Source: Zhitong Finance and Economics
Author: CSC FINANCIAL CO.,LTD
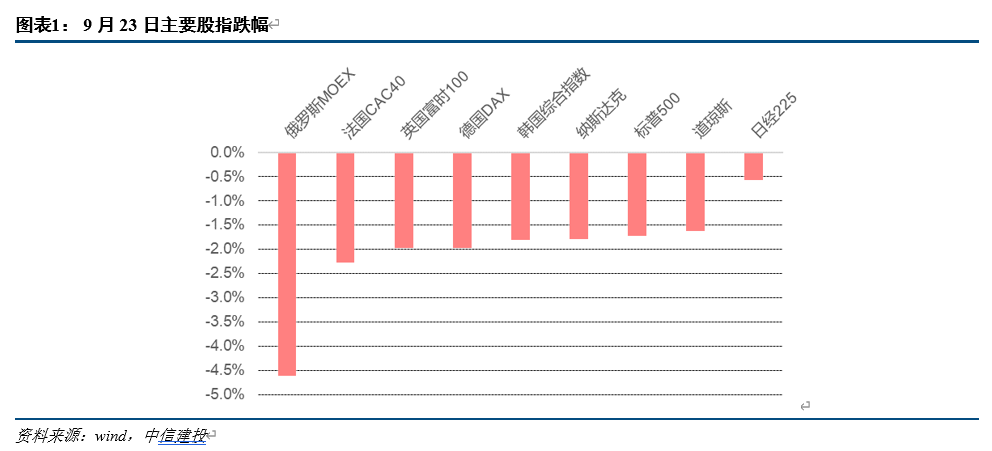
On September 23, European stock indexes fell across the board, and then the decline quickly spread around the world.France's CAC40, Germany's DAX, the UK's FTSE 100and European STOXX50 fell 2.35 per cent, 1.87 per cent, 2.04 per cent and 2.3 per cent respectively, while the Dow Jones industrial average fell for the fourth day in a row to close at 29590, down 1.6 per cent on the day, breaking the year's low set in June and down 19.9 per cent from its January high, approaching a technical bear market.
The S & P 500 fell 1.7 per cent to 3693.23. The Nasdaq fell 1.8 per cent to 10867.93, already in a bear market. In addition, emerging markets in Japan and South Korea also fell to varying degrees. The FTSE global index fell 2.1 per cent, a weekly decline of 5 per cent, the biggest drop since June.
In the bond marketOn the 23rd, the yield on the two-year US Treasury rose 9bps to 4.20 per cent, a 15-year high, while the yield on the 10-year Treasury note fell 1bp to 3.69 per cent, maintaining its highest level since October 2012. the spread between the two spreads widened further to 51bps.
In Europe, eurozone government bonds were sold off frantically and bond market yields rose collectively as risk aversion heightened. Yields on 10-year government bonds in Britain, Germany, France, Italy, Spain and Portugal rose by 33bp, 6bp, 7bp, 15bps and 10bps respectively, all by more than 100bps since the beginning of August.
Among them, the UK rose 199bps. The yield on German two-year bonds rose to 2 per cent for the first time since 2008, rising to its highest level since December 2011. 2Y-10Y yield spreads are hanging upside down in many countries in the UK, Germany and even Asian emerging markets.


On the exchange rate side, the dollar index reached its highest level since April 2002. The dollar index rose 1.5%, while the euro fell 1.5% to $0.97, falling below dollar parity again this week. The pound fell 3.59 per cent to $1.09 and fell 5 per cent this week to a 37-year low.

For commodities.As the dollar continued to rebound and gold tumbled, gold closed near its lowest level since April 2020, silver and oil tumbled about 5 per cent, WTI crude broke through the 80 mark, and natural gas prices continued their decline.

