Source: Wall Street
Author: according to you
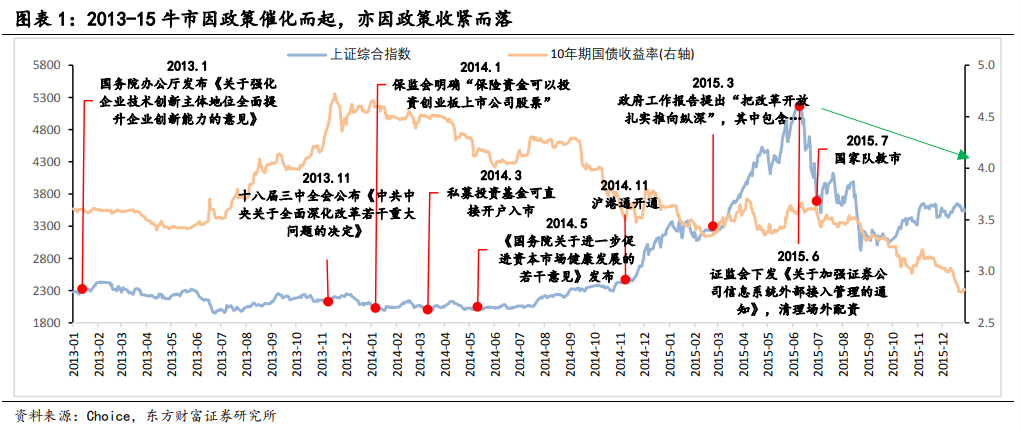
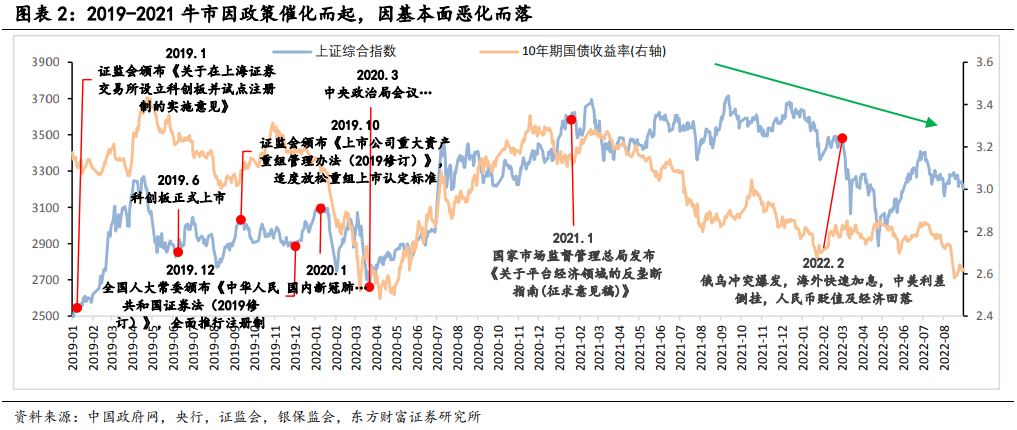
Oriental Wealth Securities said policy promotion and improved liquidity were key to the formation of a bull market. In addition, during the two bull markets, the domestic economy began to shift gears, giving birth to reform policies.
The 2013-2015 Internet bull market and the 2019-2021 new energy bull market are both track-type bull markets with similar macro downside, loose liquidity and sustained policy support.
In 2013, in the 4G era, the proliferation of Internet users offered many possibilities for the explosion of Internet applications:With the large-scale expansion of the bull market in securities, banking, insurance, P2P and stock speculation software, cloud computing has expanded to smart cities, smart security, smart medical care, intelligent rural areas and other fields. the prosperity of Internet media has led to online literature, education, literature and tourism, film and television, media applications.
In 2019, China has entered a long-term national strategy in the dual-carbon era, laying a solid methodological foundation for the new energy track:With the support of the policy, the newly installed capacity of photovoltaic wind power has been greatly expanded to occupy the core of the market, lithium mining resources companies have realized the realization of endowment and profits have soared, and lithium battery materials and power battery manufacturers have also enjoyed the dividend of new energy vehicles.
From the "Internet bull market" to the "new energy bull market", what are the similarities and differences between the two bull markets? Qu Yiping and Chen ran, analysts at Oriental Fortune Securities, said in their report "reviewing the similarities and differences between the 19-21 New Energy Bull Market and the 13-15 Internet Bull Market from the Perspective of Ten shares and permeability" that policy promotion and liquidity improvement are the key to the formation of the bull market.
Oriental Wealth Securities has analyzed the macro reasons for the formation of the past two bull markets, a total of four points:
1. Policy promotion and liquidity improvement are the key to the formation of a bull market.
Oriental Fortune Securities said that two rounds of bull markets emerged in the capital market reform:
The capital market reform in 2013 mainly focused on encouraging scientific and technological innovation and improving the multi-level capital market system, introducing a number of policies to speed up the construction of equity market, bond market, futures market, etc., while 2019 focused on the establishment of Science and Technology Innovation Board and the pilot implementation of the registration system to reduce obstacles to enterprise financing.
