Happiness Biotech Group Limited's is so sudden!
As the national manufacturing PMI index fell to 49.4% below the boom line in December 2018, the lowest since March 2016, the deterioration in the manufacturing sector caused market concern, causing A shares and Hong Kong stocks to be "open green" in 2019, with the Shanghai Composite Index falling more than 1% and the Hang Seng Index down 2.77%. The market is "cloudy".
Just yesterday, the central bank announced that in order to further support the development of the real economy, optimize the liquidity structure and reduce financing costs, the people's Bank of China decided to cut the deposit reserve ratio of financial institutions by 1 percentage point in exchange for some medium-term lending facilities.
On the news, the stock market rose on hearing the wind. The Shanghai Composite Index rose more than 2%, and the Hang Seng Index rose 2.24%. The central bank threw a wave of "red envelopes" for the market. However, how big the "welfare" this time is and how long it can last is the next focus.
Is there a good chance that the stock market will rise in four trading days next week?
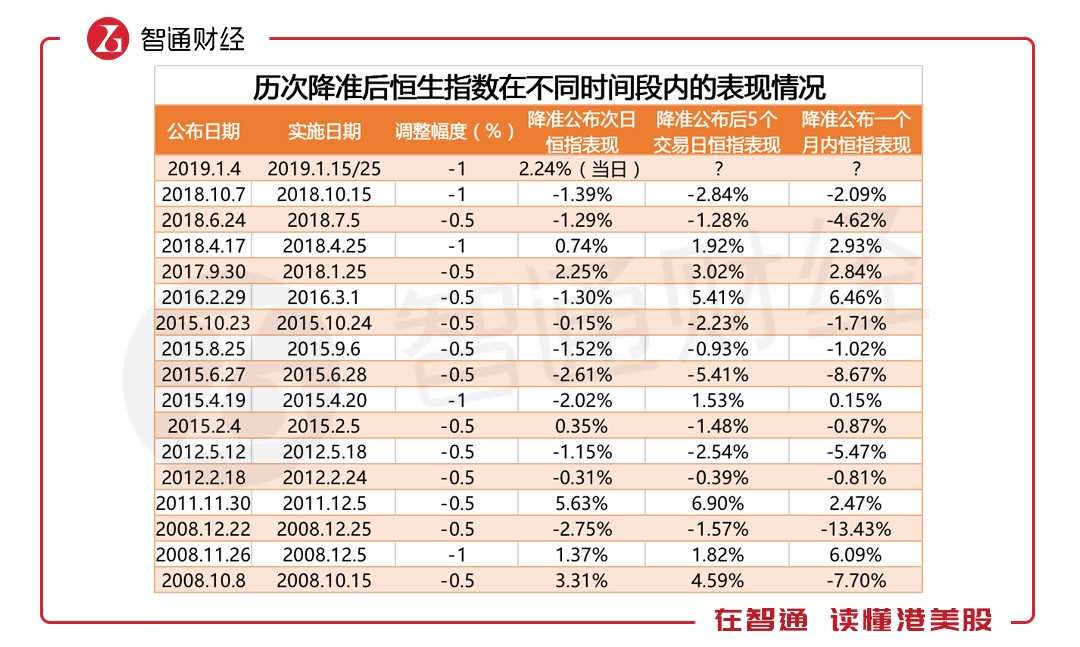
To this end, Zhitong Financial APP collated statistics on the basic situation of previous RRR cuts and the impact of RRR cuts on the Hang Seng Index in different periods of time, in order to explore the secret of RRR reductions to the stock market.
Since the financial crisis in 2008, it has been reduced 17 times, of which the largest number of reductions was five in 2015, and four were implemented in 2018. Naturally, the number of reductions this year will not be too small.
Ren Zeping of Evergrande Research Institute said that at present, the downward pressure on the economy is increasing, the signs of deflation are obvious, the risk appetite of financial institutions is still low, and there is plenty of room for reserve requirement cuts in 2019. Does this mean that there are still three "red packets" to grab this year? Not exactly!
According to the statistical data, the probability of the rise of the Hang Seng Index is 37.5% the day after the RRR reduction is announced. Within five trading days, the probability of the HSI rising is 43.75%. Within one month of the RRR reduction, the probability of HSI rising has dropped to 37.5%.
To put it simply, reserve ratio cuts do not always boost the stock market, because they are designed to deal with liquidity constraints and hedging risks, and the economy is not so sound at this time, so in such a short period of time, the stock market is more likely to be on a downward trend.
But it's worth noting thatIf the Hang Seng Index rises the day after the RRR cut is announced, it is more likely that the Hang Seng Index will continue to rise in the next five trading days.Taking historical data as an example, the Hang Seng Index rose six times the day after the cut, five of which continued to rise over the next five trading days, with a probability of 83.33%.