Second, multiple factors worsen market expectations, and the dark clouds of recession in Europe and the United States do not go away.
The sharp fall in Europe was triggered by the UK government's plans for massive tax cuts and an increase in government bond issuance, fuelling fears of a deterioration in Britain's public finances.According to the 2022 Mini Budget released on the 23rd, the Truss government will cancel its plan to raise corporate tax to 25 per cent and maintain it at 19 per cent; abolish the 1.25 per cent increase in national insurance tax (an extra £17 billion per year); reduce the basic rate of income tax from 20 per cent to 19 per cent; and abolish the top rate of 45 per cent for high earners and set it at 40 per cent. Raise the tax threshold for stamp duty and first-time home purchases, abolish the cap on bankers' bonuses, relax regulation on entrepreneurs, take measures to reduce restrictions on land use planning, issue tax rebates for tourists, and cancel tax increases on alcohol.According to the plan, UK revenue will be reduced by 37 billion pounds between 2023 and 2024.
The move comes after the UK government unveiled a £150 billion package of energy price limits for households, businesses and the public sector, liquidity support for companies in the face of energy fluctuations and a suspension of green taxes.
When the Truss government tries to solve the problem of energy supply by means of fiscal relaxation, administrative price restrictions and subsidies, there may be great hidden dangers in itself, and the fiscal and government debts and deficits will face great pressure.
According to the newly announced bond issuance plan, the UK plans to issue 193.9 billion pounds of government bonds this fiscal year, 60 billion pounds more than originally planned and exceeding market expectations. However, the market expects UK borrowing to jump to £230 billion this year to meet fiscal easing, accounting for about 3.5 per cent of economic output and more than 30 per cent higher than the average over the past 74 years.

Under the impact of the epidemic in 2020, the British government debt exceeded 2 trillion pounds. If the government does not tighten fiscal policy in the future, debt could more than triple to nearly 320 per cent of GDP within 50 years, according to the UK budget watchdog.
During the election campaign, Truss's rival, former Chancellor of the Exchequer Sunak, strongly advocated tax increases and debt reduction. However, Truss, who came to power with the help of populism, quickly launched such a large amount of fiscal easing, which has shaken investors' confidence in the British economy and its currency.Markets were alarmed by aggressive tax cuts in the UK, triggering investors to sell sterling and flee UK government bonds, and fears of rising risk in the UK rocked markets in Europe and even the US.
The Bank of England will raise interest rates sharply further to offset the inflationary impact of fiscal stimulus. The market expects the Bank of England to raise interest rates by 0.75 percentage points in each of the next three meetings to 4.5 per cent. The Bank of England announced on the 22nd that it would start shrinking its table next month, further increasing the pressure on gilts.
Behind the recent fall in global markets is the rise in recession expectations against the backdrop of interest rate hikes by central banks around the world.The Fed's sharp rate hike heightened fears of a recession and led to a surge in selling of risky assets. The Fed raised interest rates by 0.75 percentage points for the third time this week, raising the benchmark federal funds rate to the range of early 2008 and continuing its most aggressive growth path in decades. the Fed's signal that high US interest rates will last until 2023 caught the market off guard.
Investors expect market volatility to increase and the VIX index to climb again. Meanwhile, six central banks, including Britain, Sweden, Switzerland and Norway, this week raised interest rates to fight inflation, leaving all central banks in Europe out of negative interest rates.
Recession expectations have been transmitted to the real economy.The strong earnings of US stocks in the first half of the year supported market sentiment, but the risk of a recent hard landing has appeared in the real economy, and the overall economic environment tends to deteriorate. Expected earnings for the s & p 500 grew 4.6% in the third quarter, down from 5% last week.
Us companies, including Ford Motor Company and FedEx Corp, have issued profit warnings in recent weeks, sparking fears that inflation and recession are starting to erode corporate profits. PMI in major European countries continued to decline, with many countries falling below the 50 per cent rise and fall line, and recession expectations continued to heat up.

Russia and Ukraine expect the winter war situation to be tight, increasing global systemic risks.Since August, the Ukrainian army has launched a large-scale counter-offensive on the southern front, and this week Putin announced "partial mobilization". On the 23rd, the Donbass region opened a referendum, heralding another large-scale fighting in the Russian-Ukrainian battlefield in winter. As the conflict between the two sides lasts longer than expected, the West continues to increase its sanctions against Russia. Europe's energy problem is difficult to solve, and getting rid of Russian energy demand requires a huge economic price in the short term. Food commodity prices are rising again, and international food prices are ushering in a new upswing as the European energy crisis leads to a shortage of fertiliser supplies, which may affect sowing production in autumn.
Third, the global stock market "eagles hit the sky", and the bond market yield continues to peak.
Central banks around the world have launched an inflation sniper war, and the Federal Reserve has made it a top priority to control inflation, suggesting that Volcker was not firm in controlling inflation in the early days of his tenure, leading to a decade of stagflation, hawkish central banks and faster global dollar returns. We have always stressed that stubborn inflation and firm determination to control inflation must result in a recession in the United States and a slow stock market. Under the trading recession logic, base metals will fall and the dollar will be strong; under the trading logic of raising interest rates, US bond yields will continue to rise and gold will be weak.
Risk Tips:The global recession exceeded expectations
Edit / ping