Similarly, two bull markets ended with policy and overseas factors:
After clearing up the over-the-counter allocation in 2015, the balance of the two financial institutions fell all the way from 2.26 trillion in 2015.6 to 920 billion in 2015.9, and the leveraged bull came to an end. After that, 2016-2017 entered the Fed interest rate hike cycle, and the domestic deleveraging policy continued. In 2022, under the circumstances of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, high global inflation, rapid overseas interest rate increases and upside-down interest rate differentials between China and the United States, the domestic economy adjusted and lasted three years of structural bull market correction.
two。 Macro level: similar downward pressure, very different economic structure
Oriental Fortune Securities said that during the two bull markets, the domestic economy began to shift gears, giving rise to reform policies, with GDP growth from "breaking 7" to "breaking 6":
During the two bull markets, the domestic economy is in a shift period of growth. The real growth rate of GDP in 2015 was 6.9% year-on-year, 0.4 percentage points lower than that in 2014, the first "breaking 7" since 1991; in 2019, GDP actually grew 6.0% year-on-year, 0.6 percentage points lower than in 2018, with GDP growth below 6% in the third and fourth quarters of 2019.
Demand was insufficient and inflation fell to a low level. Domestic inflation fell rapidly after 2010, falling to 1.4 per cent in 2015, far below the level of about 3 per cent in the past decade. CPI also fell sharply in 2020, with CPI growth of-0.5 per cent year-on-year in November of that year, the first negative since the financial crisis.
In addition, in the face of downward economic pressure, the focus of counter-cyclical policy has shifted from "soft power" to "hard technology":
The development and cultivation of new kinetic energy was proposed during 2013-2015 and 2019-2021. The former mainly focuses on "soft power" represented by TMT, while the latter pays more attention to "hard science and technology" such as new energy and semiconductors. The fundamental reason is that major changes have taken place in the domestic economic structure.
First, there is an increasing demand for the development of physical manufacturing. Second, with the continuous expansion of China's economic volume, a new development pattern with the domestic great cycle as the main body and the domestic and international double cycles promoting each other has gradually taken shape, and the demand for scientific and technological self-reliance and self-reliance has been strengthened.
3. Liquidity: interest rate cuts and liquidity investment continue the high boom in the capital market
During the bull markets of 2014 and 2019, the central bank cut interest rates sharply, reducing the cost of capital significantly:
The interest rate adjustment triggered a large amount of low-cost capital entry.From 2013 to 2014, the rapid rise in the balance of the two financial institutions led to active trading in the market. driven by a large amount of over-the-counter leveraged funds, the balance of the two financial institutions reached 2.2 trillion yuan at one time in 2015. During the period from 2019 to 2020, the balance of finance and finance rose sharply again, and H1 fell after reaching a peak of 1.9 trillion in 2021, and the market began to differentiate substantially. The two bull markets were affected by policy promotion and large capital inflows, and the amount of funds raised by A-share listed companies increased significantly. For example, the amount of funds raised by A-share listed companies increased by 110% and 39% respectively in 2015 and 2020 compared with the same period last year.
The continued net inflow of foreign capital contributed to the boom in the A-share market.After the opening of Shanghai Stock Connect in November 2014, the road for foreign investors to enter A-shares officially opened. The first wave peaked from the end of 2014 to the first half of 2015, when the northbound capital expanded rapidly to 120 billion yuan. The northward capital expansion accelerated again in the second half of 2019, exceeding 1 trillion yuan, accounting for more than 2% of the current market value of A shares, which has become one of the important factors affecting China's capital market.
During the bull market, fund issuance accelerated to promote the theme, the track market.Under the influence of the high boom in the A-share market, the issuance of funds has increased significantly. In the first half of 2015, the average daily share of newly established funds exceeded 10 billion yuan, much higher than that of the same period in previous years. In the second half of 2020, the average daily share of newly established funds further rose to more than 18 billion yuan. A large number of professional funds have entered the market and concentrated on hot tracks to speed up the evolution of the capital market to the structural market.
4. Overseas factors: low economic growth and RMB appreciation in the early days of the bull market
Oriental Wealth Securities believes that at the beginning of the bull market, global economic growth slowed and the rate of return on investment fell:
Around 2013 and 2019, the global GDP growth rate showed a downward trend. At the same time, international trade and investment have shrunk sharply, the international financial market is volatile, and overseas funds are facing a "asset shortage". It is urgent to seek stable and high-yielding investment assets.
In addition, overseas interest rates are low and RMB assets are more attractive to foreign investors:
From 2013 to 2015, the US federal funds rate remained at 0.25%, and the spread between China and the United States was more than 1 percentage point. Hit by the COVID-19 epidemic after 2019-2020, the Federal Reserve quickly cut the federal funds rate to 0.25%, and the spread between China and the United States widened to more than 2 percentage points. In these two periods, RMB assets have a high comparative advantage.
The main content of this article comes from "reviewing the similarities and differences between the 19-21 new energy bull market and the 13-15 Internet bull market from the perspective of tenfold shares and permeability." the original author: qu Yiping and Chen ran of Oriental Wealth Securities.
Edit / tolk