If the time is extended to one month, even if the Hang Seng Index rises the day after the RRR cut is announced, the subsequent performance also weakens. It rises the day after the RRR cut is announced, continues to rise in five trading days, and continues to rise only twice a month, and the probability of rising is reduced to 33.33%.
Therefore, if you do not consider other factors, only from a statistical point of view, the January 4 cut was announced in intraday trading (previously mostly announced on the weekend), which can be understood as a rise the day after the announcement, then, for the remaining four trading days next week, the probability of the Hang Seng Index strengthening as a whole is 83.33%.
There may be 3-4 reserve cuts this year?
The short-term change of the reserve ratio cut on the stock market is worth considering, but the long-term and macro impact is more worth thinking about.
Excluding the January 4 RRR cut, China has made a total of 16 RRR cuts since the 2008 financial crisis, mainly in 2008, 2015 and 2018. The number of RRR reductions in these three years is 3, 5 and 4, respectively. And these three years have common characteristics, that is, the stock market is "thin". Take the Hang Seng Index as an example, it fell 48.27% in 2008, and the Hang Seng Index rose and fell back in 2015. The largest decline for the year was 28.09%, and it also went up and down in 2018, with the largest decline of 26.7%.
In 2008 and 2015, after cutting reserve requirements to stimulate the economy, the stock market improved the following year. The Hang Seng Index rose 52.02% in 2009. Although the Hang Seng Index did not rebound significantly in 2016, it recorded a weak increase of 0.39% for the whole year, and in these two years, the number of RRR reductions decreased significantly, with 0 RRR cuts in 2009 and 1 RRR cut in 2016, indicating that the economy had picked up that year and there was no need to lower or lower the number of RRR cuts.
However, after the implementation of four RRR cuts in 2018, the number of RRR cuts in 2019 may not be reduced, because according to the incomplete statistics of Zhitong Financial APP, Evergrande Research Institute, Ping an Securities, Tianfeng Securities and China China Minsheng Banking Corp have all said that there will be 3-4 RRR cuts this year, and some brokerage institutions believe that not only will there be a RRR cut, but also that there may be a comprehensive interest rate cut.
Thus it can be seen that the economic trend in 2019 is not so optimistic, as investors should be prepared.
Real estate bottomed out?
In addition to the stock market, the impact of the RRR cut on the property market is also a hot topic of public discussion. after all, most people have a deep understanding of the powerlessness of wages "unable to run away" housing prices. Excluding this time, there have been four 1 percentage point cuts since the 2008 financial crisis, namely in 2008, 2015 and 2018.
The cut in 2008 was mainly in response to the international financial crisis, and the 1 percentage point cut in 2015 was the strongest reduction in six years since the financial crisis. The launch of the cut is due to downward pressure on the economy because GDP growth shrank to 7 per cent in the first quarter of 2015, compared with 7.3 per cent in 2014.
In 2015, the property market, in the context of destocking, supported rigid demand and improved demand, and the policy tone was relatively loose. After the RRR cut, China's property market as a whole continued to recover. At the end of 2015, house prices rose 47.5% in Shenzhen, 18.2% in Shanghai, 10.4% in Beijing and 9.2% in Guangzhou.
The two one-percentage-point RRR cuts in 2018 highlight the urgency of the market to adjust, the downward pressure on the economy is greater, and after the interest rate hike cycle in the United States, the liquidity of market funds has gradually shrunk, and the financing problem of small enterprises has become increasingly prominent.
The implementation of the four reserve requirement cuts in 2018 is not small, but unlike in 2015, the property market in 2018 has cooled down under more than 400 policy controls, and the growth rate of property market sales has slowed down. According to Anjuke's "2018 property Market Summary" data, housing prices in first-tier cities rose slowly in 2018 as a whole, while prices in Shenzhen declined steadily.
The two different trends of house prices are mainly due to different policies. the central bank also set the tone for the January 4 reserve cut, which is targeted regulation and control, not flooding, and the prudent monetary policy orientation has not changed.
In terms of property market policy, according to the arrangements of the Central Economic work Conference, we should still insist that houses are used for living, not for speculation, and at the same time emphasize "implementing policies and classified guidance according to the city, and tamping the main responsibility of the city government."
In fact, the RRR cut is good for mortgage loans to some extent, and mortgage interest rates in some cities have loosened since October last year, which is good for users with rigid demand. For housing enterprises, the comprehensive cut does not clearly limit the flow of funds, which can improve the tight cash flow of housing enterprises, from which the head housing enterprises will benefit, and the first-and second-tier land market is expected to gradually heat up.
Therefore, under the current economic situation and property market policy, real estate is more likely to maintain a stable or moderate rise after a decline, such as the previous surge is impossible, that is, there is no housing speculation.
According to the cycle King Zhou Jintao's "Kangbo cycle", the real estate cycle has a 20-year cycle, rising in 15 years and declining in 5 years. The current real estate cycle started in 1999 and bottomed out in 2019.
