Edited by Haitong: "the reincarnation and Enlightenment of debt-- looking at previous crises from the Perspective of Financial cycle"
In the past October, against the backdrop of continued interest rate increases in the US dollar, global assets have been adjusted to varying degrees except for the strengthening of the US dollar and gold. Understanding the impact of US dollar credit on the global economic order is a required course for investors to grasp opportunities and avoid risks at the macro level.
1. Asset price revaluation caused by interest rate hike of US dollar
Us bond interest rates hit new highs and US stock markets tumbled.Since the beginning of this year, with the gradual acceleration of the pace of interest rate increases by the Federal Reserve, the dollar index has rebounded and US bond yields have continued to rise. Recently, the US dollar index has rebounded to more than 96, and the 10-year Treasury yield has also risen to 3.23% at one point, the highest level since 2011. The rise in US bond interest rates is often associated with risk, which has led to a recent adjustment in the US stock market, with the S & P 500 index falling more than 3 per cent in a single day.
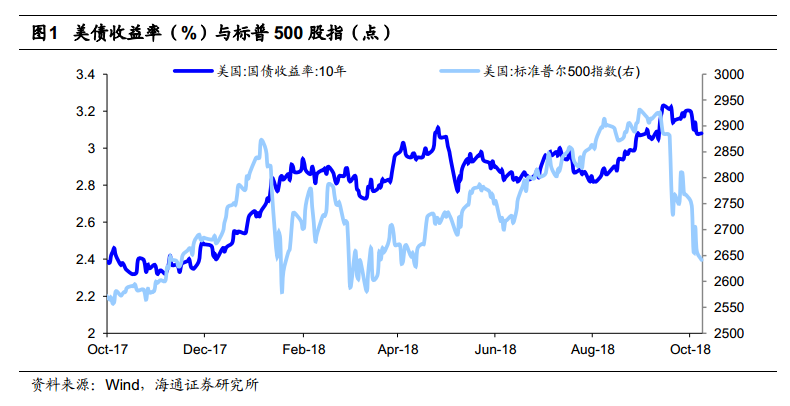
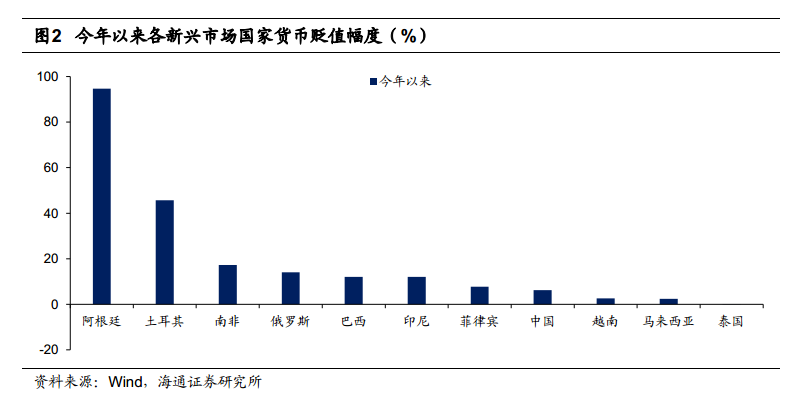
The risk is not just for the US market, the stronger dollar and higher US bond yields have also raised concerns about the global financial crisis.Affected by the rise in US bond yields, a large number of funds have returned to the United States, resulting in pressure on the currencies of some emerging market countries. Since the beginning of this year, Argentina and Turkey have successively experienced sharp short-term devaluations of their currencies, while South Africa, Russia, Brazil and Indonesia have also depreciated by more than 10%.
2. Us dollar interest rate hike-liquidity contraction-the transmission chain of the financial crisis
Higher US dollar interest rates and higher US debt interest rates always seem to be closely related to the crisis because US monetary policy will impact global liquidity, which in turn has an impact on the financial cycle of the US and even other economies.
When the Fed cut interest ratesExcess money flows from the US to other regions with higher returns on investment, particularly in emerging markets, leading to capital inflows, credit expansion, rising asset prices and an upward phase of the financial cycle.But it also left the consequences of debt inflation and asset price bubbles.
Once the Fed starts to raise interest rates,Expectations of a stronger dollar and higher US bond yields will attract money back to the US, leaving these regions facing inflection points in the financial cycle, characterized by shrinking liquidity, debt defaults and falling asset prices. For countries with prominent debt problems, liquidity reversal will lead to a vicious circle of debt default and falling asset prices, leading to a financial crisis.

Throughout history, financial crises often occur in the middle and later stages of every interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve.For example, the Latin American debt crisis in the early 1980s, the Japanese real estate bubble in the early 1990s, the Southeast Asian financial crisis in 1997 and the American subprime crisis in 2008, and analyzing the formation and evolution of these crises, it is helpful to judge the impact and risks of this round of Fed interest rate hikes on the financial cycle of major economies.

3. judging the financial cycle is the key to deal with the financial crisis.
Haitong believes that financial crises often occur at the top of the financial cycle after a rapid rise, so examining the financial cycle will help to identify the potential risks after this round of interest rate hikes in the United States.According to BIS, there are two indicators that can better describe the financial cycle: private sector credit / GDP and real house prices.

BIS also uses HP filtering method to get the trend value of private sector credit / GDP, and the difference between the actual ratio and the trend is the gap of private sector credit / GDP. The private sector credit / GDP gap is greater than 0, indicating that the credit expansion exceeds the long-term trend, the gap value is getting larger and larger, and the financial cycle is expanding upward, while when the gap falls back or even falls to a negative value, it indicates a contraction in the financial cycle. In terms of house price performance, the upward phase of the financial cycle tends to expand the increase in house prices, while in the contraction phase, the increase in house prices tends to shrink or even fall.
4. The current financial cycle in major developed economies
The United States and Britain are in the stage of expansion of the financial cycle.

Financial cycles in Germany and Japan are also rising and may be closer to the top than countries such as the UK and the US.

5. China's financial cycle
So where is China's financial cycle?From a credit perspective, China's private sector credit / GDP has consistently exceeded the long-term trend since 2009, especially since 2012, when the private sector credit / GDP gap rose sharply from 6.5 per cent to 29 per cent at the beginning of 2016. But China's credit expansion has slowed significantly in the past two years, with the private sector credit / GDP gap falling to about 15 per cent. From the perspective of house prices, China's real housing price index has risen rapidly since 2015, but the growth rate has also shown signs of slowing since 2017.Therefore, China's current financial cycle may have passed the peak and gradually started to decline.

Since the 2008 crisis, China's private sector credit / GDP and house prices have risen rapidly to the historical peak. According to BIS statistics, since 2008, China's macro leverage ratio has risen from about 145% to more than 255%, and the private sector leverage ratio has risen from about 115% to 210%, which is the largest increase compared with other major emerging markets.Several crises in history show that the peak of the financial cycle is often the closest to the financial crisis, so the problem of high leverage has indeed made our country face a more severe moment in the past two years.Fortunately, at that time, the Fed was still in the early stage of raising interest rates, raising interest rates only once in 15 and 16 years, and the external pressure was relatively limited.
