Author: Li Xunlei
2017Year comparison2016In the macro policy, it should be tight money and tight credit.2018In the first half of the year, we gradually changed to loose money and tight credit. In the second half of the year, with the increase of trade friction between China and the United States, credit began to loosen obviously. In the fourth quarter of this year, as a result of the sharp fall in the stock market, the problem of equity pledge financing became more and more serious, and companies complained a lot about the rising operating costs caused by environmental protection, demolition of illegal buildings and social security payments. at the same time, the growth rate of investment has declined significantly. According to this logic2019The macro policy of 2000 should be broad in currency and credit. But2019Can years really make the credit of the whole society expand again? This paper tries to make an analysis.
From the demand side, the credit contraction in the past two years
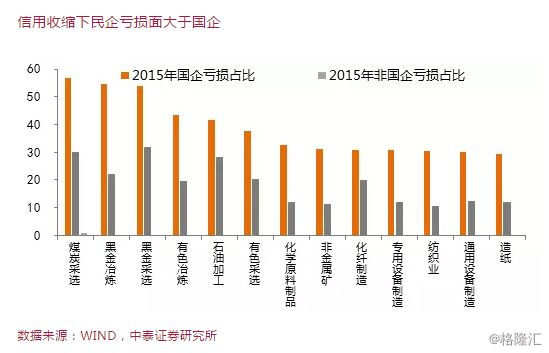
Demand includes domestic demand and external demand, while domestic demand includes investment demand and consumer demand.2016Since 2000, there has been a marked decline in both domestic investment growth and consumption growth.2015In 2000, the losses of state-owned enterprises in most industries exceeded those of private enterprises.
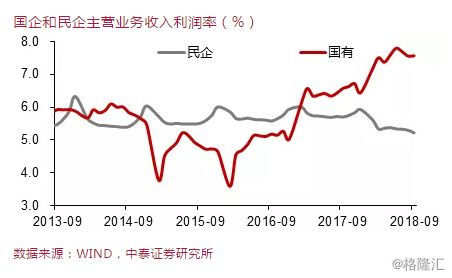
However, in 2016, capacity was eliminated through supply-side structural reform and higher environmental protection requirements, resulting in a substantial increase in profit growth of state-owned enterprises, which surpassed that of private enterprises. Due to rising financing costs and environmental protection costs, private enterprises were significantly less willing to invest, and their fixed asset investment growth rate dropped sharply. In order to avoid a sharp decline in the growth rate of fixed asset investment, the growth rate of investment in the state-owned sector rose sharply to nearly 20% in 2016, behind which was a sharp increase in the scale of fiscal expenditure in a broad sense.
The lack of willingness of private enterprises to invest is not only the problem of difficult and expensive financing, because this problem always exists, and the key problem is that the return on investment decreases due to overcapacity in most industries. There are two reasons for overcapacity. The first situation is that terminal consumption "has money but no demand", which shows that there is really excess; the second situation is"No money, no need."That is, the effective demand is insufficient.China is still in the ranks of middle-and high-income countries, and I am afraid there is more of the second situation.
2016Since 2000, there has been a significant rebound in investment in real estate development, and the rise in house prices has also brought residents to buy houses with leverage. Accordingly, the expenditure on consumption in residents' disposable income has been reduced accordingly. In addition to housing-related consumption growth to maintain a high growth rate, such as home appliances, furniture, home decoration, other consumption growth rate is more obvious, which also suppressed the overall investment growth in the traditional manufacturing industry and the increase in the wage growth of workers.
On the other hand, the rise in house prices has brought about a high increase in residents' property income, but after all, only a small number of households own multiple homes, which leads to2016Since 2000, the Gini coefficient has increased, that is, the income gap has widened. For example, according to the data of the National Bureau of Statistics2017The annual income growth rate of migrant workers is only6.3%And account for the population20%The income growth rate of the high-income class is9.5%。
The widening income gap is obviously not conducive to consumption growth, because the low-and middle-income groups have a strong willingness to consume but the income growth rate is low, while the high-income class has a weak willingness to consume but a high income growth rate. Sluggish consumption leads to insufficient demand for downstream products of the manufacturing industry, but due to the price increase brought about by the upstream suppression of supply, while the downstream demand does not expand accordingly, the price increase is difficult to transmit from the upstream to the downstream.The result of asymmetric price increase is the sluggish downstream manufacturing industry, which is dominated by private enterprises.
The investment willingness of the manufacturing industry is insufficient, and the financial enterprises, as social financing intermediaries, do not dare to expand their credit, because when the expectation is not optimistic, the risk appetite decreases.
