Edited by Societe Generale Securities: "Why do things always go wrong in some emerging markets?" -- the deep-seated reasons behind the Argentine and Turkish phenomena. "
Since the beginning of the year, the depreciation of emerging market currencies has increased, and there has been an overall outflow of funds. Recently, problems in countries such as Turkey and Argentina have further raised concerns about emerging market crises. Why can't emerging markets avoid the fate of "leeks"?Societe Generale Securities believes thatIn addition to the basic attributes of emerging markets, there are also external reasons for a strong dollar.
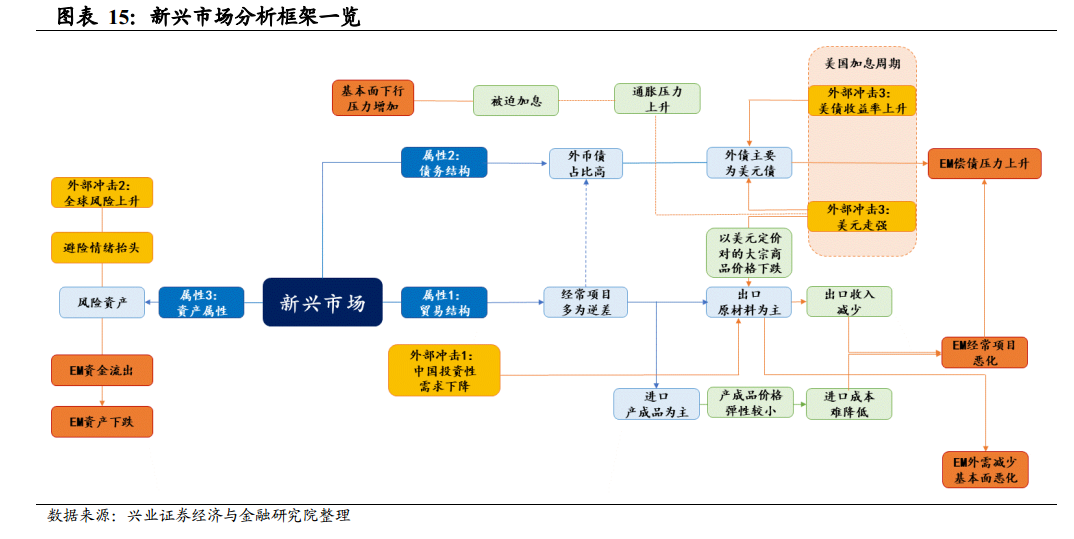
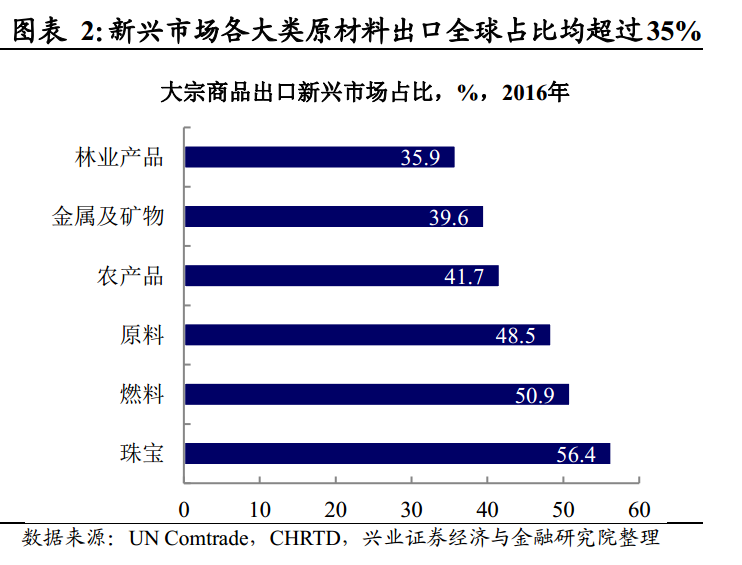
In terms of trade structure, emerging markets are over-reliant on raw material exports and have no pricing power.In the global trade division of labor, emerging markets are important exporters of raw materials (excluding China, emerging markets account for about 56% of global exports of raw materials, and emerging markets account for more than 35% of all kinds of raw materials). And it is also highly dependent on raw material trade (after deducting China, raw material exports account for 22% of total emerging market exports).
In terms of debt structure, emerging market financing is highly dependent on external debt, especially dollar debt.Because the sovereign credit of emerging market countries is relatively poor, and the credit of their own currencies is relatively low, emerging markets have to borrow funds mainly in the form of developed countries' currencies in the international financial markets, of which US dollar-denominated debt accounts for the vast majority. After the outbreak of the financial crisis in 2008, the United States, Europe, Japan and other developed countries have adopted monetary easing to stimulate the economy. On the one hand, falling interest rates have reduced borrowing costs in emerging markets and stimulated the expansion of foreign debt in emerging markets; on the other hand, with lower yields, bonds in developed countries have become less attractive, driving large inflows of capital into high-risk, high-yield emerging markets. All this has pushed up the external debt of emerging markets.

