Guide reading
Recently, the Politburo meeting stressed the need to strengthen institutional construction and stimulate market vitality around the reform of the capital market. On November 5th, General Secretary Xi Jinping proposed to establish a branch-building board and pilot the registration system, which triggered a discussion on the construction of the stock market system. What are the key problems in China's stock market at present? How to solve?
Abstract
Since its establishment in 1990, the stock market has achieved remarkable results in promoting the development of the real economy and guiding the optimal allocation of resources. However, it must be noted that there are still four institutional problems in China's stock market that need to be solved.
1. Establish a market-oriented stock issuance system.At present, China's stock market adopts the approval system for the listing of enterprises. From the perspective of implementation effect, there are the following problems: first, some enterprises overpack themselves in order to meet the standards of corporate governance and financial indicators set by the CSRC, and some are even suspected of financial fraud. Second, it causes the market to overvalue the enterprises, resulting in unreasonable pricing. Third, the approval system makes listing qualifications a scarce resource, causing market hype on shell resources. In order to maintain listing qualifications, some companies choose illegal means such as financial fraud to whitewash statements and disrupt market order. Fourth, the approval system gives regulatory departments more power to examine and approve relevant business posts, which can easily lead to power rent-seeking and corruption.
The approval system is the result that the issuance system has not yet completed the market-oriented reform. China's new share issuance system has experienced three stages: long supervision, examination and approval system and approval system. The overall degree of marketization has been significantly improved, but it is still necessary to further improve the market reform and stimulate market vitality.
Registration system is the reform direction of stock issuance system in our country. Since it was proposed in 2013, the reform of the registration system has been moving forward despite twists and turns. We believe that in order to do a good job in the reform of the registration system, we must first improve the market-oriented distribution system. It is necessary to establish a market-oriented delisting mechanism to ensure that the market can constantly spit out the old and accept the new and form a healthy competition mechanism. It is necessary to establish a strict information disclosure system to ensure true, complete and timely information disclosure. It is necessary to improve the intensity of supervision, improve the level of supervision during and after the event, and improve the deterrent force of supervision.
two。 Improve the investor structure of A shares.At present, the proportion of institutional investors holding positions in China's A-share market is only 16.1%, which is obviously lower than that in developed countries. Individual investors account for 82 per cent of turnover, and the average annualised turnover rate in Shanghai and Shenzhen is 189.6 per cent, significantly higher than in major developed markets, and A-share market pricing is dominated by retail investors. The high proportion of retail transactions leads to excessive volatility in the A-share market; emphasis on policy trend rather than fundamental analysis; retail institutional behavior and other three major problems, the price discovery mechanism can not be brought into full play.
The main reason why the proportion of institutional investors in A-share market is relatively low is that at the beginning of the establishment of China's stock market, there are no institutional investors specializing in securities investment business, which makes individual investors dominate. Since 2000, the proportion of professional institutional investors' positions has increased, but it is still low as a whole. On the one hand, it is due to the lack of long-term and stable sources of funds for institutional investors, on the other hand, due to the strong atmosphere of A-share speculation and the constraint of trust responsibility, institutional investors tend to reduce their positions and reduce risks.
It is suggested that the proportion limit of pension investment in the stock market not higher than 30% should be appropriately relaxed, and the speed of provincial and municipal pensions investing in the stock market by signing contracts with the Social Security Fund Council should be accelerated. When assessing the pension income, we should focus on the medium-and long-term and absolute income, and introduce a stable medium-and long-term capital source for the stock market. In addition, it is suggested that on the basis of full study, the pilot fund industry should change from short-term performance ranking to long-term absolute performance assessment, reverse the trend of short-term behavior in the fund industry, and gradually form the concept of long-term investment and value investment. increase the proportion of shares held by institutional investors and promote the healthy development of China's stock market.
3. Improve the design of the trading system.1) further standardize the suspension of trading of listed companies. The random suspension and long-term suspension of listed companies seriously affect the liquidity of stocks, and cause harm to investors' right to know and trading rights, which is an important problem for A-shares. Under extreme market conditions, the collective suspension of listed companies will also have a significant impact on the liquidity and price discovery mechanism of the whole market. At present, regulators have been aware of the relevant problems, and through improving the system, strengthening supervision and other ways to solve. We think that strengthening supervision should focus on enforcement. For listed companies that have no clear reason to suspend trading for a long time, or whose reasons for suspension are more ambiguous, the exchange can force the resumption of trading. For major asset restructuring or asset restructuring, appropriately shorten the suspension time, and should not be complex transactions, involving many parties and other general reasons to extend the suspension time at will. When the market is obviously abnormal and liquidity collapses, the exchange should deal with it decisively and suspend the enterprise's application for suspension of trading so as to ensure the normal operation of the market function.
2) abolish the stamp duty on stock transactions and reduce market transaction costs. In the era of paper vouchers, due to the frequent use of paper stocks endorsed by the government "decal endorsement", it is reasonable for the government to levy stamp duty. However, with the advent of the era of electronic and paperless trading, the tax base has changed greatly, and the rationality of continuing to levy stamp duty on stock transactions has declined. Historically, stamp duty rate adjustment has also been entrusted with the function of regulating the market, but can not change the overall trend of the stock market, but aggravate the short-term volatility. The United States, Germany, Japan and other developed countries have successively abolished stamp duty on securities transactions. We propose to abolish the stamp duty on securities transactions in the light of market conditions. There are two advantages: on the one hand, from this year's data, stamp duty on securities transactions accounts for only 0.5% of the general budget revenue, and there is little financial pressure after it is cancelled. On the other hand, the abolition of stamp duty on securities transactions will reduce market transaction costs, enhance investor confidence and capital market vitality, and promote the healthy development of the market.
