.
On the other hand, with the transformation and upgrading of China's economy, the advantages of the old industrial base no longer exist, coastal economy, foreign trade economy, Internet economy, high and new technology rise one after another, the Northeast has failed to seize the opportunity in these urban changes.
In recent years, there has been a continuous outflow of population in Northeast China, and the phenomenon of young people "running away" is relatively serious.This will naturally lower the local birth rate and increase the rate of aging.
Take Liaoning as an example, in 2018, the proportion of people aged over 65 in Liaoning was as high as 15.17%, while the proportion of the population aged 0-15 was only 10.96%. The elderly population far exceeded the young population, which markedLiaoning has entered a deep aging society.Not only is there a demographic problem, but pensions will also become a serious burden.
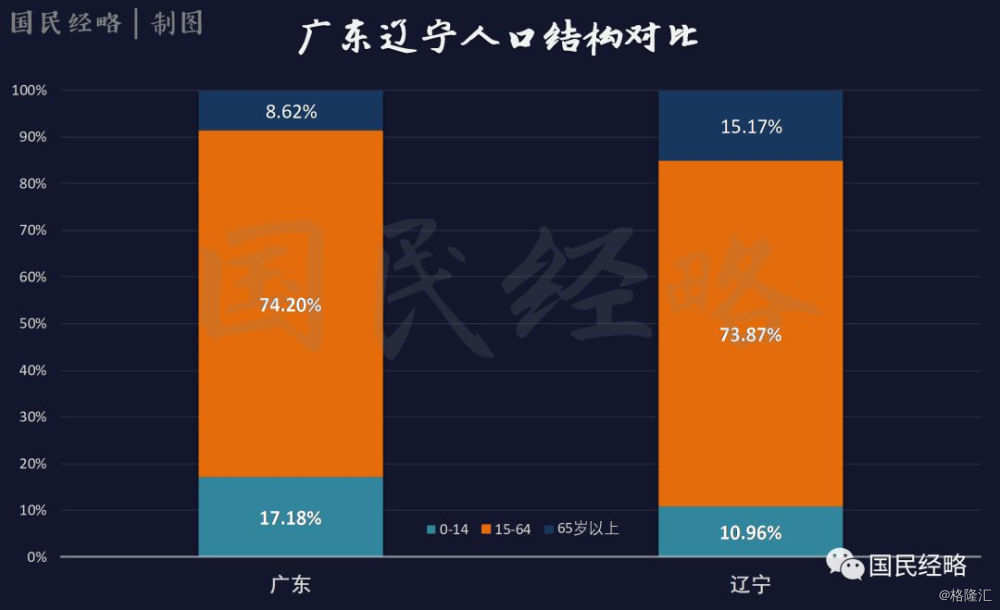
Compared with Guangdong, we can see the seriousness of the problem better.
In 2018, the proportion of people aged over 65 in Guangdong was only 8.62%. The proportion of people aged 0-15 was 17.18%, and the population structure was relatively healthy.
05
Several conclusions
The decline in fertility is both a cultural and economic phenomenon.
First, the national birth rate will continue to decline.According to the estimates of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, by 2028, the population of the whole country may show negative growth. In other words, there will be fewer births than deaths, which will have a serious impact on economic development.
Second, the decline in the birth rate, the decline in the number of young people, while the increase in the elderly population, will have a serious impact on house prices.Population is the fundamental factor that determines house prices. The fewer young people, the fewer people will take over in the future; the more older people are, the more conservative they are about asset investment. If the population shrinks, then the demand for housing is bound to drop sharply, and the long-term support of house prices will no longer exist.
Third, go to a young city.Due to the decline in the birth rate and the outflow of population in Northeast China, pensions have long been unable to make ends meet, and payment has become a problem. Guangdong, on the other hand, has a strong birth rate and an influx of population, and its population structure is very healthy, which not only leads the country in terms of surplus pension funds, but also contributes strongly to economic development.
Only in such areas can there be an active spirit of entrepreneurship and innovation, the long-term prosperity of assets such as the property market, and the long-term and healthy development of the economy.

 全国如此,各省市的问题更加严峻。
全国如此,各省市的问题更加严峻。