Edited by Tianfeng Securities: those things that have been deleveraged in history
Why deleverage? Generally speaking, excessive macro leverage can easily lead to the following two problems: one is the heavy debt burden, weak economic growth, and high interest burden, which leads to economic entities' unwillingness to invest and consume. Second, the debt crisis, but when interest payments are higher than economic growth, it is easy to fail to repay interest, and debt default is inevitable.
1. Three times of deleveraging in Chinese history
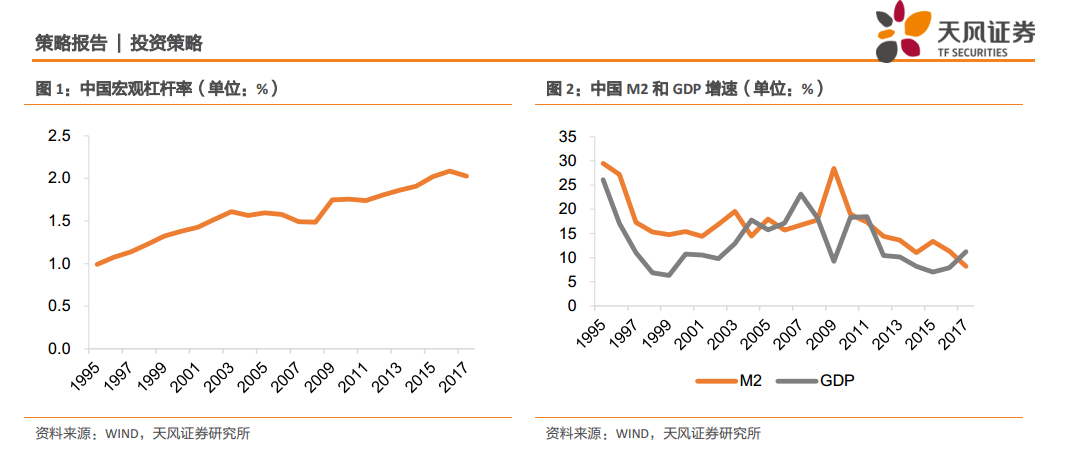
In terms of M2/GDP ratio, China's macro leverage ratio (trend is basically consistent with BIS's total debt / GDP), China's macro leverage ratio has declined three times since 1995.
The first time lasted for a long time, from 2004 to 2008, lasted for five years, the macro leverage ratio fell from 161% to 149%, a total of 12 percentage points.
The second decline in macro leverage lasted only a year, in 2011. At that time, the government realized that the 4 trillion yuan stimulus package may have some sequelae, and the most representative problem was local government debt, so it strengthened restrictions on local government debt and strictly controlled banks to provide credit to financing vehicles. This also led to the rapid rise of shadow banking, non-standard financing and so on.
The third decline in macro leverage occurred in 2017. Under the effect of supply-side reform, PPI reversed its long-term downward trend and rose sharply compared with the same period last year, driving nominal GDP growth up to 11.2%, while M2 growth slowed to 8.2% under the effect of financial deleveraging. Macro leverage fell by 5 percentage points, from 208 per cent to 203 per cent.
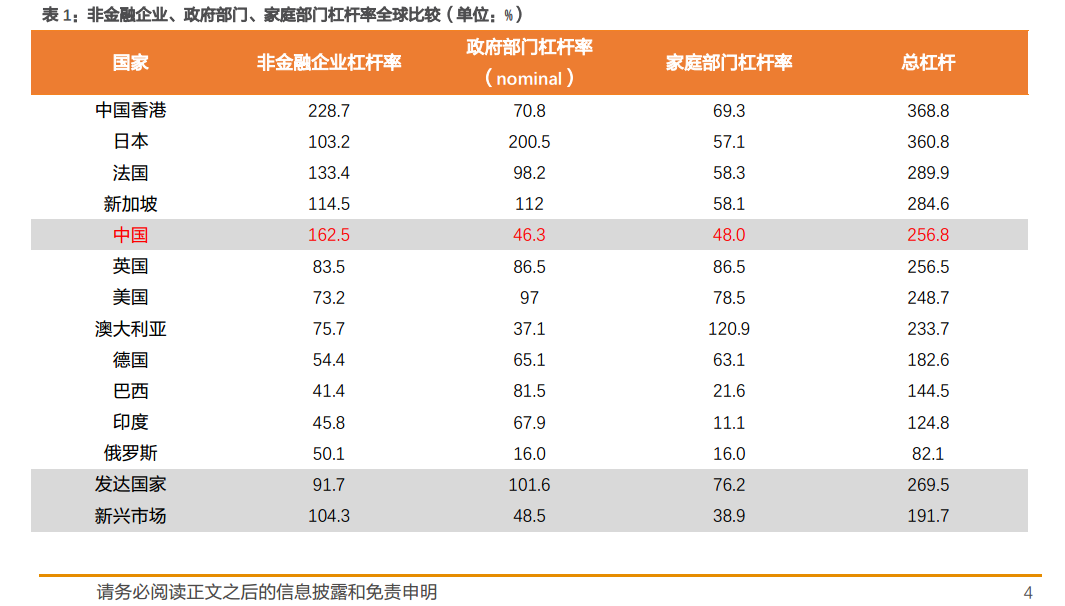
2. The first way of deleveraging: one is to deleverage by reducing debt, which includes both active debt reduction and spontaneous debt reduction by the market.

South Korea in 1998 and the United States in 2008 were cases of spontaneous debt reduction by the market. When the level of leverage was too high and the economy could not bear it, the market tended to remove the debt through crisis. In crisis situations, spontaneous deleveraging of the market often leads to recession, economic growth and inflation will decline significantly, and GDP growth has dropped to negative in both the United States and South Korea. China in 2004, China in 2011 and Japan in 1989 are all cases in which the government took the initiative to shrink and deleverage debt growth. In these cases, taking the initiative to control debt growth has led to a decline in economic growth and deflation, of which China's PPI growth has been negative for more than 50 months from 2012 to 2015.
3. Deleveraging method 2: reducing leverage through more efficient economic growth is often accompanied by an increase in inflation, which itself is also a key means of reducing leverage.

In the cases of China in 2006-2007, China in 2017, the United States in 2010-2011 and South Korea in 1999-2000, we can see a V-shaped reversal in nominal GDP growth, corresponding to a relatively significant decline in the private sector or total leverage. Economic growth at this time does not come from leveraging, but is not dependent on debt growth.
4. Asset performance in deleveraging environment
Based on the above discussion, we believe that the impact of deleveraging on asset performance can be clearly divided into two types:
In the de-debt phaseDeleveraging by reducing debt growth tends to lead to a decline in economic growth and price levels. On asset performanceThere will be greater pressure on risky assets, with downward pressure on stocks, commodities and real estate.National debt, on the other hand, tends to rise. In the early stages of a decline in debt growth, corporate bonds are also more likely to fall.Within the stock market, defensive industries such as consumption will have excess returns.


When the deleveraging phase is over and the economy can return to healthy growth, leverage levels generally continue to decline.. At this stage, inflation is more likely to rise. In terms of asset performance, risky assets will achieve better returns.There are opportunities for stocks, commodities and real estate.The performance of treasury bonds will be relatively weak. Within the stock market,Aggressive industries with periodic categories are more likely to get excess returns.
For more wonderful content, please mark: the past period of the rich way research election.