4. Improve the legal system and enhance the deterrent force of supervision.At present, the upper limit of punishment for many illegal acts in the Securities Law is 600000 yuan. The maximum sentence for divulging inside information in the Criminal Law is 10 years, but the actual sentencing is generally 3-5 years. Compared with the developed capital market, the punishment of illegal and criminal acts in the relevant laws of our country is lighter, so it is difficult to play a sufficient deterrent role. In addition, with the continuous development of the market, the current securities law still has the problem of being unable to adapt to the new situation of the market, so it needs to be revised to solve it.
We propose to speed up the revision of the Securities Law, significantly reduce the regulation of securities issuance and other areas, and at the same time strengthen law enforcement, increase the punishment for securities crimes, and enhance the deterrent force of supervision. Improve the level of supervision during and after the event. In terms of criminal responsibility, for serious securities crimes, we should appropriately raise the sentencing standards, effectively crack down on disturbing market order, price manipulation, illegal fraud and other acts, and constantly improve the legal environment of China's securities market.
Risk hint: policy promotion is not as expected
Catalogue
1 to establish a market-oriented distribution system
1.1 there are four major drawbacks in the approval system, such as excessive packaging, unreasonable pricing, hype of shell resources, power rent-seeking and corruption.
1.2 the approval system is the result that the marketization of the stock issuance system has not yet been completed.
1.3 the reform of registration system is conducive to the formation of a more market-oriented system in the stock market.
1.3.1 improve the supporting system to protect the pilot registration system
2 improve the investor structure of A-share market
2.1 the proportion of market capitalization held by institutional investors in A-share market is low, and the proportion of retail trading volume is on the high side.
2.2 strong hype atmosphere, lack of long-term stable funding sources and other reasons make it difficult for institutional investors to develop and grow.
2.3 continue to encourage pension to enter the market and improve the registration system for the assessment of institutional investors is conducive to the formation of a more market-oriented system in the stock market
2.3.1 raise the upper limit of the proportion of pension funds investing in stocks
2.3.2 change the short-term tendency of performance evaluation in fund industry
(3) perfect the construction of transaction system.
3.1 further standardize the suspension of trading of listed companies
3.1.1 arbitrary suspension of trading of listed companies affects normal trading in the stock market
3.1.2 improve the regulatory system and stop arbitrary suspension of trading
3.2 abolish stamp duty on securities transactions and reduce market transaction costs
(4) improve the legal system and enhance the deterrent force of supervision.
4.1 the punishment for some illegal acts of securities in China is too light.
Text
On October 31, the political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee held a meeting, emphasizing the need to focus on capital market reform, strengthen system construction, stimulate market vitality, and promote the long-term and healthy development of the capital market. Since its establishment in 1990, the stock market has achieved remarkable results in promoting the development of the real economy and guiding the optimal allocation of resources. However, it should also be noted that at present, there are still four major institutional problems in China's stock market that need to be solved.
1 to establish a market-oriented distribution system
1.1 there are four major drawbacks in the approval system, such as excessive packaging, unreasonable pricing, hype of shell resources, power rent-seeking and corruption.
At present, China's stock market adopts the approval system for the listing of companies. The CSRC shall formulate the measures for the Administration of initial Public offering and listing (hereinafter referred to as the measures) to examine the listing applications of enterprises, and approve the public offering of shares after approval. From the actual effect, there are the following problems in the approval system.
First, it is easy to lead to excessive packaging. The CSRC makes it clear in the "measures" that reporting enterprises should: 1) the net profits of the last three fiscal years are all positive and the cumulative amount exceeds RMB 30 million; 2) the net cash flow generated by operating activities in the last three fiscal years has totaled more than RMB 50 million; or the cumulative operating income in the last three fiscal years exceeds RMB 300 million; 3) the total share capital before issuance is not less than RMB 30 million 4) at the end of the most recent period, the proportion of intangible assets (after deducting land use rights, surface aquaculture rights and mining rights, etc.) to net assets is not higher than 20% of the net assets. 5) there is no uncompensated loss at the end of the most recent period. The original intention of these financial requirements is to ensure that listed enterprises are in good operating condition, to prevent companies from listing money, and to protect the legitimate rights and interests of investors. But in practice, some enterprises will beautify the financial statements to achieve the above requirements, and even suspected of financial fraud, but infringed on the legitimate rights and interests of investors.
Second, it is easy to lead to unreasonable pricing. As the application of enterprises for listing needs to be examined and approved, the primary market is easy to overprice the approved enterprises. After listing, the secondary market price of the stock continues to fall, causing injustice to the secondary market investors. In order to solve this problem, the CSRC issued a notice on issues related to IPO pricing in 2012, requiring that if the price-to-earnings ratio of the issue price based on the results of the inquiry is higher than the average price-to-earnings ratio of listed companies in the same industry by 25%, the issuer should convene a board of directors to confirm the issue pricing, discuss and analyze the risk factors of pricing and its related impact, and in fact guide the upper limit of the issue price. However, this limits the issuing price of some enterprises, which leads to the continuous rise of the limit after the listing of the stock, which leads to other problems such as irrational trading in the secondary market. The examination and approval system weakens the market-oriented pricing mechanism and interferes with the pricing of the primary stock market.