From the perspective of asset attributes, emerging market financing needs to bear a higher risk premium.First of all, compared with developed countries, emerging markets overall sovereign credit rating is low, sovereign debt default probability, sovereign credit default swap (CDS) is relatively high, in terms of asset attributes, the risk is relatively high.

From the perspective of external factors, dollar liquidity is not only the core factor of emerging markets, but also the main trigger of the crisis.While Chinese demand and global volatility have an impact on external demand and capital flows in emerging markets, they do not actually trigger emerging market crises directly. An analysis of several emerging market crises shows that emerging market crises are often accompanied by a stronger dollar. Therefore, the tightening of US dollar liquidity during the US interest rate hike cycle is the core factor of emerging markets and the main trigger of emerging market crises.

Societe Generale Securities points out that, in theory, the potential impact of a stronger dollar on emerging markets is mainly as follows:
Path1. The pressure of foreign debt repayment increases, and the risk of debt default increases.Emerging market countries have a strong external dependence on financing, and the proportion of US dollar debt is relatively high. Higher US bond yields during the US interest rate hike cycle will push up the debt service cost of US dollar debt. At the same time, most emerging market countries adopt a floating exchange rate system, and their currencies are very sensitive to changes in the US dollar. The stronger US dollar, the weaker local currencies of emerging market countries, and the rising cost of debt denominated in local currencies will increase the pressure on foreign debt service of emerging market countries, thereby increasing the risk of debt default of emerging market countries.
Path2. Deterioration of fundamentals: deterioration of current account + upward inflation.① dollar-denominated commodity prices fell and current accounts worsened. As mentioned earlier, the trade structure of most emerging market countries is "export raw materials + imported finished goods". As a significant proportion of commodities are denominated in the dollar, the dollar strengthens and commodity prices tend to fall. For emerging markets, on the revenue side, there is a decline in income from exports per unit of goods sold, while on the cost side, since the price of finished goods fluctuates relatively little and emerging markets have no pricing power over finished goods, this means that importers need to exchange more local currencies for finished goods at the same price, resulting in higher costs. As a result, the current account of emerging market countries will deteriorate.

② inflationary pressures are rising and the country may be forced to raise interest rates, exacerbating fundamental downward pressure. At the same time, emerging market currencies fall against the backdrop of a strong dollar, inflationary pressures are likely to rise further, and central banks may have to raise interest rates to cope with inflation. Higher interest rates will increase borrowing costs for domestic residents and the corporate sector, which could further exacerbate downside risks to fundamentals.
Path3. The attractiveness of assets decreases and the outflow of funds.With the depreciation of their currencies, emerging market countries tend to have higher risks, deteriorating fundamentals, declining asset attractiveness and capital outflows, so the performance of emerging market assets is highly correlated with the trend of their currencies, which will further create a vicious circle.
 For more wonderful content, please mark: a review of the past of Fu Tu Research.
For more wonderful content, please mark: a review of the past of Fu Tu Research.
