In a previous article, "man-made financial crisis" probably means that the new rules cut off off-balance-sheet channels for banks to save capital, but no alternative channels have been established, which is why there is a wave of bond defaults, P2P thunderstorms, corporate financing difficulties and a series of knock-on effects of the subsequent macroeconomic downturn.
Some time ago, it was said that banks should be encouraged to issue permanent bonds. I was still wondering that such illiquid bonds could not be of a large scale. No, the central bank has already taken this into account. The central bank said that in order to improve the liquidity of banks' perpetual debt, the central bank decided to create a central bank bill swap tool.
That is, the perpetual debt can be exchanged for the central bank bill. At the same time, the bank perpetual debt with a main rating not lower than AA will be included in the qualified collateral of the people's Bank of China medium-term Lending facility (MLF), targeted medium-term Lending facility (TMLF), standing Lending facility (SLF) and re-loan.
What does this mean? Is to make the sustainable bonds issued by banks equal to the central bank bills (bonds issued by the central bank). It has greatly improved the credit of the perpetual debt, that is to say, the perpetual debt issued by the bank has the same credit rating as the central bill. So this will greatly reduce the cost of banks issuing sustainable bonds.
But what are the side effects? That is, the central bank created a way to generate the base money. Although the central bank's explanation said that the exchange of bonds for bonds is neutral to the creation of the base money, it also gave the functions of sustainable debt and central bill mortgage, so the next step is the creation of the base currency. The central mother is going to expand the table. To put it simply, the central bank lends money to banks and meets the capital requirements of banks, and the central mother wants to attach the legs cut off by the new rules of capital management.
What will be the specific impact? The transmission mechanism of money will be smoother, companies will be able to borrow money again, and the flood of liquidity between banks will be transmitted to the real economy, that is, they can be less pessimistic about the future.
This measure has a very positive impact on industries with high debt ratios, such as real estate, the real estate industry chain, and, of course, on banks.
This is different from the meaning of lowering the reserve ratio, which can only release money to the interbank market, but because the problem of capital adequacy cannot reach the real economy, this problem has been solved this time. In addition, the cut is to release the base money, this time to create the base money. So the meaning is much heavier than the reserve reduction.
However, it is important to note that perpetual debt replenishes the bank's tier one capital, and banks' lending is also affected by the core capital adequacy ratio. So the loan space that can be released by issuing perpetual debt this time actually depends on how high the core capital adequacy ratio of each bank is.
First of all, let's popularize science about what the capital adequacy ratio and core capital adequacy ratio are:
Capital adequacy ratio is the ratio of a bank's capital to its risk-weighted assets. Capital includes core tier one capital (shareholders' equity), other tier one capital (preferred shares, perpetual bonds, etc.), and ancillary capital (mainly long-term bonds).
Risk-weighted assets refers to setting a risk weight for all kinds of assets held by banks. The higher the risk of assets, the higher the weight, while the risk-free assets, the weight is zero (such as cash, treasury bonds, etc.). And then it adds up to risk-weighted assets. In addition, operational risk and market risk will also be converted into risk-weighted assets. At present, the requirements for capital adequacy ratio stipulated in the measures for Capital Management of Commercial Banks of China Banking Regulatory Commission are:
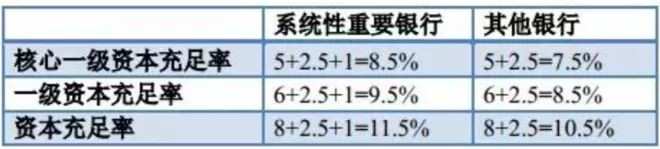
5%, 6% and 8% in the above table are minimum requirements, while 2.5% are additional reserve capital requirements and 1% are additional capital requirements for systemically important banks. Domestic systemically important banks include five major banks and China Merchants Bank.
Well, now let's take a look at the core capital adequacy ratio of several banks. The core capital adequacy ratio of the four major banks plus China Merchants Bank basically exceeds the regulatory requirements by about three points. Other joint-stock banks exceed one point or so. So assuming that perpetual bonds are issued casually, how much credit resources can be released? Bank of China Ltd., for example, has 12.6 trillion risk-weighted assets in 2018, which will free up more than 4 trillion yuan of credit space, along with several others, enough to take over more than 10 trillion shadow banks off the balance sheet.
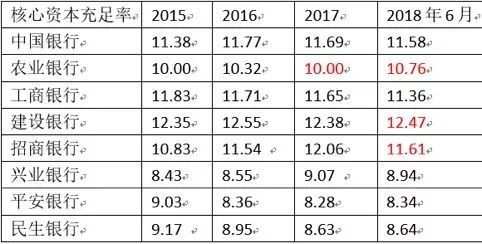
So this is a good opportunity for banks with high core capital adequacy ratios to expand. Similarly, after the landing of this matter, M2, social integration, etc., will be reversed. We have gone back to the past after so many difficulties, but only shadow banking has been standardized, but it has also paid a price.
According to the ancient wisdom of China, good fortune leads to misfortune and misfortune depends on it. After a year of abuse, the love of Yang Ma came, the second-class dog can rest assured to do more, I also think I should study the inner housing stock. (article / five fans)