Third, it has encouraged the hype of shell resources in the A-share market. Under the approval system, the value of listed enterprises is not only reflected in the performance of the company, the listing qualification itself is also valuable. This has led to the hype of shell resources that has plagued the A-share market for many years. Some listed companies have poor operating performance and should have been gradually eliminated by the market, but under the current system, these enterprises improve their statements through merger and reorganization, so as to avoid the fate of being delisted. There are also some enterprises listed on the curve by acquiring listed shell companies. However, in this process, it gives rise to a series of problems such as financial fraud. For example, in order to prevent stocks from being specially treated by the Shenzhen Stock Exchange and to retain the qualification for restructuring and listing, St. Laida, a company listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange, carried out a series of financial frauds in 2015 by falsely increasing its income and profits. In 2018, the CSRC imposed penalties such as market ban and fines on those responsible. From the performance of the secondary market, recently, Hengli Industrial, * ST Changsheng and other shell stocks rose continuously, obviously deviating from the fundamentals of the company, indicating that the problem of shell stock speculation still exists.
Fourth, it breeds power rent-seeking and corruption. Listing financing is very important for the development of many enterprises, and under the approval system, the staff of the relevant departments of the Securities Regulatory Commission have a great say on the listing of enterprises, which naturally leads to rent-seeking and corruption. From the situation of the officials who have fallen from the CSRC system disclosed since the 18th CPC National Congress, most of them are closely related to the examination and approval of the listing of enterprises, and most of their crimes of embezzlement and bribery occur during the period of holding office or in charge of the issuing department.
1.2 the approval system is the result that the marketization of the stock issuance system has not yet been completed.
The approval system of A-share market is the result of the unfinished market-oriented reform. Reviewing the reform history of the A-share market, the IPO system has experienced a process from multi-sector examination and approval to the CSRC-led examination and approval system, and then to the approval system. Although the overall degree of marketization continues to improve, it has not yet formed a comprehensive market-oriented system.
The power to examine and approve the issuance and listing of new shares from 1990 to 1992 is vested in different government departments: the shareholding system reform of enterprises is examined and approved by the Planning Commission and the system Reform Commission, the stock issuance is examined and approved by the people's Bank of China, and the stock listing and trading is examined and approved by the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges.
In April 1993, A-share listing changed to the examination and approval system. The interim regulations on the Administration of Stock issuance and Trading stipulates that the central departments in charge of enterprises and local governments shall respectively examine and approve the issuance applications of relevant enterprises in accordance with their subordinate relations, and the CSRC shall review them and send them to the Securities Commission. The regulations established a two-level administrative examination and approval system and laid the foundation for a national unified review system for the issuance of new shares.
In 1999, the A-share issuance system was changed to the approval system. The Securities Law of the people's Republic of China, which formally came into force in July, states that "the securities regulatory authority under the State Council shall be responsible for approving applications for stock issuance in accordance with legal conditions, and the approval procedures shall be made public." a decision shall be made within three months from the date of accepting the application documents for securities issuance; if it is not approved or examined and approved, an explanation shall be given. The degree of marketization of IPO is obviously improved. The issuance of the interim measures for the recommendation system of Securities issuance and listing in February 2004 marks the stage of the recommendation system for the issuance of new shares. Since then, the CSRC has further improved the market-oriented reform in the establishment of the sponsor system, the pricing of new shares and the scale of issuance, but still retains the power to finally approve the listing of companies. The issuing mechanism of A-share market is not yet fully market-oriented.
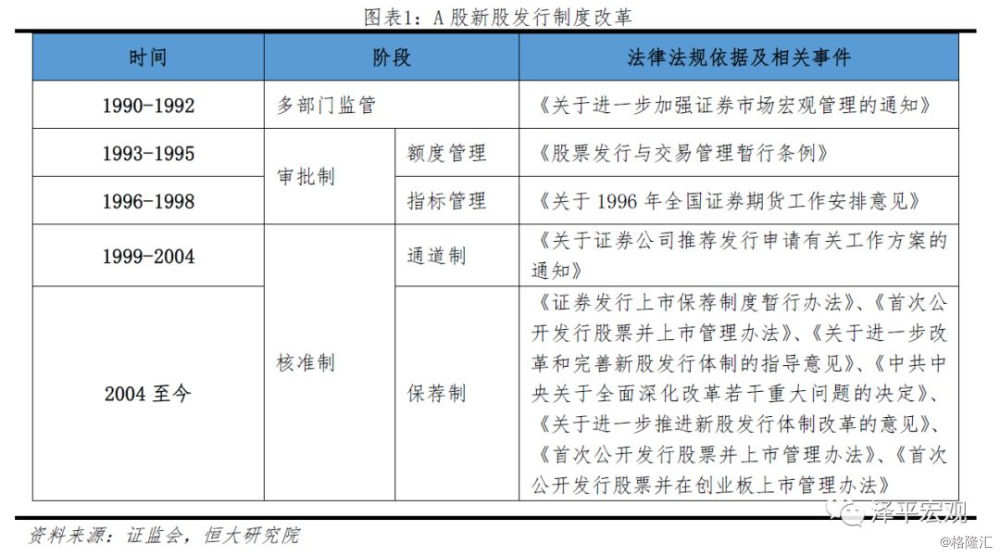
1.3 the reform of registration system is conducive to the formation of a more market-oriented system in the stock market.