Enter2018Two years later, there are signs of a slowdown in the income growth of the high-income class, which may be related to the slower increase in house prices.PPIThe decline in growth rate is related to the decline in the profit growth rate of financial companies (the financial services industry is the second highest-earning industry of all industries). Because high-income earners make the greatest contribution to high-end consumption, this leads to a decline in the growth rate of high-end consumption.
From the sales income growth rate and profit growth rate of eight famous liquors in China (Maotai, Fenjiu, Wuliangye, Luzhou laojiao Tequ, Jiannanchun, Xifeng Liquor, Gujinggong Liquor, Dong Liquor)Their peaks all appear in2017In the third quarter ofIn addition, the growth rate of domestic luxury car sales has also slowed down significantly, such as2017Overall growth in luxury car sales17%, higher than2016Year. But sales growth in the first three quarters of this year is10%,9The month has fallen to single digits.
Another interesting data is that the "China Gaming Index", which represents the changes in the share prices of listed companies in Macau's gaming industry, and the share price index of leading companies with brands among domestic listed companies both reached a downward inflection point from April to May this year, and fell sharply.
As there is a high correlation between the gross income of Macao gaming industry and China's housing price index.10The gross revenue of Macau gaming industry grew at a rate of only 5% in April.2.3%This actually reflects the weak trend of domestic house prices. According toBainAccording to the statistical report, the growth rate of global personal luxury consumption last year was6%And China is as high as11%1/3 of the world's luxury goods are bought by Chinese people. Estimation2018The growth rate of domestic high-end consumption will slow down significantly in 2008.
Although the gross revenue figures for Macau's gaming industry are not leading, they may reveal a trend that domestic house prices will weaken in 2019. In fact, China's economic cycle is the real estate cycle, and the real estate cycle is closely related to the financial cycle, and these three cycles have actually turned downwards.
In fact, society always shrinks in the process of declining economic growth, because expectations tend to be pessimistic and investment and financing will be cautious. In addition, there are many structural problems in China's economy, such as high Gini coefficient, prominent overcapacity and high leverage of enterprises and residential sectors, which further hinder the expansion of social credit.
For example,2017In 2000, the monetary policy was tight money and credit, but due to the upward economic growth, banks'on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet business were more active, so social credit did not shrink as a result. Since the second half of this year, although the credit of macro policies has been gradually relaxed, social credit has been further tightened. therefore,The relaxation of credit in policy is not necessarily synchronized with the expansion of social credit.
Whether Credit can be expanded from the Perspective of Financial data
From the perspective of financial data, the top-down credit tightening starts from2016It began in the second half of 2000, because although the supervision of financial institutions has been strengthened, house prices have risen, resulting in an endless stream of innovative models of regulatory arbitrage, leading to a substantial increase in the off-balance sheet business of banks.2017In 2000, the central bank controlled the "general floodgate" of money, the overreserve rate of financial institutions dropped sharply, and the interest rates of inter-bank funds, loans and bonds all rose sharply.
Judging from the implementation results,2017The contraction in leverage within the financial system was more obvious inM2The growth rate is from11.3%Descend to8.1%It is mainly due to the contraction outside the banking committee, while the growth rate of social finance is only from12.8%Descend to12%The contraction of solid leverage is limited.2018Since 2000, the central bank has cut reserve requirements four times to release liquidity, money market interest rates have fallen sharply, and the margin of monetary policy has been relaxed. However, various regulatory policies such as the new regulations on asset management and non-standard channels have been implemented one after another, the macro-prudential pillar has begun to work, non-standard financing has shrunk substantially, and some credit creation channels have been blocked.The latest growth rate of social integration from that at the end of last year.13.4%Descend to10.6%。
Although credit was far less than expected in October, growth picked up in the first three quarters, but there are also structural problems with credit delivery. Medium-and long-term loans that most directly reflect the changes in corporate financing needs10Monthly increase only1429100 million yuan, not only lower than9Monthly3800Billion yuan, which is far less than last year.10Monthly2366100 million yuan. At the same time, the scale of bill financing has seen a high growth of more than 100 billion for six consecutive months, reflecting that under the guidance of the broad credit policy, although the bank credit line has been increased, it is still more cautious about corporate credit.
Although the central bank argued in its third-quarter monetary policy implementation report that the liquidity provided by the central bank was not "silted up" in the banking system, that is, money flowed into the real economy, why did the real economy still feel short of money? First, as mentioned earlier, off-balance sheet business has shrunk substantially, and non-standard financing channels have been strictly restricted.