Due to the above problems in the approval system, registration is the direction of the reform of China's listing system. Compared with the approval system, under the registration system, the CSRC formulates information disclosure requirements and basic listing standards, is responsible for reviewing the authenticity of information disclosed by listed companies, and does not put forward clear requirements for the operating performance and qualifications of listed companies. as long as the enterprise meets the basic standards and provides true information, it can be registered and listed, and pricing is also completed by the market independently. The registration system maximizes the role of the market mechanism in the process of listing, while reducing the problems of excessive packaging for listing, unreasonable market pricing and power rent-seeking. At present, the stock markets of the major developed countries in the world, such as the New York Stock Exchange, NASDAQ and London Stock Exchange, all adopt the registration system.
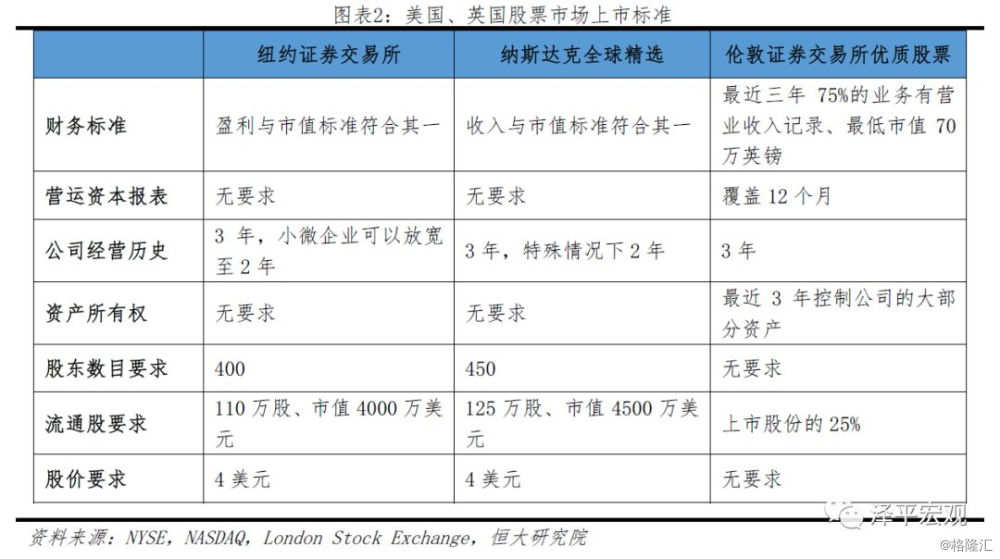
The reform of registration system in China has been moving forward in twists and turns since it was launched in 2013. In November 2013, the third Plenary session of the 18th CPC Central Committee proposed to promote the reform of the registration system of stock issuance. In May 2014, the New Nine articles proposed to actively and steadily promote the reform of the stock issue registration system. In March 2015, a spokesman for the CSRC said that the first draft of the registration reform plan had been completed and submitted to the State Council. Subsequently, abnormal fluctuations occurred in China's stock market, and the reform of the registration system was blocked. In March 2018, the standing Committee of the National people's Congress decided to extend the authorization for the reform of the stock issue registration system for two years.
On November 5, 2018, General Secretary Xi Jinping proposed on China's Import Expo that the Shanghai Stock Exchange should set up Science and Technology Innovation Board and pilot the registration system. Compared with the previous stock reform ideas, this reform is incremental reform. The change of thinking reflects a more prudent policy orientation. At present, the scale of China's main board market is large, and the reform is more difficult. The reform of registration system directly in the main board market is easy to impact on the existing financial system. It is necessary to set up an additional Kechuang board and implement the reform of the registration system, explore effective rules and measures such as issuance, listing, trading, information disclosure, supervision and delisting, and then promote it to the main board market in due course after gaining successful experience. it will effectively reduce the cost of China's capital market reform and be conducive to the promotion of market-oriented reform.
1.3.1 Improve the supporting system to protect the pilot registration system
The international experience of developed markets shows that in order to achieve the desired results, the registration system should not only rely on the reform of the listing link, but should establish a series of supporting measures such as trading, supervision, delisting and so on. to ensure that the reform of the registration system can achieve corresponding results.
1) the construction of listing system and delisting system is equally important. On the one hand, adopting the registration system in the issuing stage can effectively reduce regulatory intervention in the listing process and effectively reduce corruption and rent-seeking. On the other hand, only by establishing an effective delisting system and strictly implementing it, constantly spitting out the old and accepting the new, and forming healthy competition, can the market continue to maintain its vitality. If a large number of low-qualified and low-turnover enterprises are allowed to flood the market, it will weaken the vitality of the market and is not conducive to the long-term and stable development of the market. A perfect delisting system should be established, the whereabouts of delisting enterprises should be clearly defined and strictly implemented. At the same time, we should also prevent malicious delisting and protect the legitimate rights and interests of investors.

2) strict information disclosure system is the core of registration system. Under the registration system, the focus of the regulatory department is no longer to examine the qualifications of listed enterprises, but to supervise the quality of enterprise information disclosure. Therefore, we must establish a unified, standardized and efficient information disclosure system, and seriously punish companies that violate information disclosure rules and disclose false information.
3) perfect the legal system of capital market. At present, the upper limit of penalty stipulated in China's Securities Law is only 600000 yuan. in the capital market where illegal income is often over 100 million, too low penalty can not play a deterrent role in supervision. on the contrary, it has given rise to a variety of acts that infringe upon the rights and interests of investors in the capital market. The new round of revision of the Securities Law was launched as early as 2014, but in recent years, due to the changing market environment, the consideration of the Securities Law has been continuously delayed, resulting in obstacles to the relevant reform process. We should take the establishment of Science and Technology Innovation Board as an opportunity to accelerate the relevant legislative work and promote the construction of the legal system of China's capital market.
2 improve the investor structure of A-share market
2.1 the proportion of market capitalization held by institutional investors in A-share market is low, and the proportion of retail trading volume is on the high side.
Compared with the developed markets, the main problem facing the A-share market is that the market value of institutional investors is low, the proportion of general legal persons and individual investors (retail investors) is high, and the trading volume of individual investors is relatively high. A large number of retail-led transactions lead to a serious herding effect in the A-share market, which leads to excessive price fluctuations in the market.
According to data disclosed by the Shanghai Stock Exchange, at the end of 2017, China's institutional investors (including) accounted for 16.1% of the market value, of which investment funds accounted for only 3.3% of the market value. The proportion of shares held by individual investors is 21.2%, and that of general legal persons (industrial capital) is as high as 61.5%.

The proportion of institutional investors in the stock market of developed countries is higher than that of China as a whole. At the end of 2017, the market capitalization of institutional investors in the US stock market (NASDAQ and NYSE) accounted for 61 per cent of the total market, of which mutual funds accounted for 23 per cent, government and private pensions accounted for 11.9 per cent, and foreign investors accounted for 15 per cent. Individual investors account for 39% of the market capitalization.
The market value of shares held by institutional investors in the British stock market is as high as 83.3%, of which domestic institutional investors account for 29.4% and foreign investors account for 53.9%, mainly including all kinds of international financial institutions, pensions, charities, investment funds and so on. It shows that the British capital market is highly open. Individual investors account for only 12.3% of the market capitalization. The British stock market shows the characteristics of strong institutional dominance.
Japanese institutional investors account for 61 per cent of the market capitalization, with domestic and international institutions each accounting for 30 per cent. General corporate shareholding accounts for 21%, which is relatively high in the markets of developed countries, but it is still far lower than the level of 61% in China.

Due to the low proportion of shares held by institutional investors in China, and the circulation of some shares held by legal persons is restricted, the transaction proportion of retail investors in the secondary market is obviously on the high side. In 2017, the trading volume of individual investors accounted for 82%, while that of professional institutional investors accounted for 14.76%, of which the trading volume of investment funds accounted for only 4.15%.

In terms of turnover rate, the turnover rate of A-share market continues to be higher than that of other major stock exchanges. Since 2009, the average annualized turnover rate has been 194.1 per cent in Shanghai and 335.9 per cent in Shenzhen, higher than 108.6 per cent on the New York Stock Exchange and 63 per cent on the London Exchange. During the abnormal volatility of the stock market in 2015, the turnover rate of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange once exceeded 800%, with a strong speculative atmosphere in the market.

The high proportion of retail trading shows that A-share pricing is dominated by retail investors, which leads to three problems: first, retail trading has a strong characteristics of chasing the rise and fall, herding effect is strong, easy to magnify fluctuations, leading to market prices ups and downs. Second, compared with professional investors, retail investors lack in-depth understanding of the company's financial and operating conditions, do not pay much attention to trading technology, pay too much attention to subject hype and policies, and are easy to overestimate stock prices. Third, because institutional investors need to accept retail-dominated market prices and play games with them for a long time, some institutions also gradually show a "retail" tendency in their transactions.
2.2 strong hype atmosphere, lack of long-term stable funding sources and other reasons make it difficult for institutional investors to develop and grow.
The retail of A-share market is closely related to its development process. In the early days of the establishment of China's securities market, under the influence of the thought of planned economy, the stock market was subject to strong administrative control. For example, the "decision of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on several recent tasks in the fight against Corruption" issued in 1993 pointed out that cadres at and above the county and department level bought and sold stocks. The regulations on strictly prohibiting State-owned Enterprises and listed companies from speculating in stocks issued in 1997 clearly pointed out that state-owned enterprises should not speculate in stocks. Bank funds and insurance funds are also banned from entering the market. In addition, the fund industry has not yet been established, and there are no formal professional institutional investors in the A-share market. It is impossible to introduce foreign institutional investors. In this context, individual investors naturally become the main body of investors in the A-share market.