Second, according to our calculations, in the past10During the years30%China's economic growth is directly or indirectly contributed by real estate. Under the real estate regulation and control policy, the real estate financing business is under control, which also makes it difficult for banks to further expand their housing loan business.
Third, in the context of declining economic growth, the banks themselves are unwilling to increase leverage, although the central bank can continue to lower reserve requirements, but commercial banks do not play in "financial innovation", and the channels to create money through non-bank financial institutions in the past have also been blocked.
Fourth, the assessment mechanism of commercial banks has not changed, so the willingness to lend to private enterprises is still insufficient.
10Although the monthly data is very poor, it is after all the data of the past, and the policy effect will have a certain lag.Believe2019More and more policies aimed at solving the financing difficulties of private enterprises are falling to the ground in 2000. With the support of the policy, it is expected that the risk appetite of banks can be effectively improved at the margin, and the difficulty of financing for private enterprises may be reduced, but the judgment of overall tightening of credit will not be changed. After all, the downward trend of economic growth is the general trend, and economic transformation is the direction of efforts in the future.
Investments that do not generate traffic will accumulate risks.
From the past10Judging from the economic trend in 2000, it is not difficult to find that every time the economy is going to go down, we rely on investment to achieve steady growth. Fixed asset investment is mainly composed of manufacturing investment, real estate investment and infrastructure investment, which is the weakest in recent years because there is already excess capacity and it is difficult for the government to lead, while real estate investment can be stimulated by policies. infrastructure investment can be led by the government.
Judging from this year,Domestic car sales have been negative for five consecutive months, smartphone sales have continued to decline, and commodity prices have generally weakened, all of which indicate that the problem of overcapacity still exists. As a result, there will still be downward pressure on manufacturing investment growth next year.
Real estate investment is greatly affected by the policy, under the guidance of the current policy of "housing speculation", the growth rate of investment is bound to decline next year. The rest is infrastructure investment, which has always been growing counter-cyclically, but2018However, there was a sharp decline in growth in 2008.
In the economic downturn, the lack of willingness of the private sector to invest may cause the economy to fall into a "liquidity trap" under loose monetary policy. That was the case in Japan then.在90After the bursting of the real estate bubble in the 1990's, Japan adopted loose monetary policy but failed to revive the economy, so it stimulated the economy by increasing public expenditure and expanding infrastructure investment. as a result, the government debt ratio is rising, the effectiveness of public investment is reduced, and some private investment is squeezed out.
Therefore, infrastructure investment projects must be carefully evaluated, and public expenditure should not be expanded by flooding. To measure the effectiveness of infrastructure investment, we can evaluate the expected flow of the projects invested. For example, from the current point of view, the investment in high-speed rail is still very worthwhile, because it has generated considerable passenger flow-- to meet the travel needs of residents. At the same time, it also brings a certain amount of cash flow (economic benefits).
However, I am afraid that there are many projects that can bring neither passenger flow nor capital flow, nor create new logistics. For example, in the past, so many "high-tech parks", "high-tech development zones", "bonded zones" and "economic and technological development zones" from the national level to the county level have been set up, and many preferential policies have been given, but there are not too many projects that really generate flow.
Therefore, if we want to stabilize growth through infrastructure investment, we should find investment projects that do have shortcomings and which will bring huge flows. For example, with the aging of the population and the upgrading of consumption, the investment demand for health care and pension should exceed the demand for education, culture and entertainment, while the investment demand for education, culture and entertainment should exceed the demand for road traffic construction. because road passenger traffic has declined and passenger car sales have been negative.
At present, the leverage ratio of non-financial sector in China is close to that of developed economies, and even higher than that of developed economies such as the United States, Australia, Germany and so on. If leverage is added again by expanding investment in order to stabilize growth, debt is bound to accumulate again.
Some people say that in addition to reducing debt, deleveraging can also be done by expanding assets orGDPIn theory, but in fact, whether it is the efficiency or pull of capital formationGDPEfficiency is declining, so II don't think we can solve more than one problem on the issue of deleveraging. China's economy has continued.40With the high annual growth, it is difficult to resist the law of "returning to the mean".
Therefore, my judgment is that2019In 2000, social credit will still be tight, and it is unlikely to repeat the history of "tightening, tightening and loosening, chaos and chaos". Since credit is tight, the risk appetite of investment will still decline, and the level of risk-free interest rate will move further down, so what we need to guard against is to avoid a further rise in the "risk premium" of assets, that is,Stabilizing asset prices will be an important task of stabilizing the economy next year, while stabilizing investment or growth is less important.