In 1998, the first batch of public offering fund companies were established, and the management hopes to gradually cultivate and strengthen the group of institutional investors by introducing professional institutional investors to attract social funds. In 2003, the social security fund officially entered the stock market. Since then, the proportion of institutional investors has increased. But at present, due to various regulatory restrictions, institutional investors still lack a long-term and stable source of funding. Coupled with the quality of listed companies, market pricing mechanism and other problems, the A-share market has a strong atmosphere of "stock speculation", the concept of long-term investment and value investment has not yet been formed, and the market profit effect is not good. As most institutional investors bear trust responsibility, they tend to reduce their positions and avoid risks in the face of this environment, resulting in the market value of A-share institutional investors hovering at a low level for a long time.

2.3 continue to encourage pension to enter the market and improve the registration system for the assessment of institutional investors is conducive to the formation of a more market-oriented system in the stock market
2.3.1 raise the upper limit of the proportion of pension funds investing in stocks
The entry of longer-term and larger-scale funds into the market is not only conducive to stabilize market confidence, but also conducive to the long-term and healthy development of China's stock market. Pension is an important source of long-term funds, and the pension market in the United States has a relatively successful experience. The pension in the United States is divided into three parts: the basic social pension, the 401k supplementary pension plan and the commercial insurance savings pension account, of which 401k accounts for about 50 per cent of the total pension size, reaching 8.5 trillion US dollars by the end of 2017. The funds in 401K invest steadily in the stock market for a long time, which significantly increases the proportion of American institutional investors in the stock market, provides a long-term and stable source of funds for the American stock market, and becomes the stabilizer of the American stock market. At present, 67% of the funds in 401K are invested in the stock market, mainly in stock funds, individual stocks of companies and stocks in mixed funds. Even during the 2008 financial crisis, stocks accounted for about 56% of 401k. Long-term capital investment is an important cornerstone of the sustained and healthy development of the American stock market.

At present, China's pension investment stock market is facing relatively strict restrictions. according to the measures for the Investment Management of basic Endowment Insurance funds issued by the State Council in 2015, the proportion of investing in stocks, stock funds, mixed funds and stock pension products, the total shall not exceed 30% of the net asset value of pension funds. Judging from the actual situation of pension entering the market, by the end of September 2018, the governments of 15 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) across the country have signed entrusted investment contracts with the Social Security Fund Council, with a total contract amount of 715 billion yuan, of which 416.65 billion yuan has been accounted for and started to invest. It is suggested that the restriction on the proportion of net value of pension investment in the stock market should be appropriately relaxed, and at the same time, the signing of investment contracts entrusted by non-contracted provinces and the Council of Social Security Fund should be speeded up. When assessing pension returns, emphasis should be placed on medium-and long-term and absolute returns. Introduce stable medium-and long-term sources of funds for the stock market.
2.3.2 change the short-term tendency of performance evaluation in fund industry
At present, the funding sources of public funds are mainly retail investors, and they are more dependent on sales channels. based on sales pressure and other factors, the assessment of the fund industry is too short-term, resulting in a gradual short-term investment behavior. the emphasis on short-term returns exceeds long-term value, and the strategic position of the fund industry as a cornerstone investor and value investor has not been brought into full play. It is suggested that on the basis of full study, the pilot fund industry should change from short-term performance ranking to long-term absolute performance assessment, reverse the trend of short-term behavior of the fund industry, and gradually form the concept of long-term investment and value investment. promote the healthy development of China's stock market.
(3) perfect the construction of transaction system.
3.1 further standardize the suspension of trading of listed companies
3.1.1 arbitrary suspension of trading of listed companies affects normal trading in the stock market
The random suspension of trading of listed companies is one of the outstanding problems in the A-share market. The original intention of stock suspension is to prevent major matters planned by listed companies from leaking in advance, which will have a significant impact on stock prices and adversely affect small and medium-sized investors. However, in the process of practice, the suspension of trading of listed companies is too arbitrary, too long, the reasons for suspension are ambiguous and other problems are more prominent, and give rise to lock-in restructuring of the issue price, avoid special market conditions and so on.
The random suspension and long-term suspension of listed companies seriously affect the liquidity of stocks and hurt the investors' right to know and trade. Through the study of A-share suspension cases, we find that most of the reasons for long-term suspension are due to restructuring or major asset restructuring. In the "Business guidelines for suspension of Trading of listed companies in Planning Major matters", it has been required that, unless major asset restructuring matters are subject to prior examination and approval or there is no major precedent in accordance with the law, the cumulative suspension time for major asset restructuring of a listed company shall not exceed 5 months. But in fact, some listed companies have been suspended for more than five months. For example, Shagang shares announced on September 19, 2016 that trading was suspended due to major issues, and on June 15 of the following year, Shagang shares disclosed a major asset restructuring plan, but it is still suspended today. In response, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange has repeatedly sent letters of concern, saying that the relevant actions of Shagang shares violated Article 17.1 of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange's Stock listing rules (revised in 2014) and ordered it to apply for stock resumption in a timely manner, but failed to achieve regulatory effect.

In extreme market conditions, the random suspension of trading of listed companies may also have a significant impact on the liquidity and price discovery mechanism of the whole market. During the abnormal volatility of stocks in 2015, many stocks chose to suspend trading temporarily in order to avoid being sold by investors, and the reasons for the suspension of some stocks were vague. At its worst, the number of A-shares suspended in a single trading day is more than 1000, and the market is called "suspension of thousands of shares". In the case of the extreme shortage of market liquidity, the suspension of thousands of shares magnified the panic in the market, and some public offering products suffered serious redemption pressure, so they had to sell the unsuspended stocks sharply, which made these stocks fall to the limit rapidly. the market liquidity is frozen rapidly, and the price discovery mechanism of the stock market is almost interrupted. More importantly, the suspension can only temporarily avoid the risk of falling stock prices, can not change investors' expectations, once the stock resumes trading, the stock price still faces the risk of falling.

There is also a stop-and-resume system in the capital market of developed countries, but the system design is different from that of A-share market. Take the United States as an example, the suspension of trading of stocks in the United States market is divided into two situations. The first is Trading Halts, which is executed by the exchange. The most common situation is that when a listed company issues an announcement at trading time, the trading of the corresponding stock will be temporarily interrupted for a period of 15-30 minutes. Its main purpose is to ensure the full dissemination of information and to prevent different traders from arbitrage due to different times of learning information. The other is trading suspension (Trading Suspension), which is enforced by the US Securities Regulatory Commission and is a regulatory measure. It is used when the US Securities Regulatory Commission finds or suspects that the company has major information disclosure problems (incomplete disclosure or fraud), insider trading, market manipulation, etc., for a period of 2-3 weeks. On the whole, the supervision of the suspension of trading of listed companies in the US market is relatively strict, and the suspension time is relatively short as a whole.
3.1.2 improve the regulatory system and stop arbitrary suspension of trading
In fact, in view of the problem of random suspension of trading of listed companies, the relevant departments have been constantly improving the relevant system construction. In 2016, the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange issued the "Business guidelines for the suspension of listed companies on Major matters" and the "Memorandum on the suspension of listed companies" respectively, standardizing the scope, time limit and procedures for suspension of trading. On November 6, 2018, the CSRC issued the guidance on improving the suspension and resumption system of stocks of listed companies, stipulating that listed companies should take non-stop trading as the principle, suspension as the exception, short-term suspension as the principle, long-term suspension as the exception, intermittent suspension as the principle, continuous suspension as the exception, and shall not suspend trading at will or delay the resumption of trading without reason. The new regulations also regulate the suspension period, information disclosure and supporting mechanisms in order to improve the basic system of the capital market, optimize transaction supervision, reduce trading resistance, and enhance market liquidity.
To strengthen supervision, we should focus on implementation. At present, the relevant mechanism has been gradually improved, and the key to achieving the desired results lies in implementation. For listed companies that have no clear reason to suspend trading for a long time, or whose reasons for suspension are relatively ambiguous, the exchange may force the resumption of trading. For major asset restructuring or asset restructuring, appropriately shorten the suspension time, and should not be complex transactions, involving many parties and other general reasons to extend the suspension time at will. When the market is obviously abnormal and liquidity collapses, the exchange should deal with it decisively and suspend the enterprise's application for suspension of trading so as to ensure the normal operation of the market function.
3.2 abolish stamp duty on securities transactions and reduce market transaction costs
Stamp duty is an ancient tax established in the Netherlands in the 17th century. The main purpose of its establishment is that a large number of contracts, contracts and other paper documents need to be printed and endorsed by the government to enhance public credibility. In case of disputes, this kind of "printed" documents also have more legal effect, so the government takes a certain proportion in return. In the era of paper vouchers, stock transactions and transfer of ownership need to frequently use paper stocks endorsed by the government's "decal", so it is reasonable to pay stamp duty. However, with the advent of the era of electronic and paperless trading, the tax base has changed greatly, and the rationality of continuing to levy stamp duty on stock transactions has declined.
Stamp duty on stock transactions, as an important tax in the A-share market, has not only assumed the basic role of increasing government revenue, but also been given the function of regulating the market situation. However, from the results, the stamp duty rate adjustment can not change the long-term trend of the stock market, but aggravate the short-term volatility.
On January 24, 2005, the stamp duty rate on securities transactions was reduced from 2 per thousand to 1 per thousand, and the Prev closed up 1.73 per cent on the day, but it has continued its downward trend since then, finally hitting an all-time low of 998.23 points in June.
On May 30, 2007, the stamp duty rate was raised from 1 ‰ to 3 ‰. The next day, the Shanghai Composite Index opened 5.69% lower and fell 6.5% throughout the day, but this did not change the course of the A-share bull market. The Shanghai Composite Index continued to rise and reached a peak of 6124.04 in October of that year.
On April 24, 2008, the stamp duty on securities transactions was reduced from 3 ‰ to 1 ‰. On that day, the Shanghai Composite Index hit the daily limit, and individual stocks rose by the limit almost across the board. However, the follow-up market still moved towards a narrow volatility model, and the overall trend still failed to change.
The stamp duty on securities transactions was changed from bilateral to unilateral on September 19, 2008. on that day, the Prev closed up 9.46%, and individual stocks rose by the daily limit, but the market still fell to a low of 1664.93 in the following two months.

From the perspective of international experience, since the 1990s, with the electronic stock trading, the United States, Germany, Japan, Australia and other countries have abolished the stamp duty on securities transactions. At present, the main countries that are still levying stamp duty are China, India, the United Kingdom and so on, but the United Kingdom adopts preferential stamp duty relief policies for some small and medium-sized board stocks.
We propose to abolish the stamp duty on securities transactions in the light of market conditions. On the one hand, from the perspective of financial revenue, the financial revenue raised through stamp duty is relatively small. From January to October this year, the stamp duty on securities transactions nationwide totaled 88.8 billion yuan, while the general public budget revenue in the same period was 16.1558 trillion yuan, and the stamp duty on securities transactions accounted for only 0.5 percent. After the cancellation, there will be little pressure on revenue. On the other hand, abolishing the stamp duty on securities transactions will reduce the transaction costs of the stock market, enhance investor confidence and the vitality of the capital market, and promote healthy development.
(4) improve the legal system and enhance the deterrent force of supervision.
4.1 the punishment for some illegal acts of securities in China is too light.
Securities Law and Criminal Law are the main laws to regulate China's securities market and protect the legitimate rights and interests of investors. However, at present, the main problem is that the punishment for some illegal acts is too light. What is widely controversial is that the upper limit of administrative penalty for many illegal acts in the Securities Law is 600000 yuan. Compared with the hundreds of millions of profits of illegal acts in the securities market, the upper limit of punishment stipulated in the Securities Law is too low to effectively deter the illegal acts in the securities market.
For example, in December 2017, the CSRC issued a penalty decision on Abbott. From 2015 to September 2016, Abbott accumulated a total of 580 million yuan in operating income and 256 million yuan in profits by means of fictional overseas projects, fictitious international trade and domestic trade, which is one of the most serious cases of financial fraud in the history of China's securities industry. However, even if the penalty is imposed, the company will only bear a fine of 600000 yuan, and the fine for those responsible is only 300000, which is difficult to form a sufficient deterrent. At the same time, it is difficult for investors to sue companies to recover losses in our country, so there are few cases of civil compensation because of securities fraud, and the legitimate rights and interests are difficult to be effectively protected.
In terms of criminal responsibility, Article 181 of China's Criminal Law stipulates that the maximum sentence for insider trading and divulging inside information is 10 years. In the actual implementation, Ma Le, the largest rat warehouse case in China, involved as much as 1.05 billion yuan, made an illegal profit of nearly 20 million yuan, and was eventually sentenced to three years' imprisonment. The Xu Xiang case shocked the whole country. from 2010 to 2015, he conspired with the chairmen or actual controllers of 13 listed companies to manipulate the stock trading of listed companies, controlled 139 securities accounts, made an illegal profit of 9.338 billion yuan and was sentenced to five years and six months in prison.
In contrast, the developed capital markets have extremely severe penalties for illegal cases in the securities market. Take the United States as an example, in 2001, Enron's false profit of 600 million US dollars was exposed, and its financial fraud caused a sensation all over the world. The US Securities Regulatory Commission fined it 500 million US dollars, which led to the bankruptcy and liquidation of the company. Relevant intermediaries, such as Arthur Andersen, Citigroup and JPMorgan Chase & Co, were held accountable. Among them, the auditor Arthur Andersen was investigated by the US Department of Justice because he was suspected of colluding with Enron to conceal criminal evidence. In the end, Arthur Andersen was found guilty of obstruction of justice, fined $500000 and unable to engage in business for five years. Since then, most of its customers have stopped doing business with Arthur Andersen, which was forced to close most of its offices around the world and went bankrupt in 2002.
From the perspective of criminal responsibility, the punishment of securities violation cases in American law is extremely severe. Taking the crime of insider trading as an example, the Sarbanes Act of 2002 stipulates that anyone who gains benefits in the securities market through insider trading or price manipulation constitutes securities fraud and is punishable by up to 25 years' imprisonment or a fine of 5 million. At the same time, the identification of insiders in the United States is very extensive: directors, supervisors, executives and their partners and trustees of the company; shareholders and their partners and trustees who own more than 10% of the shares; the spouses, immediate blood relatives and family trustees of the company's employees and the above-mentioned persons; presumed insiders include any outsiders who know the inside information through the performance of their duties; the whistleblower and the leaker, and so on. In 2011, Rajaratnam, a galleon fund, was charged with insider trading involving more than $30 million and sentenced to 11 years in prison. Dozens of executives, including Intel Corp's head of strategic investment, directors of McKinsey Consulting, and senior vice president of IBM, were also involved in the case. As a result, 21 people were arrested and pleaded guilty.

In fact, in addition to the light punishment for some illegal acts, there are still some problems in the current Securities Law, such as too many strict controls on securities issuance, the role of the capital market in serving the real economy cannot be effectively brought into full play, the lack of necessary institutional arrangements for cross-border issuance and trading of securities, the imperfect market restraint mechanism, the weak protection of investors, the low quality of information disclosure and so on. Therefore, it has become a consensus from all walks of life to amend the Securities Law, and then improve the market mechanism, improve supervision, and strengthen the deterrence of illegal and criminal acts. The current round of revision of the Securities Law was launched in 2013, but due to a wide range of areas, the need for more research items, rapid changes in the market environment and other issues, are still under consideration.
We propose to speed up the revision of the Securities Law, significantly reduce the control of securities issuance and other areas, and at the same time strengthen law enforcement, improve the punishment for securities crimes, enhance the deterrent force of supervision, and improve the level of supervision during and after the event. In terms of criminal responsibility, for serious securities crimes, we should appropriately raise the sentencing standards, effectively crack down on disturbing market order, price manipulation, illegal fraud and other acts, and constantly improve the legal environment of China's securities market.
